Occupy the Atom
advertisement

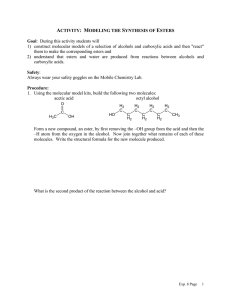
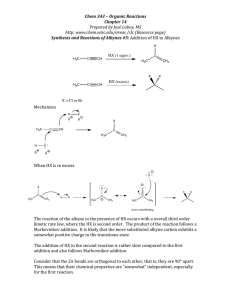
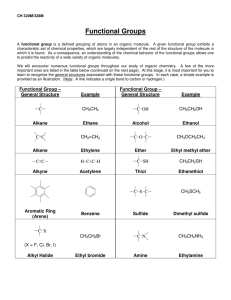
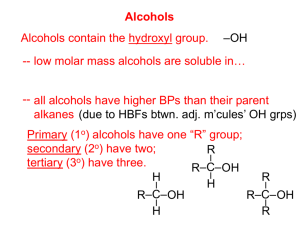
Occupy the Atom Toronto French School alum Hello, my name is 3-methyl, 4-ethyl, heptane This is one configuration of C10H22 , one of several structural isomers. Stick figures assume Cs at vertices and Hs where no other bonds are marked. Double bonds: molecule is “unsaturated” A ‘saturated’ C has bonds to 4 different neighbours. In an ‘unsaturated’ compound at least one C has fewer than 4 neighbours. When there is a double bond the ‘ane’ ending of the hydrocarbon is replaced by ‘ene’. If there is a triple bond, ‘yne’ is used instead. H H C H ethane H C H H H H H C ethene Alkanes, alkenes and alkynes. C H C C H ethyne “acetylene” H Isomers: cis vs. trans cis trans Vs. cis 2-butene trans 2-butene 2-butyne cyclohexane 1,3,5 cyclohexatriene cyclohexa-1,3,5-triene Special case of aromatic compounds H C H C H C H C C H C C H H H C C H H C C H C H = C C H C H C H C C H C C H H C H C H H H = H C molecule module ethane ethyl benzene phenyl C H The modules that make up a molecule contribute to its chemical and physical properties. This is why knowledge of the structure provides insight into the behaviour of the chemical. Heteroatoms= any atom that is not C or H. H3C H O CH2 H3C H HN CH2 H3C CH3 C2H6 gas at 25 °C, not soluble in water. HO CH2 H3C C2H5OH liquid, soluble in water. C2H5NH2 gas, pungent, corrosive. H2N CH2 H3C Alcohols R-OH (R = ‘whatever’) More soluble in water than the parent hydrocarbon. lower boiling point “ “ “ We value ethyl alcohol for its relaxing and inebriating effects, but other alcohols can be toxic or otherwise dangerous. This is just a module that can appear as part of very diverse molecules. R Primary alcohols R-CH2OH Secondary alcohols R,R’CHOH C H2 OH R CH R' OH Aromatic alcohols are weakly acidic Fig 12.13 Antiseptic: kills bacteria, acidity and solvent of membrane lipids BPA: bis-Phenol A 2,2-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)propane http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bisphenol_A Ethers R-OR‘ (R’ = ‘another whatever’) Fig 12.15 Can H-bond, Cannot H-bond this is considered to be more drastic than two different configurations of an alkane. Fig 12.16 Ethers in your day O O O diethyl ether: anaesthetic OH dioxane, solvent, pollutant O O O OH PEG = poly ethylene glycol (check your shampoo & toothpaste). Carbonyl group: >C=O Internal carbonyl: ketone Nail polish remover. Terminal carbonyl: aldehyde The C also has a bond to an H. Fragrant aldehydes (even acetone smells ‘nice’) Carboxylic acids: R-COOH It’s back !!! Acetic acid : O O + H+ OH O- carboxylic acid carboxylate Formic acid O O HC HC OH + H+ O- Butane’s acid: butanoic acid: CH3CH2CH2COOH Esters R-COO-R’ O O O ethylbutyrate ethylbutyrate ethyl butyl ether O essence of pineapple O Still one of the safest drugs known condensation with loss of water + HO H2O + O acidic phenol in addition to carboxyl Mask phenol by forming an ester