Crystal Field Theory Bonding in Transition Metal Complexes
advertisement

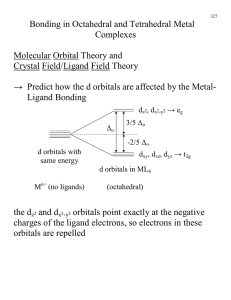
Bonding in Transition Metal Complexes Crystal Field Theory 1) Crystal Field Theory (ligand field theory) Treat Ligands as negative charges (they repel the e- in the d orbitals deals only with d orbitals 2) Molecular orbital theory Mn+ The six negative charges are equally distributed in a sphere around the metal Bonding in Coordination Compounds Isolated transition metal atom Bonded transition metal atom Crystal field splitting ( Δ) is the energy difference between two sets of d orbitals in a metal atom when ligands are present S=5/2 S=5/2 S=1/2 S=2 S=1 S = 1/2 S = 5/2 S=1 S=2 S=0 S=2 S = 3/2 S = 1/2 Bonding in Coordination Compounds Magnetic Susceptibility Δo Unpaired electrons: Paramagnetic compounds attracted to magnetic field “weigh more” Paired electrons: Diamagnetic compounds repelled by magnetic field “weigh less” Δο = hν Bonding in Coordination Compounds Spectrochemical Series Spectrochemical Series I- < Br- < Cl- < OH- < F- < H2O < NH3 < en < CN- < CO Weak field ligands Small Δ Strong field ligands Large Δ Sc Y La 3 Ti V Zr Nb Hf Ta 4 5 Cr Mn Mo Tc W Re 6 7 Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd Os Ir Pt Au Hg 8 9 10 11 12 Sc Y La 3 Valence electron count for neutral metal Quiz: A. 1 Sc Y La 3 B. 2 C. 3 Ti V Zr Nb Hf Ta 4 5 D. 4 Cr Mn Mo Tc W Re 6 7 Quiz: F. 6 G. 7 H. 8 Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd Os Ir Pt Au Hg 8 9 10 11 12 Valence electron count for neutral metal Quiz: Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd Os Ir Pt Au Hg 8 9 10 11 12 How many d electrons in? Ti(H2O)6+4 d electrons = ? E. 5 Cr Mn Mo Tc W Re 6 7 Valence electron count for neutral metal How many d electrons in? Fe(H2O)6+2 Ti V Zr Nb Hf Ta 4 5 A. 1 Sc Y La 3 B. 2 C. 3 Ti V Zr Nb Hf Ta 4 5 d electrons = ? D. 4 E. 5 Cr Mn Mo Tc W Re 6 7 F. 6 G. 7 H. 8 Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd Os Ir Pt Au Hg 8 9 10 11 12 Quiz: What is spin state? S = ? How many d electrons in? Co(NH3)4Cl2+1 d electrons = ? Fe(H2O)6+2 I- < Br- < Cl- < OH- < F- < H2O < NH3 < en < CN- < CO A. 1 Sc Y La 3 B. 2 C. 3 Ti V Zr Nb Hf Ta 4 5 D. 4 E. 5 Cr Mn Mo Tc W Re 6 7 F. 6 G. 7 H. 8 Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd Os Ir Pt Au Hg 8 9 10 11 12 Quiz: What is spin state? S = ? A. 1/2 B. 1 Sc Y La 3 Ti V Zr Nb Hf Ta 4 5 C. 3/2 D. 2 Cr Mn Mo Tc W Re 6 7 E. 5/2 F. 3 Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd Os Ir Pt Au Hg 8 9 10 11 12 Quiz: What is spin state? S = ? Fe(CN)6-3 Co(NH3)6+3 low spin. I- < Br- < Cl- < OH- < F- < H2O < NH3 < en < CN- < CO I- < Br- < Cl- < OH- < F- < H2O < NH3 < en < CN- < CO A. 1/2 A. 1/2 B. 1 C. 3/2 D. 2 E. 5/2 F. 3 B. 1 C. 3/2 D. 2 E. 5/2 F. 3 Tetrahedral Coordination Δt = 4/9Δo All tetrahedral compounds are High Spin Why do d8 metal compounds often form square planar compounds z Thought experiment: Make a square planar compound by removing two ligands from an octahedral compound L L L M L y L L x L L M Square Planar Complexes L L trans Pt(NH3)2Cl2 dx2-y2 dx2-y2 dz 2 dxy dxy dxz,dyz dz2 [Pt(NH3)4]2+ dxz,dyz Octahedral Square Planar H2O H2O OH2 Ni 2 OH2 OH2 H2O Octahedral Coordination number =6 Ni(II) d8 S = 1 Cl Cl 2- Ni Co(I) Ni(II) Pd(II) Rh(I) Pt(II) Ir(I) cis Pt(NH3)2Cl2 Pt2+ d8 Cl N N C C Ni C N C N Square Planar (CN=4) Ni(II) d8 S = 0 Cl Tetrahedral (CN=4) Ni(II) d8 S =1 2- dxy dxz,dyz dx2-y2 dz2 OH2 Ni 2 OH2 Ni(II) d8 S = 1 n+ L L 4s dxz,dyz Square Planar 3d Cl OH2 H2O Octahedral Coordination number =6 L L M L L dz 2 Tetrahedral Octahedral H2O 4p dxy dxy dxz,dyz H2O Molecular Orbital Theory for ML6 dx2-y2 dx2-y2 dz 2 Cl 2- N N Cl C C Ni 2- Ni Cl Tetrahedral (CN=4) C N N Square Planar (CN=4) Ni(II) d8 S =1 Ni(II) d8 S = 0 σ antibonding 4p salcs C Metal ligands The 4s an 4p orbitals is much more diffuse in space than are the 3d orbitals. They have a higher quantum number n and the have fewer nodes (0 or 1) versus 2 for the d orbitals. 4s This means that when a transition metal atom bonds to other atoms, the largest interactions are with the s and p orbitals, not the d orbitals. 3d salcs σ bonding dxy, dxz, dxy can’t over lap with ligand orbitals σ Antibonding eg* y y nonbonding 3d x x t2g dxy dxy dxy, dxz, dxy become nonbonding nonbonding σ bonding salcs eg σ bonding between the d orbitals and the ligand orbitals is less than that between the ligand orbitals and the s and p orbitals on the metals [Co( NH3)6] 4p 4s 4p 4s eg 3+ Co3+ d6 2 x 6L = 12eTotal 18e- eg* Δo 3d t2g 3d salcs t2g salcs 6 M-L σ bonding MO’s (12 e-) pi bonding + 4p dxy 4s 3d eg pi* - pi antibonding t2g pi salcs sigma Other combinations are non bonding. Nodes don’t match 4p 4s 4p 4s eg 3d eg 3d t2g t2g pi pi salcs salcs sigma sigma 4p 4s 4p eg 3d no pi eg 3d t2g pi* t2g salcs salcs sigma sigma Quiz. For each of the following show the d orbital electron occupancies. Count d electrons? What is the spin, S? Spectrochemical Series pi 4s pi* pi antibonding Fe(Cl)6-3 A. 0 B. 1/2 Mn(CN)6-4 C. 1 Cu(Cl)4-2 D. 3/2 E. 2 Pd(CN)4-2 F. 5/2 G. 3 The following complexes are not colored? Why not? Ti(H2O)6+4 Zn(H2O)6+2 Mn(H2O)6+2