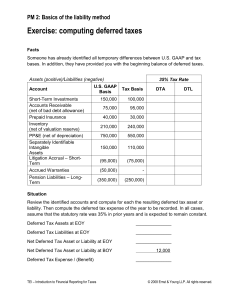
Insight into Deferred Taxes How Do Deferred Taxes Arise?
advertisement

Insight into Deferred Taxes How Do Deferred Taxes Arise? Differences exist between the accounting books and the tax books because of temporary differences » Depreciation » Inventory » Restructuring charges » Allowance for bad debts Ignore permanent differences – Examples: Goodwill, tax-free income, ... FIN 551: Fundamental Analysis FIN 551: Fundamental Analysis 2 1 Components of Deferred Taxes Deferred taxes separated into – Short-term and long-term components – Assets and liabilities Deferred tax liabilities – Debt or equity? » When is reversal expected? » Continual growth: Maybe no reversal. FIN 551: Fundamental Analysis 3 Financial Statement Presentation On the balance sheet, an enterprise should separate deferred tax liabilities and assets into a current amount and a non-current amount. Deferred tax liabilities and assets should be classified as current or non-current based on the classification of the related asset or liability for financial reporting. FIN 551: Fundamental Analysis FIN 551: Fundamental Analysis 4 2 Changing Tax Rates What is the effect of changing tax rates? Rule: – Establish deferred taxes at the rate expected to exist when the timing difference reverses Tax increase: » Debit: Tax expense » Credit: Deferred tax liability Tax decrease: » Debit: Deferred tax liability » Credit: Tax expense. FIN 551: Fundamental Analysis 5 The Thought Process Deferred tax liability – Accounting books show more income than tax books Deferred tax asset – Tax books show more income than accounting books – May have a partially/entire offsetting valuation allowance. FIN 551: Fundamental Analysis FIN 551: Fundamental Analysis 6 3 Thought Process: Deferred Tax Liability Increase in deferred tax liability – Expense more (or revenue less) on the tax books than on the accounting books Reverse the logic for a decrease in the deferred tax liability Example: – $100 depreciation on accounting books; $150 depreciation on tax books » Deferred tax liability increases $50 * tax rate. FIN 551: Fundamental Analysis 7 Thought Process: Deferred Tax Asset Increase in deferred tax asset – Expense less (or revenue more) on the tax books than on the accounting books Reverse the logic for a decrease in the deferred tax asset Example: – $100 restructuring charge on accounting books; $0 restructuring on tax books until money spent » Deferred tax asset increases $100 * tax rate » Like a prepayment of taxes. FIN 551: Fundamental Analysis FIN 551: Fundamental Analysis 8 4 Temporary Differences Effect Revenue/ Expense When recorded in books relatively to the taxable income Deferred tax effect Revenue Earlier Liability Revenue Later Asset Expense Earlier Asset Expense Later Liability FIN 551: Fundamental Analysis 9 Basic Journal Entry to Record Deferred Taxes Tax Liability Income Tax Expense xxx Def.Tax Liability Taxes Payable xxx xxx Tax Asset Income Tax Expense Def. Tax Asset Taxes Payable FIN 551: Fundamental Analysis FIN 551: Fundamental Analysis xxx xxx xxx 10 5 Valuation Allowance Deferred tax asset balance may be reduced by a valuation allowance Allowance represents management’s concern about not being able to generate enough future accounting income to utilize deferred tax assets Reduction in deferred tax asset means » Debit: Tax expense » Credit: Deferred tax asset. FIN 551: Fundamental Analysis 11 Analyze Deferred Taxes Currently payable Federal State Total Deferred Total ‘03 ‘02 ‘01 17.3 3.7 21.0 30.0 51.0 1.0 3.7 4.7 33.0 37.7 6.6 2.2 8.8 29.0 37.8 FIN 551: Fundamental Analysis FIN 551: Fundamental Analysis 12 6 Breakdown of Deferred Taxes ‘03 ‘02 Customer leases 27.6 33.8 Spare parts 59.0 Depreciation 8.3 9.3 Other 9.5 4.9 Tax loss & carryfwds -74.4 -15.0 Total 30.0 33.0 FIN 551: Fundamental Analysis ‘01 15.5 2.2 7.9 -5.4 29.0 13 Example: Deferred Tax Liability - Depreciation Bryant Corporation purchased a new machine for $100,000 on January 1, 2001 The machine has a four-year estimated service life and no salvage value Bryant’s pretax income for each year 2001 - 2004 is 200,000 before depreciation and taxes. FIN 551: Fundamental Analysis FIN 551: Fundamental Analysis 14 7 Example … Bryant Corp. uses straight-line depreciation on its books and MACRS for tax reporting For tax purposes the machine is also depreciated over 4 years using MACRS (an accelerated depreciation method) The depreciation percentages for each of the years are 33%, 44%, 15% and 8% Assume a 40% tax rate. FIN 551: Fundamental Analysis 15 Example … A. Compute financial (book) income after depreciation but before taxes. What is income tax expense? B. Compute taxable income. What is income tax payable? C. Give the journal entries to record taxes. D. Give the balance of the deferred tax liability at the end of each of the years. FIN 551: Fundamental Analysis FIN 551: Fundamental Analysis 16 8 Solution A. Financial (book) income 2001 Income before Depreciation Depreciation Expense ($100,000/4) Income after depreciation but before taxes Income Tax Expense (40%) 2002 2003 $200,000 $200,000 $200,000 (25,000) (25,000) 2004 $200,000 (25,000) (25,000) $175,000 $175,000 $175,000 $70,000 $70,000 $70,000 $175,000 $70,000 FIN 551: Fundamental Analysis 17 Solution … B. 2001 2002 2003 2004 Pre-Tax Income before Depreciation $200,000 $200,000 $200,000 $200,000 Depreciation Deduction: (33,000) (44,000) (15,000) (8,000) Taxable Income $167,000 $156,000 $185,000 $192,000 Income Taxable Payable (40%) $66,800 $62,400 $74,000 $76,800 FIN 551: Fundamental Analysis FIN 551: Fundamental Analysis 18 9 Solution … C. Journal entries: 2001 Income Tax Expense Tax Payable Deferred Tax Liability 70,000 66,800 3,200 2002 Income Tax Expense Tax Payable Deferred Tax Liability 70,000 62,400 7,600 FIN 551: Fundamental Analysis 19 Solution … 2003 Income Tax Expense 70,000 Deferred Tax Liability Tax Payable 4,000 74,000 2004 Income Tax Expense 70,000 Deferred Tax Liability Tax Payable 6,800 76,800 FIN 551: Fundamental Analysis FIN 551: Fundamental Analysis 20 10 Solution … D. The deferred tax liability account Dr. Cr. 3,200 2001 entry 3,200 12/31/2001 7,600 2002 entry 10,800 12/31/2002 4,000 2003 entry 6,800 6,800 12/31/2003 2004 entry 0 12/31/2004 The liability has reversed itself FIN 551: Fundamental Analysis 21 Example: Deferred Tax Liability – Advances from Customers Miller Co. received $30,000 of subscriptions in advance at the end of 2001 Subscription revenue will be equally recognized in 2002, 2003, and 2004, for financial accounting purposes – All of the $30,000 will be recognized in 2001 for tax purposes Pretax income for each year 2001-2004 is $100,000 -- assume a 40% tax rate. FIN 551: Fundamental Analysis FIN 551: Fundamental Analysis 22 11 Questions A. Compute Financial (book) income including subscription revenue but excluding taxes. What is income tax expense? B. Compute taxable income. What is income tax payable? C. Give the journal entries to record taxes. D. Give the balance of the deferred tax asset at the end of each of the years. FIN 551: Fundamental Analysis 23 Questions … E. For this requirement only, assume that as a result of examining available evidence in 2004, it is more likely than not that $10,000 of the deferred tax asset will not be realized • Give the journal entry to record this reduction. FIN 551: Fundamental Analysis FIN 551: Fundamental Analysis 24 12 Solution A. 2001 2002 2003 2004 100,000 100,000 100,000 100,000 0 10,000 10,000 10,000 100,000 110,000 110,000 110,000 40,000 44,000 44,000 44,000 Financial (book) income Income before subscription Subscription revenue received in 2004 Income before taxes Income tax expense (40%) FIN 551: Fundamental Analysis 25 Solution … Pretax income Subscription received in 2001 Taxable Income Taxes Payable (40%) 2001 2002 2003 2004 100,000 100,000 100,000 100,000 30,000 - - - 130,000 100,000 100,000 100,000 52,000 40,000 40,000 40,000 FIN 551: Fundamental Analysis FIN 551: Fundamental Analysis 26 13 Solution … C. Journal entries 2001 Income tax expense Deferred tax asset Tax payable 40,000 12,000 52,000 2002 - 2004 Income tax expense Deferred tax asset Tax payable 44,000 4,000 40,000 FIN 551: Fundamental Analysis 27 Solution … D. The deferred tax asset account Dr. Cr. 12,000 2001 entry 12,000 12/31/2001 4,000 8,000 2002 entry 12/31/2002 4,000 4,000 2003 entry 12/31/2003 4,000 2004 entry 0 12/31/2004 The asset has reversed itself. FIN 551: Fundamental Analysis FIN 551: Fundamental Analysis 28 14 Solution … E. Income Tax Expense Allowance to Reduce Deferred Tax Asset To Expected Realizable Value 10,000 10,000 To record the reduction in the deferred tax asset FIN 551: Fundamental Analysis 29 Example: Permanent Differences Calculation Hunter Corporation reports the following information for 2004: Financial (Book) Income before Income Taxes Income Taxes Payable (for 2004) Income Tax Expense $548,000 157,500 210,000 • Hunter Corp. has both temporary and permanent differences between book income and taxable income • Temporary difference results from depreciation • Permanent difference results from a fine that the company has to pay (but can not be deducted on its tax return). FIN 551: Fundamental Analysis FIN 551: Fundamental Analysis 30 15 Question What is the amount of the permanent difference for the year? The tax rate is 35%. FIN 551: Fundamental Analysis 31 Solution Step 1: Find the change in the deferred tax liability Income Tax Expense (Book) $210,000 Income Taxes Payable 157,500 ∆ Deferred Tax Liability 52,500 Step 2: Find the temporary difference ∆ Deferred Tax Liability/0.35 $52,500/0.35= 150,000 Step 3: Find taxable income Income Taxes Payable (from current year)/0.35 $157,500/0.35= 450,000 FIN 551: Fundamental Analysis FIN 551: Fundamental Analysis 32 16 Solution … Step 4: Find the permanent difference Taxable Income (IRS) $450,000 Temporary Differences 150,000 Financial (Book) Income before Taxes Excluding Permanent Differences 600,000 Permanent Differences (P.N) 52,000 Financial (Book) Income before Taxes 548,000 FIN 551: Fundamental Analysis 33 The End FIN 551: Fundamental Analysis FIN 551: Fundamental Analysis 34 17