Chapter 17 Financial Planning and Forecasting

Chapter 17
Financial Planning and Forecasting
Companies base their operating plans on forecasted financial statements. The company must first forecast sales for the next few years. Then determine the assets required to meet the sales targets. Next comes forecasting the financial requirements necessary.
Forecasting financial requirements involves:
1.
Project the asset requirements for the coming period
2.
Project the liabilities and equities that will be generated under normal operating conditions during the same period
3.
subtract the projected liabilities and equity from the required assets to estimate the additional funds needed (AFN) to support the level of forecasted operations.
Projected Balance Sheet Method
Steps: 1. Forecast income statement
2.
Forecast balance sheet
3.
Determine how to raise the additional funds needed
4.
Financing feedbacks
Example:
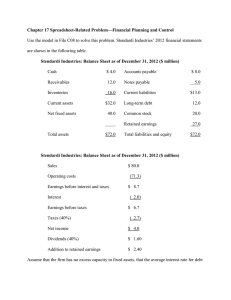
NWC 2003 sales were $2 billion, and the marketing department is forecasting a 25% increase for
2004. Assume that the company was operating at full capacity with respect to all assets in 2003.
Assume that a) Each type of asset, as well as payables, accruals, and costs, and depreciation, grows at the same rate as sales b) The dividend payout ratio is held constant at 30% c) External funds needed are financed 50 percent by notes payable and 50 percent by long-term debt (no new common stock will be issued) d) All debt carries an interest rate of 8%
Actual 2003 and Projected 2004 Income Statement
( millions of dollars)
Actual 2003 Forecast basis 2004Forecast
Sales
Costs except deprec.
Depreciation
EBIT
Interest Expense
EBT
Taxes (40%)
Net Income
$2,000.00
(1,800.00)
(100.00)
$ 100.00
(16.00)
1.25 x 2003 Sales
.90 x 2004 Sales
.05 x 2004 Sales
→
$ 84.00
(33.60)
$ 50.40
Dividends (30%)
Addition to R.E.
$ 15.12
$ 35.28
2004 Balance Sheet ( millions of dollars)
Forecasted balance sheet items are a percent of forecasted sales
2004 sales forecasted to be $2,500.
Cash and securities
Accounts receivable
Inventories
Total current assets
Net fixed assets
Total assets basis
1 st Pass
AFN 2004
2nd Pass
$ 20
240
240
.01 x FS*
.12 x FS
.12 x FS
500
500 .25 * FS
1,000
Liabilities and equity
Accounts payables & accruals
Notes payable
100
100
.05 x FS
→
Total current liabilities
Long-term debt
Common stock
200
100
500
200
→
→
+$46** Retained earnings
Total liabilities and equity 1,000
*FS=2004 forecasted sales **increase in retained earnings from the first pass income statement.
What are the additional funds needed (AFN)?
Forecasted total assets = $
Forecasted total claims = $ __________
Forecast AFN = $ __________
AFN =
A *
S
0
∆ S −
L *
∆ S − M × S
1
× RR
S
0
How AFN will be raised?
No new common stock will be issued, any external funds needed will be raised as debt, 50% notes payable, and 50% L-T debt.
Additional notes payable =
Additional long-term debt =
This additional financing will add to interest expense
8 % × =
which will lower net income and the addition to retained earnings
Other Considerations in Forecasting
1.
excess capacity. Can we always assume 100% capacity utilization? What if asset use is less than 100% of capacity? Let’s assume that in fixed assets in 2003 were being utilized to only
90% of capacity.
Full capacity sales =
%
Actual capacity sales at which
=
$ 2 , 000
90 %
= $ 2 , 222
FA were operated
T arg et FA
Sales
=
Actual FA
Full capacity sales
=
$ 500
$ 2 , 222
= 22 .
5 %
Forecasted balance sheet items are a percent of forecasted sales
2004 sales forecasted to be $2,500.
Cash and securities
Accounts receivable
Inventories
Total current assets
Net fixed assets
Total assets basis
1 st Pass
AFN 2004
2nd Pass
$ 20
240
240
.01 x FS*
.12 x FS
.12 x FS
500
500 .225 * FS
1,000
Liabilities and equity
Accounts payables & accruals
Notes payable
100
100
.05 x FS
→
Total current liabilities
Long-term debt
Common stock
Retained earnings
200
100
500
200
→
→
+$46**
Total liabilities and equity 1,000
*FS=2004 forecasted sales **increase in retained earnings from the first pass income statement.
2.
economies of scale -- variable cost of good sold ratio may change with the size of the firm
3.
lumpy assets -- not all assets can be acquired in small increments, but must obtained in large discrete amounts. A small increase in sales can require significant increase in plant and equipment