Organic Chemistry Exam 1 - CHE 230 (1999)
advertisement

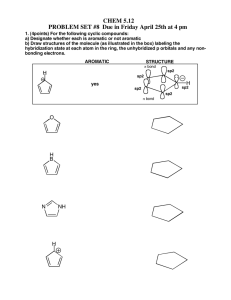
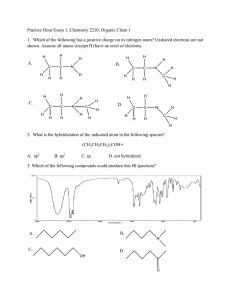
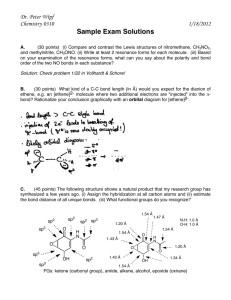
CHE 230 Organic Chemistry Exam 1, September 22, 1999 Name KEY Student ID No. Before you begin this exam: First: You are allowed to have a calculator and a simple model set at your seat. Please put away all other materials. Second: Place your student identification on your desk. A proctor will come around to check everyone’s ID. Third: Read through the entire exam. Your goal, as always, is to score as many points as possible. Do not waste time on problems that you can’t do if there are others that look easy. Fourth: It is critically important that your answers be written in a clear, unambiguous manner. Answers in which your intentions are unclear will not receive credit. Fifth: READ THE INSTRUCTIONS FOR EACH PROBLEM. You have until 8:50 to complete this exam. There will be no extensions, so budget your time carefully. Problem Number Points possible 1. 14 2. 8 3. 6 4. 10 5. 8 6. 8 7. 5 8. 3 9. 4 10. 10 11. 6 12. 8 13. 10 Total 100 1 Score 1. (14 points) Assign the hybridization at the indicated atoms in the molecules below. sp2 sp3 sp2 Amoxicillin (a penicillin antibiotic) sp2 sp2 sp2 sp3 Viagra (a recreational drug) 2. (8 points) Give the Lewis dot structures for the following species: a) CH3 + (the methyl cation) b) CH3 - (the methyl anion) 2 3. (6 points) Which of the following molecules would have a net dipole moment? (Circle them) 4. (10 points) Assign the formal charge at the central atom in each of the following compounds (assign the charge on B in a) and on N in b)). a) b) Charge is -1 5. Charge is +1 (8 points) Draw a 3-D drawing of an sp2 hybridized carbon atom. Please be sure to show the lobed shaped of each of the orbitals present, and label each hybrid orbital (as sp3 , sp2 , or sp) and each atomic orbital (as s or p). It will help if you draw fairly large. 3 6. (8 points) Draw two additional resonance forms for the molecule shown below (more than 2 are possible - just draw any two acceptable forms). Be sure to use the appropriate arrow to denote resonance forms. 7. (5 points) Peptides and proteins contain numerous amide groups, shown below. The nitrogen in an amide is sp2 hybridized. Provide a brief explanation for why nitrogen adopts this hybridization rather than sp3 . Please do not exceed the space provided, and a convincing answer can be given in one or two sentences. Sometimes a picture helps a lot too. The N is sp2 hybridized because this places the lone pair in a p orbital where it can be delocalized through resonance. 8. (3 points) How many π molecular orbitals are there in the allyl cation (below)? 3 4 9. (4 points) Draw the resonance hybrid for the allyl cation (one resonance form is shown below). Indicate partial π bonding (if any) with a dotted line and be sure you show any fractional charges. 10. a) (5 points) Circle the favored side of the following equilibrium. + + pKa = 5 pKa = 9 b) (5 points) What is the value of the equilibrium constant for this equilibrium? Note: you should not need a calculator. Simply writing the correct answer will earn full credit, but for any partial credit, all of the work must be shown. 11. (6 points) Draw 3 different structural isomers for C4 H8 . If you give more than 3, I will only grade the first 3. 5 12. (8 points) For each of the compounds below, state that they are isomers or that they are the same compound. 6 13. (10 points) Acetone (shown below) is much more acidic than a hydrocarbon like propane (also shown below). Provide a brief explanation for the relatively low pKa of acetone. Acetone pKa = 20 Propane pKa = 50 The conjugate base of acetone is stabilized by resonance, which places the anion on oxygen, an electronegative atom. The conjugate base of propane is not stabilized. END OF EXAM 7