Reactions of Alcohols: Review of Reactions of Alcohols Reaction with hydrogen halides
advertisement

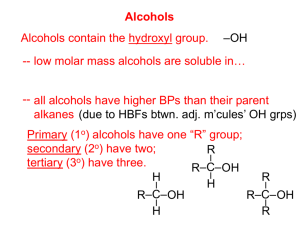
Review of Reactions of Alcohols Reaction with hydrogen halides Reaction with thionyl chloride Reactions of Alcohols: Reaction with phosphorous trihalides Review and New Acid-catalyzed dehydration Conversion to sulfonate esters New Reactions of Alcohols Oxidation Conversion to ethers Esterification Oxidation of Alcohols Oxidation of Alcohols Primary alcohols RCH2OH Strong Oxidizing Agents In aqueous solution: O O RCH RCOH Mn(VII) Cr(VI) KMnO4 CrO 3/ H 2SO4 = H2CrO 4 K2Cr2O7 / H 2SO4 = H2Cr2O7 Secondary alcohols OH O RCHR' RCR' from H2O Oxidize 1o alcohols to carboxylic acids. Cannot stop at aldehydes. aldehydes. Aqueous Cr(VI) Question H FCH2CH2CH2CH2OH K2Cr2O7 OH H2SO4 H 2O Na2Cr2O7 H2SO4 H 2O • Treatment of 1-propanol with K2Cr2O7, H2SO4, and heat will produce: • A) • C) B) O O FCH2CH2CH2COH (74%) (85%) Specialized Oxidizing Agents [Nonaqueous Sources of Cr(VI)] Question Used in CH 2Cl2 Jones Reagent: Pyridinium dichromate (PDC) CrO 3/ H 2SO4 acetone (C5H5NH+)2 Cr2O72– Pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC) “Collins Reagent” Reagent” Example: Oxidation of a Primary Alcohol with PCC A) B) • C) D) Question • What is the product of the reaction of 1butanol with PCC in CH2Cl2? H CH2Cl2 • ClCrO3– +N PCC • Treatment of 1-propanol with CrO3, H2SO4, and acetone will produce: (does not affect Carbon=Carbon double bonds) C5H5NH+ ClCrO 3– CH3(CH2)5CH2OH D) O • A) B) • C) D) CH3(CH2)5CH (78%) Example: Oxidation of a Primary Alcohol with PDC Question • (CH3)3C CH2OH • PDC • CH2Cl2 • O (CH3)3C • CH For the following reaction, select the statement that best describes it. RCH 2OH + PDC [(C (C5H 5NH +)2 Cr2O72–] → A) The alcohol is oxidized to an acid, and the Cr(VI) is reduced. B) The alcohol is oxidized to an aldehyde, and the Cr(VI) is reduced. C) The alcohol is reduced to an aldehyde, and the Cr(III) is oxidized. D) The alcohol is oxidized to a ketone, and the Cr(VI) is reduced. (94%) Conversion of Alcohols to Ethers RCH2O CH2R H OH Conversion of Alcohols to Ethers H+ RCH2O CH2R + H OH Acid-catalyzed Referred to as a "condensation" Equilibrium; most favorable for primary alcohols Example Intramolecular Analogue 2CH3CH2CH2CH2OH HOCH2CH2CH2CH2CH2OH H2SO4 via: 130° 130° H2SO4, 130° 130°C •• CH3CH2CH2CH2OCH2CH2CH2CH3 (76%) (60%) • •O O H Reaction normally works well only for 5- and 6-membered rings. H O •• + H Question • When 1-propanol is treated with Na2Cr2O7/H2SO4 followed by treatment with CH3OH, H2SO4 the product isolated is: Esterification • A) propanal B) propanoic acid • C) propanol D) methyl propanoate Example of Fischer Esterification Esterification O O ROH ROH + R'COR R'COR + R'COH COH + CH3OH O H+ 0.1 mol H 2O 0.6 mol H2SO4 condensation Fischer esterification O acid catalyzed COCH3 + reversible H 2O 70% yield based on benzoic acid Reaction of Alcohols with Acyl Chlorides Example CH3CH2 O ROH ROH + R'CCl OH + O R'COR R'COR + O HCl O 2N CCl CH3 pyridine High yields Not reversible when carried out in presence of pyridine. CH3CH2 O NO2 OC CH3 (63%) Reaction of Alcohols with Acid Anhydrides Example O O O O ROH ROH + R'COCR' O R'COR R'COR + O C6H5CH2CH2OH + F3CCOCCF3 R'COH pyridine analogous to acyl chlorides O C6H5CH2CH2OCCF3 (83%)