O = O Problems With Valence Bond Theory Cause of Magnetism ELECTRON SPIN
advertisement

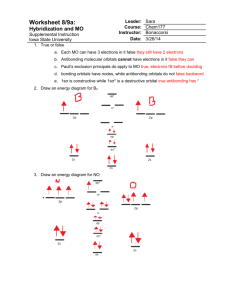
Problems With Valence Bond Theory VSEPR Theory - electron pair repulsions influence molecular shape Valence Bond Theory - atoms form bonds by overlapping hybrid orbitals Applied to O2 O=O There’s a problem with this Lewis structure for oxygen, however, and it has to do with magnetism in atoms - Cause of Magnetism = ELECTRON SPIN Diamagnetic materials = all electron spins are “paired”, so the magnetic fields cancel out N S S N = Zn = [Ar]3d104s2 Paramagnetic materials = unpaired electrons so there is a net magnetism Mn = [Ar]3d54s2 N = S 1 In the Lewis structure for oxygen, all of the electrons are paired up, so the molecule should be diamagnetic, but experiments prove that it is PARAMAGNETIC. An additional refinement in bonding theory is necessary = Molecular Orbitals - Preliminary Ideas Don’t forget that electrons behave like WAVES, and there are WAVE FUNCTIONS () that describe the electron position in space = ATOMIC ORBITALS (2) e' 2 Waves (electrons) can interfere with each other, either CONSTRUCTIVELY or DESTRUCTIVELY Principles of Molecular Orbital Theory 1. The total number of molecular orbitals = total number of atomic orbitals contributed by the bonding atoms 2. Bonding MO’s are lower in energy (more stable) than antibonding MO’s 3. Electrons occupy molecular orbitals following the Pauli Exclusion Principle (spins pair up) and Hund’s Rule (remain unpaired as long as an empty orbital is available of the same energy) 3 Types of Molecular Orbitals Bonding and Antibonding -bond formation involving p-orbitals *2p 2p 4 -bond formation involving p-orbitals *2p 2p *2p 2p Molecular Orbital Energy Levels Atomic orbitals *2p *2p 2p 2p 2p 2s 2p Atomic orbitals 2s *2s 1s 2s 1s *1s 1s 5 Molecular Orbital Diagram: H2 The two 1s orbitals may be added or subtracted to yield two sigma MOs (1 bonding/1 antibonding). 6 Bond Order and Stability Bond Order = 1/2 (number or bonding e− − number or antibonding e−). Bond order in H2 = 1 (Stable). Bond order in He2 = 0 (Not Stable). MO Diagrams for N2 and O2 7 MO Scheme for N2 Electron configuration for N2 = Bond order = • N2 has three bonds. • N2 has no unpaired electrons. MO Scheme for O2 Electron configuration for O2 = Bond order= • O2 has two bonds • O2 has two unpaired electrons in π2p* 8 Other Diatomic Molecules MO Theory correctly predicts both the magnetic properties and bond orders of diatomic molecules. MO Theory: Summary Advantages: • Provides the most complete picture of covalent bonding, including bond types and bond orders. • Accounts for magnetic properties. Disadvantage: • The most difficult to apply to large molecules; does not account for molecular shape. 9