Lecture 2 The First Law of Thermodynamics (Ch.1) Outline
advertisement

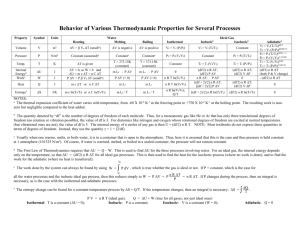
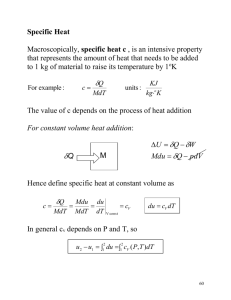
Lecture 2 The First Law of Thermodynamics (Ch.1) Outline: 1. Internal Energy, Work, Heating 2. Energy Conservation – the First Law 3. Quasi-static processes 4. Enthalpy 5. Heat Capacity Internal Energy The internal energy of a system of particles, U, is the sum of the kinetic energy in the reference frame in which the center of mass is at rest and the potential energy arising from the forces of the particles on each other. Difference between the total energy and the internal energy? system boundary system U = kinetic + potential “environment” B P T A V The internal energy is a state function – it depends only on the values of macroparameters (the state of a system), not on the method of preparation of this state (the “path” in the macroparameter space is irrelevant). In equilibrium [ f (P,V,T)=0 ] : U = U (V, T) U depends on the kinetic energy of particles in a system and an average inter-particle distance (~ V-1/3) – interactions. For an ideal gas (no interactions) : U = U (T) - “pure” kinetic Internal Energy of an Ideal Gas The internal energy of an ideal gas with f degrees of freedom: f U = Nk BT 2 f ⇒ 3 (monatomic), 5 (diatomic), 6 (polyatomic) (here we consider only trans.+rotat. degrees of freedom, and neglect the vibrational ones that can be excited at very high temperatures) How does the internal energy of air in this (not-air-tight) room change with T if the external P = const? ⎡ f PV ⎤ f U = N in room k BT = ⎢ N in room = ⎥ = PV k BT ⎦ 2 2 ⎣ - does not change at all, an increase of the kinetic energy of individual molecules with T is compensated by a decrease of their number. Work and Heating (“Heat”) We are often interested in ΔU , not U. ΔU is due to: Q - energy flow between a system and its environment due to ΔT across a boundary and a finite thermal conductivity of the boundary WORK HEATING – heating (Q > 0) /cooling (Q < 0) (there is no such physical quantity as “heat”; to emphasize this fact, it is better to use the term “heating” rather than “heat”) W - any other kind of energy transfer across boundary - work Work and Heating are both defined to describe energy transfer across a system boundary. Heating/cooling processes: conduction: the energy transfer by molecular contact – fast-moving molecules transfer energy to slow-moving molecules by collisions; convection: by macroscopic motion of gas or liquid radiation: by emission/absorption of electromagnetic radiation. The First Law The first law of thermodynamics: the internal energy of a system can be changed by doing work on it or by heating/cooling it. ΔU = Q + W conservation of energy. Sign convention: we consider Q and W to be positive if energy flows into the system. For a cyclic process (Ui = Uf) ⇒ Q = If, in addition, Q = 0 then W = 0 P W. T V An equivalent formulation: Perpetual motion machines of the first type do not exist. Quasi-Static Processes Quasi-static (quasi-equilibrium) processes – sufficiently slow processes, any intermediate state can be considered as an equilibrium state (the macroparamers are welldefined for all intermediate states). Advantage: the state of a system that participates in a quasi-equilibrium process can be described with the same (small) number of macro parameters as for a system in equilibrium (e.g., for an ideal gas in quasiequilibrium processes, this could be T and P). By contrast, for nonequilibrium processes (e.g. turbulent flow of gas), we need a huge number of macro parameters. Examples of quasiequilibrium processes: isochoric: isobaric: isothermal: adiabatic: V = const P = const T = const Q=0 For quasi-equilibrium processes, P, V, T are well-defined – the “path” between two states is a continuous lines in the P, V, T space. P T 2 1 V Work A – the The work done by an external force on a gas enclosed within a cylinder fitted with a piston: piston area W = (PA) dx = P (Adx) = - PdV force Δx P The sign: if the volume is decreased, W is positive (by compressing gas, we increase its internal energy); if the volume is increased, W is negative (the gas decreases its internal energy by doing some work on the environment). V2 W1− 2 = − ∫ P(T , V )dV W = - PdV - applies to any shape of system boundary V1 dU = Q – PdV The work is not necessarily associated with the volume changes – e.g., in the Joule’s experiments on determining the “mechanical equivalent of heat”, the system (water) was heated by stirring. W and Q are not State Functions - we can bring the system from state 1 to state 2 along infinite # of paths, and for each path P(T,V) will be different. V2 W1− 2 = − ∫ P (T , V )dV V1 P T 2 Since the work done on a system depends not only on the initial and final states, but also on the intermediate states, it is not a state function. V 1 ΔU = Q + W U is a state function, W - is not ⇒ thus, Q is not a state function either. B Wnet = WAB + WCD = −P2 (V2 −V1 ) − P1 (V1 −V2 ) P P2 P1 A = −(P2 − P1 )(V2 −V1 ) < 0 D V1 PV diagram C V2 V - the work is negative for the “clockwise” cycle; if the cyclic process were carried out in the reverse order (counterclockwise), the net work done on the gas would be positive. Comment on State Functions U, P, T, and V are the state functions, Q and W are not. Specifying an initial and final states of a system does not fix the values of Q and W, we need to know the whole process (the intermediate states). Analogy: in classical mechanics, if a force is not conservative (e.g., friction), the initial and final positions do not determine the work, the entire path must be specified. In math terms, Q and W are not exact differentials of some functions of macroparameters. To emphasize that W and Q are NOT the state functions, we will use sometimes the curled symbols δ (instead of d) for their increments (δQ and δW). d U = T d S − P dV y - an exact differential U V S dz = Ax ( x, y ) dx + Ay ( x, y ) dy - it is an exact differential if it is the difference between the values of some (state) function z(x2,y2) dz = z ( x + dx, y + dy ) − z ( x, y ) z(x,y) at these points: ∂Ax ( x, y ) ∂Ay ( x, y ) x = A necessary and sufficient condition for this: ∂x ∂y ∂z ( x, y ) ∂z ( x, y ) ⎛ ∂z ⎞ If this condition ⎛ ∂z ⎞ Ax ( x, y ) = Ay ( x, y ) = d z = ⎜ ⎟ dx + ⎜⎜ ⎟⎟ dy holds: ∂x ∂y ⎝ ∂x ⎠ y ⎝ ∂y ⎠ x T ⎛f ⎞ e.g., for an ideal gas: δQ = dU + PdV = Nk B ⎜ dT + dV ⎟ - cross derivatives V are not equal ⎝2 ⎠ z(x1,y1) Problem Imagine that an ideal monatomic gas is taken from its initial state A to state B by an isothermal process, from B to C by an isobaric process, and from C back to its initial state A by an isochoric process. Fill in the signs of Q, W, and ΔU for each step. P, 105 Pa 2 A T=const 1 Step Q W ΔU A→B + -- 0 B→C -- + -- C→A + 0 + B C 1 2 f U = Nk BT 2 V, m3 PV = Nk B T Quasistatic Processes in an Ideal Gas isochoric ( V = const ) P W1→2 = 0 2 PV= NkBT2 PV= NkBT1 1 V1,2 V 3 Q1→2 = NkB (T2 − T1 ) > 0 2 P (see the last slide) dU = Q1→2 isobaric (= CV ΔT ) ( P = const ) 2 W1→2 = −∫ P(V , T )dV = − P(V2 −V1 ) < 0 2 1 V1 1 PV= NkBT2 PV= NkBT1 V2 V 5 Q1→2 = NkB (T2 − T1 ) > 0 2 dU = W1→2 + Q1→2 (= CPΔT ) Isothermal Process in an Ideal Gas P isothermal ( T = const ) : PV= NkBT W V2 Wi − f dU = 0 V2 V1 V V = Nk BT ln i Vf Wi-f > 0 if Vi >Vf (compression) Wi-f < 0 if Vi <Vf (expansion) V2 V dV = − Nk BT ln 2 V V1 V1 W1→2 = − ∫ P (V , T )dV = − Nk BT ∫ V1 Q1→2 = −W1→2 Adiabatic Process in an Ideal Gas Q1→2 = 0 adiabatic (thermally isolated system) dU =W1→2 The amount of work needed to change the state of a thermally isolated system depends only on the initial and final states and not on the intermediate states. V2 W1→2 = − ∫ P(V , T )dV P V1 2 V2 PV = Nk BT dV V 1 PV= NkBT2 PV= NkBT1 V1 V to calculate W1-2 , we need to know P (V,T) for an adiabatic process U= ∫ γ ⇒ dU = f Nk B dT = − PdV 2 ( f – the # of “unfrozen” degrees of freedom ) ⇒ PdV + VdP = Nk B dT ⎛ 2 ⎞ dP =0 ⎜⎜1 + ⎟⎟ + f P ⎝ ⎠ f Nk BT 2 , γ = 1+ 2 PdV ÷ PV f V P dV dP γ∫ +∫ =0 V P V1 P1 PdV + VdP = − 2 Adiabatic f exponent ⎛V ⎞ ⎛P ⎞ γ ln⎜⎜ ⎟⎟ = ln⎜ 1 ⎟ ⇒ PV γ = P1V1 = const ⎝P⎠ ⎝ V1 ⎠ Adiabatic Process in an Ideal Gas (cont.) γ PV γ = P1V1 = const P 2 V2 1 PV= NkBT2 PV= NkBT1 V1 V An adiabata is “steeper” than an isotherma: in an adiabatic process, the work flowing out of the gas comes at the expense of its thermal energy ⇒ its temperature will decrease. V2 V2 V1 V1 W1→ 2 = − ∫ P(V , T )dV = − ∫ γ V2 PV 1 − γ +1 γ 1 1 dV PV V = − 1 1 Vγ −γ + 1 V1 1 ⎛ 1 1 ⎞ = PV ⎜ γ −1 − γ −1 ⎟ 1 1 γ − 1 ⎝ V2 V1 ⎠ γ γ ⇒ 1+2/3≈1.67 (monatomic), 1+2/5 =1.4 (diatomic), 1+2/6 ≈1.33 (polyatomic) (again, neglecting the vibrational degrees of freedom) Prove W1→ 2 = f f Δ ( PV ) = Nk B ΔT = ΔU 2 2 Summary of quasi-static processes of ideal gas ΔU ≡ U f − U i Quasi-Static process ΔU f f isobaric ΔU = Nk B ΔT = P ΔV 2 2 (ΔP=0) isochoric ΔU = f Nk ΔT = f ΔP V ( ) B 2 2 (ΔV=0) isothermal 0 (ΔT=0) adiabatic ΔU = f Nk ΔT = f Δ PV ( ) B 2 2 (Q=0) Ideal gas law Q W f +2 PΔV 2 − PΔV Vi V f = Ti T f 0 Pi Pf = Ti T f f ( ΔP )V 2 −W 0 − Nk B T ln ΔU Vf Vi PV i i = Pf V f γ γ PV i i = Pf V f Problem Imagine that we rapidly compress a sample of air whose initial pressure is 105 Pa and temperature is 220C (= 295 K) to a volume that is a quarter of its original volume (e.g., pumping bike’s tire). What is its final temperature? Rapid compression – approx. adiabatic, no time for the energy exchange with the environment due to thermal conductivity P1V1 = Nk BT1 P2V2 = Nk BT2 P2 = P1V1γ = P2V2γ γ P1V1 V2γ P1V1 P1V1 Nk T = = T2 B 2 V2γ −1 T1 For adiabatic processes: ⎛ V1 ⎞ T2 = T1 ⎜⎜ ⎟⎟ ⎝ V2 ⎠ γ −1 γ γ −1 ⎛ V1 ⎞ ⇒ ⎜⎜ ⎟⎟ ⎝ V2 ⎠ γ −1 T1 V1 = T2 V2 also P γ −1 / T γ = const γ −1 = = const = 295 K × 4 0.4 ≈ 295 K × 1.74 ≈ 514 K - poor approx. for a bike pump, works better for diesel engines T2 T1 Non-equilibrium Adiabatic Processes Free expansion 1. 2. TV γ −1 = const V – increases ⇒ T – decreases (cooling) On the other hand, ΔU = Q + W = 0 U ~ T ⇒ T – unchanged (agrees with experimental finding) Contradiction – because approach #1 cannot be justified – violent expansion of gas is not a quasistatic process. T must remain the same. TV γ −1 = const - applies only to quasi-equilibrium processes !!! The Enthalpy Isobaric processes (P = const): dU = Q - PΔV = Q -Δ(PV) ⇒ ⇒ Q = Δ U + Δ(PV) H ≡ U + PV - the enthalpy The enthalpy is a state function, because U, P, and V are state functions. In isobaric processes, the energy received by a system by heating equals to the change in enthalpy. isochoric: Q=ΔU isobaric: Q=ΔH in both cases, Q does not depend on the path from 1 to 2. Consequence: the energy released (absorbed) in chemical reactions at constant volume (pressure) depends only on the initial and final states of a system. f ⎞ ⎛f The enthalpy of an ideal gas: H = U + PV = Nk BT + Nk BT = ⎜ + 1⎟ Nk BT 2 ⎝2 ⎠ (depends on T only) Heat Capacity The heat capacity of a system - the amount of energy transfer due to heating required to produce a unit temperature rise in that system T C is NOT a state function (since Q is not a state function) – it depends on the path between two states of a system ⇒ f1 δQ ΔT f2 f3 T1+dT T1 i V ( isothermic – C = ∞, adiabatic – C = 0 ) The specific heat capacity C≡ C c≡ m CV and CP C= δQ dT = ⎛ ∂U ⎞ the heat capacity at CV = ⎜ ⎟ ⎝ ∂T ⎠V constant volume dU + PdV dT ⎛ ∂H ⎞ CP = ⎜ ⎟ ⎝ ∂T ⎠ P the heat capacity at constant pressure To find CP and CV, we need f (P,V,T) = 0 and U = U (V,T) ⎛ f ⎞ f H = + 1 U = Nk BT ⎜ ⎟ Nk BT ⎝2 ⎠ 2 f f ⎛ f ⎞ CP = ⎜ + 1⎟ nR CV = Nk B = nR ⎝2 ⎠ 2 2 For an ideal gas # of moles For one mole of a monatomic ideal gas: CV = 3 5 R CP = R 2 2 P Another Problem During the ascent of a meteorological helium-gas filled balloon, its volume increases from Vi = 1 m3 to Vf = 1.8 m3, and the pressure inside the balloon decreases from 1 bar (=105 N/m2) to 0.5 bar. Assume that the pressure changes linearly with volume between Vi and Vf. (a) If the initial T is 300K, what is the final T? (b) How much work is done by the gas in the balloon? (c) How much “heat” does the gas absorb, if any? Pi Pf Vi Vf V P(V ) = −0.625 bar/m 3 × V + 1.625 bar (a) PV = Nk B T (b) δWON PV T= Nk B 0.5bar × 1.8m 3 = 300K = 270K T f = Ti 3 1bar × 1m Pi Vi Pf V f Vf Vf Vi Vi = − ∫ P (V )dV - work done on a system δWBY = P (V )dV - work done by a system ∫ Vf δWON = −δWBY δWBY = ∫ P(V )dV = (0.5 × 0.8 bar ⋅ m3 + 0.5 × 0.4 bar ⋅ m3 ) = 0.6bar ⋅ m3 = 6 ⋅10 4 J (c) ΔU = δQ + δWON Vi ⎛T ⎞ δQ = ΔU − δWON = NkB (T f − Ti ) − WON = Pi Vi ⎜⎜ f − 1⎟⎟ + δWBY = 1.5 ⋅105 J × (− 0.1) + 6 ⋅104 J = 4.5 ⋅104 J 2 2 ⎝ Ti ⎠ 3 3