1. POWER – MEASUREMENT for balanced ...
advertisement

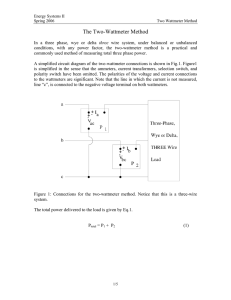
1. POWER – MEASUREMENT for balanced THREE-PHASE LOAD Task: To measure the input power of asynchronous motor by no–load test – using ONE – Wattmeter Method – the artificial Neutral wire, with. To compute with respect to the wattmeter consumption P´. Diagram (lab 107): Diagram for lab 57: Instruments: VAC…ferromagnetic voltmeter 250V Rn … resistance multiplier for wattmeter AAC…ferromagnetic ammeter 5A ASM … asynchronous motor W… ferrodynamic wattmeter cos φ 0,2 The measuring Current transformer is used in lab 57 ( the transformer secondary winding has to be shortened – during the as. motor start). Measured and computed values: VL1L2 kW IL1 αW [V] [A] [W/d] [d] RW [Ω] RV [Ω] P1 [W] P'W [W] P'V [W] P3 [W] cos ϕ [-] Wattmeter reading: P1 = k W α W Wattmeter and voltmeter consumption: PW′ = Three phase input power: P3 = 3 ( P1 − PW′ − PV′ ) = 3 PL1 Power factor: cos ϕ = U L21 RW kW = PV′ = U L21L 2 RV rV .rA cos φw d U U L1 = L1L 2 3 PL1 U L1 I L1 2. POWER MEASUREMENT for Unbalanced FOUR-WIRE, WYE-Connected Load (the neutral conductor, with). Task: Having been realized, the 3 – PHASE-WYE connected LOAD (the three various resistors); by the electronic wattmeter using, to measure: - either the average power in each phase; and either the total average power, too. Diagram: Instruments: PMP3 … the electronic programmable ELKO ŠŤOVÍČEK RZ1 … load resistor 250 Ω (lab 57 … 400 Ω) RZ2 … load resistor 450 Ω (lab 57 … 600 Ω) RZ3 … load resistor 600 Ω (lab 57 … 1200 Ω) Measured and computed values: VL1 IL1 PL1 VL2 IL2 [V] [A] [W] [V] [A] PL2 [W] VL3 [V] IL2 [A] PL3 [W] P3 [W] cos ϕ [-] Note: The electronic wattmeter has to be controlled in agreement the enclosed instructions, with. 3. TWO WATTMETER METHOD (Aron´s Method) - for the TOTAL POWER MEASUREMENT in a THREE-PHASE system (no-neutral conductor, with). Task: Two Wattmeter Method - being applied to the THREE resistors DELTA -connected LOAD; to measure the input power. To compute – being respected – the instruments consumptions. Instruments: VAC…ferromagnetic voltmeter 500V AAC…ferromagnetic ammeter 2A W… ferrodynamic wattmeter 360V/2A RZ1 … load resistor 410 Ω RZ2 … load resistor 600 Ω RZ3 … load resistor 1200 Ω Diagram: L1 A W1 V1 V3 RZ1 RP L2 A RP L3 RZ2 A Measured and computed values: V L1L2 I L1 αW1 kW1 VL2L3 I L3 [V] [A] [d] [W/d] [V] [A] V2 RZ3 W2 αW2 [d] kW2 [W/d] I2 VL1L3 [A] [V] Calculation: wattmeter consumption; and voltmeter consumption: 2 U L2L U L21L2 U2 3 P´W 1 = P´W 2 = P´V 1 = L1L2 RV1 ( RW1 + RP ) ( RW2 + RP ) RW [Ω] P´V 2 = RV [Ω] P' [W] 2 U L2L 3 RV2 3 – phase input power: P3 = k W 1 α W1 + k W 2 α W 2 − P′ P ′ = PW′ 1 + PW′ 2 + PV′1 + PV′2 P3 [W] 4. REACTIVE POWER MEASUREMENT in a THREE-PHASE system Task: To measure the reactive input power Q of asynchronous motor by no–load test – using ONE – Wattmeter Method. To sketch the phasor diagram – the measured voltages, for. Diagram: L1 A W ASM L2 V RP L3 Note: To be measured the reactive power (by the average power wattmeter using) – the voltage coil has to be connected the voltage lags 90˚, on – with respect to the corresponding voltage. These one voltage is the line – to line voltage: - (between line L2 and L3), if it’s measured in line L1; - (between L3 and L1), if measured in L2; - (between L1 and L2), if measured in L3; Instruments: VAC…ferromagnetic voltmeter 500V AAC…ferromagnetic ammeter 2A Measured and computed values: k W1 α W1 α W2 [VAr/d] [d] [d] W… ferrodynamic wattmeter 360V/2A k W2 [VAr/d] Calculation: Q= 1 ( k W 1 α W1 + k W 2 α W 2 + k W 3 α W 3 ) 3 Simplification – for the one – phase measurement, only:. Q=3 1 ( k W1 α W1) 3 α W3 [d] k W3 [VAr/d] Q [VAr]