Instrumental or Operant? Habits and Instrumental Learning 10/20/2011 Learning & Memory
advertisement

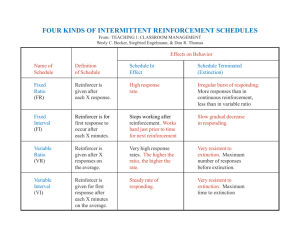
10/20/2011 Instrumental or Operant? • Same thing, definition Habits and Instrumental Learning Learning & Memory Arlo Clark-Foos • Law of Effect Habits Voluntary behaviors that are brought about and influenced by reinforcers presented predictably after the behaviors Classical vs. Instrumental • Differences History of Instrumental Cond. • Edward Thorndike’s (1898) puzzle boxes – Instrumental • Reflexive, automatic behavior • Reinforcement follows CS, regardless of response – Initially random acts – Decrease in time to escape – Classical • Voluntary behavior • Reinforcement only follows the response • Similarities – Blocking, conditioned inhibition, spontaneous recovery, generalization and discrimination… Superstitious Behavior – Law of Effect • “Annoying” vs. “Satisfying” events • Reinforcer is not part of association! Reinforcing Any Behavior? • Staddon & Simmelhag (1971) – Only behaviors the occurred right before the reinforcement increased in frequency B.F. Skinner (1938) showed that any behavior a pigeon performs during reinforcement will increase in frequency. • Terminal vs. Interim Responses • Thorndike’s cats • Timberlake & Lucas (1989) • Belongingness 1 10/20/2011 Belongingness • Breland & Breland (1961) – What makes Sammy dance? Thorndike vs. Rescorla • Is the reinforcer part of the learned association? – Rescorla (1988) • Reinforcer devaluation • Shettleworth (1975) – Reinforcing with food only reinforces feeding behaviors Learned Helplessness Losing Streaks • Seligman & Maier (1967) – Rats and yoked shocks – Later extended to college students and anagrams Willard Small Mazes in Research • 1901: Introduced mazes to animal research 2 10/20/2011 Mazes in Research • T-Maze – Alternation learning – Better at win-shift than win-stay Mazes in Research • Morris Water Maze – Cued (Response) Learning • S-R Association – Place Learning • Radial Arm Maze • Explicit, cognitive memory – Random without repetition – Memory Load: 16+ Conditioning Takes Time • Skinner’s Free Operant Protocol – Skinner box – Secondary Reinforcer Shaping Behavior • Shaping vs. Autoshaping • Jenkins & Moore (1973) – More like classical conditioning – Light (CS) predicts food (US) which naturally follows food seeking behavior (UR) so it shapes pecking (CR). Conditioning is Useful Not All Conditioning is Equal • Child rearing • Weight loss • Partial Reinforcement Effect • Behavioral Modification • Fixed vs vs. Variable & Ratio vs vs. Interval – Partial Reinforcement Extinction Effect (PREE) • Frustration (Amsel) vs. Sequential (Capaldi) Theories – Child rearing, pet training, gambling, supersition • Token Economies – Conestogas – Tickets for prizes 3 10/20/2011 What explains the PREE? Frustration Theory (Amsel) CRF R+ Extinction R- Sequential Theory (Capaldi) Frustration Punishes Response Evidence for Frustration: • Behavior of pigeons • Children tantrums CRF: R+ R+ R+ R+ R+ R+ • Develop (R-O) expectancy PRF: R+ R+ R- R+ R- R• Develop (R-O) and (R-no O) expectancy S (frustration) What explains the PREE? R O Choosing Between Behaviors • Matching Law B1 / (B1 + B2) = R1 / (R1 + R2) B = The rate of the behavior R = Maximum rate of rewards for the behavior Outcome of previous trial serves as a cue for subsequent behavior PRF: R+ R+ Fm R- R+ R- R- Fm NFm Fm NFm NFm • NFm – R (S-R) strengthened by next R+ What happens with long ITI?....Decay • Frustration? • Memory? Stronger PREE with long ITI Complex Behavior • Response Chaining – Backward Chaining – Breaks in the “chain” – Animal intelligence • Probability Matching – Animals smarter than humans? Human Skills and Habits • Walking – feedback from vision/muscles? 1 Lashley (1951): RTs > 100ms 1. • Pianists: 16+ movements per second 2. Damage to sensory feedback 3. Sequencing errors 4. Time to initiate depends on length Human Skills and Habits • Motor Programs – Initiated complete – General outline, malleable (Schmidt, 1988) • Skill Acquisition (Anderson, 1982) 1. Cognitive Stage 2. Associative Stage 3. Autonomous Stage 4 10/20/2011 Striatum and Skill/Habit Double Dissociation • Broca vs. Wernicke • Caudate, putamen, nucleus accumbens • Organizes somatosensory representations and motor responses for planning and executing goal-oriented behavior. Packard et al. (1989) Response vs. Place Learning • Radial Arm Maze (8 arms) • Win-Stay vs. Win-Shift Habit Learning in Humans • Parkinson’s Disease Weather Prediction Game • Knowlton et al. (1996) – Impaired dopaminergic system in striatum • Huntington’s Disease – Loss L off some striatal i l ffunction i (Gabrieli, 1995) 5 10/20/2011 Weather Prediction Game • Knowlton et al. (1996) Weather Prediction Game • Poldrack et al. (1999) Neurophysiological Data • Mintz (1996) – Neurons in striatum fire in anticipation of movement Loose Ends • Addiction and Drug Use – Dopamine and Reward • Schultz (2006) – DA Neurons from brain stem into striatum – Fire with expectation and reception of rewards • Blocking and expectation • Stress St and dM Memory – “Autopilot” 6