Basic Electrical Engineering Laboratory_An Overview
advertisement

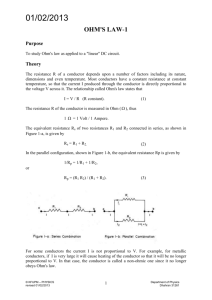
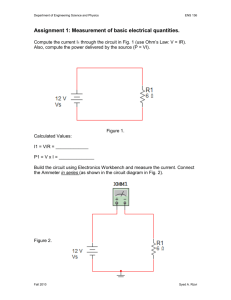
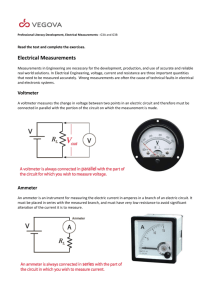
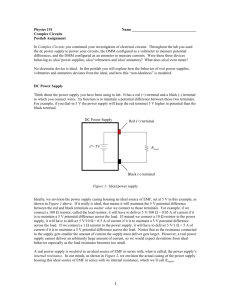
Course No: EE 1104 Course Title : Basic Electrical Engineering Laboratory Credits: 1.5 Course Teacher : Dr. Md. Rafiqul Islam Md. Jahirul Islam Al-Ahsan Talukder Special thanks to Abu Farzan Mitul & Md. Tawabur Rahman (Lecturer, Dept. of EEE) Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Khulna University of Engineering & Technology Marks Distribution: Attendance: Lab Reports and Class Performance: Quizzes: Central Viva: Total 10% 50% 20% 20% 100% List of Experiments: Exp. No. 01 02 03 Name of the Experiment Familiarization with some electric meters and circuit equipments Study of Series circuit and verification of Kirchoff’s Voltage Law (KVL) Study of Parallel circuit and Verification of Kirchoff’s Current Law (KCL) 04 Measurement of Power by Wattmeter 05 Verification of Superposition Theorem List of Experiments :(contd.) Exp. No. Name of the Experiment 06 Verification of Reciprocity Theorem 07 Determination of circuit parameters of an ac RL series circuit Determination of circuit parameters of an ac RLC series circuit Study of Series Resonance Circuit 08 09 10 Verification of Maximum power Transfer Theorem Today’s Experiment Exp. No. : 01 Name of the Experiment: Familiarization with some electric meters and circuit equipments Electric meters and circuit equipments: Equipments: Electric Meters: 1. Resistor (R) Ammeter 2. Inductor / Choke / Ballast (L) Voltmeter 3. Capacitor (C) AVO meter, Commercially 4. Electric lamps 5. Switches called Multimeter 6. Voltage Sources Wattmeter 7. Connecting wires Ammeter Measures The amount of Current flow through the circuit Types: 1. DC Ammeter 2. AC Ammeter Schematic Diagram of Ammeter: Ammeter Should be always connected in Series with Load Connection Diagram of Ammeter: Pictorial View of DC & AC Ammeter DC Ammeter AC Ammeter Voltmeter used for measuring Electrical potential difference between two points in an electric circuit Types: 1. DC Voltmeter 2. AC Voltmeter Schematic Diagram of Voltmeter: Voltmeter must be connected in Parallel with Load Connection Diagram of Voltmeter: Pictorial View of DC & AC Voltmeter DC Voltmeter AC Voltmeter Multimeter/AVO meter: Analog multimeter Digital multimeter Wattmeter Measures the Electric power in watts Types: 1. Analog Wattmeter 2. Digital Wattmeter Schematic Diagram of Wattmeter: CC PC Measured Power, P=VI Cosϴ ϴ= angle between v and i Pictorial View of Wattmeter: Report Writing: 01. Objectives 02. Introduction 03. Apparatus Required 04. Experimental Setup or Circuit Diagram 05. Experimental Data 06. Calculation 07. Graphs (if any) 08. Results and Discussion 09. Conclusion 10. References Objectives: Purpose of Experiment e.g.To be familiar with the working principle of various electric meters. Should be mentioned in points Introduction: Introductory Description. e.g. Why and where ammeter, voltmeter & wattmeter are used. Written in one Para Apparatus Required: Should be mentioned in serial numbers Name of equipments with rating Quantity Experimental Setup: The diagram of the work Specify the Equipments Direction of current flow Polarity (if any) Experimental Data: Should be written in table Draw Table using Pencil & scale. Calculation: Elaborate Calculation of the whole work [will be written in the board] Graph: Proper Scaling of axis Encircle the plotted data points Labeling [Units should be included] Figure No. along with figure name should be mentioned Example Result & Discussion: Discuss your results Is there any error in results & why? Is there any deviation in your result from ideal value & why? Comparison between measured and ideal value. Conclusion: What have you learnt from this experiment? What is the necessity of this experiment? What is the way to abase the error [if any] Question and Answer: Questions must be written in your report. Relevant answer should be written. Reference: Sources- you have used to write the report For more references – write in numbers e.g. [1] writer name, “source name”. [2]…………….. References of Today’s Experiment: [1] B.L. Theraja, “A Textbook of Electrical Technology”,Volume I. [2] Robert L. Boylestad, “Introductory Circuit Analysis”. Top page of Sessional Report: Place of Collection: THANKS TO ALL