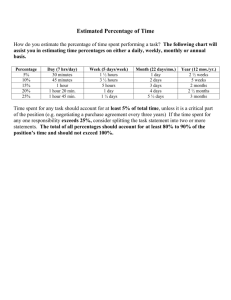
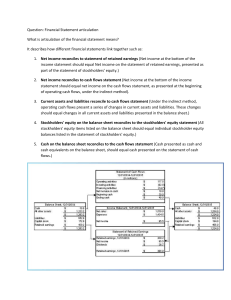
FINANCIAL STATEMENT ANALYSIS
advertisement

FINANCIAL STATEMENT ANALYSIS Tools for Financial Statement Analysis The three basic tools to highlight the significance of financial statement data is vertical analysis, horizontal analysis, and ratio analysis. Vertical and horizontal analysis is explained in the following along with a demonstration problem on the next page. A. Vertical analysis or common size analysis is a technique for evaluating financial statements data that expresses each item within a financial statement in terms of a percent of a base amount. The analysis shows the relationship of the component parts to the total in a single period statement. 1. Applying vertical analysis to the income statement, each item is expressed as a percent of net sales or total sales. 2. Applying vertical analysis to the balance sheet, each asset item is expressed as a percent of total assets, and each liability and stockholders’ equity item is expressed as a percent of total liabilities and stockholders’ equity. 3. In some cases common-size statements are presented where all items are expressed only in relative terms or percentages as a result of applying vertical analysis. Common-size statements are used to compare percentages of the current period with past periods, compare individual businesses, or compare one business to industry averages. 4. In Problem M15, each item in the Statement of Cash Receipts and Expenses is expressed as a percent of total revenue. B. Horizontal analysis or trend analysis is a technique for evaluating a series of financial statement data over a period of time. Its purpose is to determine the increase or decrease in the same items on financial statements that cover two or more time periods, expressed as an amount and percentage. 1. A change and related percent is determined between the same corresponding items among two or more different time periods. 2. An item on the most recent statement is compared with the same corresponding item on one or more earlier statements, and an increase or decrease is determined along with the percent of the increase or decrease. 3. When the comparison is made between two statements, the earlier statement is used as the base amount when determining the change amount and related percents. Amount of change = Current year amount – Base (earlier) year amount Percent of change = Current year amount – Base (earlier) year amount Base (earlier) year amount