Basic Organic Chemistry Homework 1 Basic Principles Answer Key
advertisement

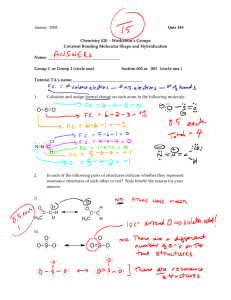
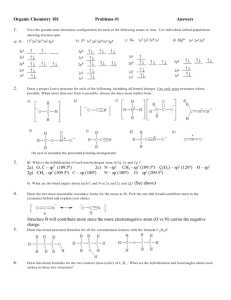
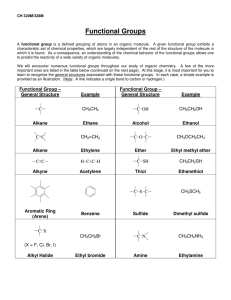
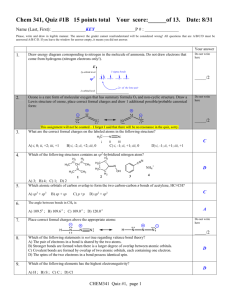
******************************************** Basic Organic Chemistry Homework 1 Basic Principles Answer Key ************************************************* ************************************************************************************************** Basic Organic Chemistry Homework Sheet One - Basic Principles ************************************************************************************************** Q1: Assign formal charges (on the atoms that require them) to the following molecules and ions. All lone pairs are shown already. a) b) H3C H2C CH e) O N f) O c) Se H O H H3N C H d) a) C C O H g) N O N b) h) k) O F S N O F F B O amines H Br Br H CH H H H H H Br H Br C C H C C H a) _H H3C H C C H H a) H3C—Br Et2C=O O b) imines unbranched C N cyclic Q5: Use the δ+ / δ- convention to indicate the direction of polarity for each of the bonds indicated by lines (— or =). Also, state whether the molecule is polar or non-polar overall. e) Q6: a) Draw (in skeletal form) the resonance structures (if any) for the four anions shown, using curly arrows to show the movement of the π electron pair. O O C C C C C H2C f) c) Q3: Put these molecules in order of increasing dipole moment (polarity), drawing each as a skeletal structure. H Q4: Draw skeletal structures of all the isomers of C3H7N (there are at least 11). Classifying each structure as an amine or imine and as unbranched or cyclic. Then draw out the following table and place each structure in its correct box. N N H H l) N N H O C H e) H j) H N d) C H H2C P(CH3)3 H3C N Br CH2 H2N O O i) Q2: Determine the bonding hybridisation for every p-block atom present in each of the following species: b) H3C—Li c) f) g) d) H3C—OMe H3C—CH3 F—CH3 Cl3C—Cl h) H3C—MgBr 7) Each of the four compounds below can lose its NH proton to produce an organic anion. _ N H N O O S S O O O O _ c) N O S O O d) H N+ NH2 N O H H N H N O S O O a) By considering resonance, decide which compound produces the most stable anion. b) Which produces the least stable anion? c) Hence, put the four nitrogen compounds above in order of increasing acidity (80 marks) 1 Q1: Assign formal charges, where required to the following molecules and ions. All lone pairs are shown already. _ a) b) c) d) H3C H2C CH e) Se H f) +O O H H3N C H H g)_ N_ O H j) i) + N h) + H2C_ P(CH3)3 N H _ O F _B F +O F l) N N+ O _ + O _ _ k) N H3C N C C+ O _ + O O S (12 marks) Q2: Determine the bonding hybridisation for every p-block atom present in each of the following species: a) sp2 sp3 H2N 3 CH2 d) sp2 sp2 O C 2 H sp sp sp2 N H sp2 sp3 C H sp2 sp2 b) N sp2 sp2 sp2 c) sp3 sp3 sp3 e) H2C N H H f) sp2 sp2 sp2 sp3 O C sp sp3 sp2 sp3 sp2 sp2 O sp3 sp3 CH sp2 C sp N sp (12 marks) 2 Q3: Put these molecules in order of increasing dipole moment (polarity), drawing each as a skeletal structure. Br H Br Br H C C H Non polar µ= 0 H2C H H C C Br H C C H H Slightly asymmetrical distribution of electron density H3C H C C H H H C C H H Br Electronegative Br pulls electron density to one side of the molecule Br CH2 Br Br Br increasing polarity Br (5 marks) Q4: Draw skeletal structures of all the isomers of C3H7N (there are at least 11). Classifying each structure as an amine or imine and as unbranched or cyclic. Then draw out the following table and place each structure in its correct box. amines imines NH 2 NH 2 NH N N unbranched HN H 2N NH 2 cyclic (saturated) NH N N not possible from empirical formula (11 marks – 1 for each compound) 3 Q5: Use the δ+ / δ- convention to indicate the direction of polarity for each of the bonds indicated by a line (—). Also, state whether the molecule is polar or non-polar overall. a) δ+ δH3C—Br b) δ+ δ- Et2C=O polar molecule δ+ polar molecule polar molecule e) δ- H3C—Li f) No bond polarity H3C—CH3 NON-polar molecule c) δ+ δ- H3C—OMe polar molecule g) δ- δ+ F—CH3 polar molecule d) δ+ δCl3C—Cl NON-polar molecule h) δ- δ+ H3C—MgBr polar molecule (8 marks) Q6: a) Draw (in skeletal form) the resonance structures (if any) for the four anions shown, using curly arrows to show the movement of the π electron pair. H_ O _ N _ O S N O O H +N NH2 (4 x 3 marks) 4 Q6: a) Draw (in skeletal form) the resonance structures (if any) for the four anions shown. _ H H O O_ _ N No π-bonds ⇒ no resonance stabilisation _ O S _O N O O S N O H H N NH2 N O O_ O O +N S + NH2 (4 x 3 marks) O S O O H N S O N O O H N H H N O S O O O 7) Each of the four compounds above can lose its NH proton to produce an organic anion. a) Which compound produces the most stable anion? b) Which produces the least stable anion? c) Hence, put the four nitrogen compounds above in order of increasing acidity N H N O H O amine pKa = 35 (least acidic) (least stable; not at all resonance stabilised) S H N O O amide pKa = 28 sulphonamide pKa = 12 (conjugate base has 2 resonance forms) (conjugate base has 3 resonance forms) O S O O H N S O O O bis-sulphonamide pKa = 10 (most acidic) (most stable; has 5 resonance forms) (3 + 3 + 4 marks, Total: 80 marks) 5