Financial Statement Analysis: Ratios & Interpretation
advertisement

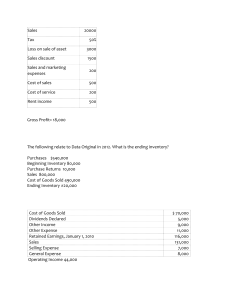
Analysis & Interpretation of Financial Statements Financial Statement Analysis The application of analytical tools and techniques to financial statement data. Allows users to focus on how numbers are related and how they have changed over time Objective of Financial StatementAnalysis External users rely on general purpose financial statements Make predictions about an organization as an aid in making decisions Users highlight important trends or changes Risk and Return Users try to balance the risk of an investment with its expected return Generally the greater the risk, the higher the return Financial statement analysis is one source of information for assessing risk and return Sources of External Information Sources of External Information Public companies must publish an annual financial report Government reports SEC 10K, 10Q Financial service information Moody’s, Dow-Jones Financial newspapers and periodicals Wall Street Journa Financial Analysis Tools Horizontal analysis Vertical analysis Ratio analysis Horizontal Analysis Horizontal Analysis: Amounts and Percentages of Change Amount of change = later year amount - Earlier year amount Percentage change = Amount of change / Earlier year amount Look for significant change Horizontal Analysis: Trend Percentages Horizontal Analysis: Trend Percentages Set all amounts in base year at 100% Compute percentages for a number of years Divide each statement amount by respective amount in base year Shows degree of increase or decrease in individual statement items Used to explain changes in operating performance Horizontal Analysis: Trend Percentages Set all amounts in base year at 100% Compute percentages for a number of years Divide each statement amount by respective amount in base year Shows degree of increase or decrease in individual statement items Used to explain changes in operating performance Vertical Analysis Shows how each item in a financial statement compares to the total of that statement Balance sheet Set both total assets and total equities at 100% Income statement Set net sales at 100% Analysis Days’ Sales in Receivables How many days’ sales remain uncollected in accounts receivable Net sales Net sales per day = 365 days Average net accounts receivable Net sales per day Inventory Turnover Cost of goods sold Average inventory Number of times the company sells and replaces its inventory during the period Holding inventory results in financing and storage costs Cost of goods sold Average inventory Analysis Debt Ratio Total liabilities Total assets Shows amount of total assets creditors provide Higher levels of debt financing means company has a higher risk of not meeting interest and principal payments Total liabilities Total assets Net income + Income tax expense Times Interest Earned Number of times the company earned interest expense with current income Creditors want to know the firm’s ability to pay annual interest charges Net income + Income tax expense + Interest expense Interest expense Analysis cont’d Profitability Profit margin Total asset turnover Return on total assets Return on owners’ equity Earning per share Profit Margin Net income Net sales Percentage each sales dollar contributes to net income Net income Net sales Analysis Cont’d Total Asset Turnover Net sales Average total assets Measures the efficiency of the company is using its investment in assets to generate sales Net sales Average total asset Analysis Cont’d Return on Total Assets Net income Average total assets Measures the amount a company earns on each dollar of investment in assets Net income Average total assets Return on Owners’ Equity Measures the earnings in relation to the owners’ investment in the company Net income - Preferred dividends Average owner’s equity Price/Earning (P/E) Ratio Number of times earnings per share the stock is currently selling for in the market Market price per share of common stock Earnings per share Dividend Yield Dividends per share Market price per share Measure of dividend-paying performance of a company Investors buy stock for two reasons Receive cash dividends Sell stock at a higher price Dividends per share Market price per shar Limitations of Financial Analysis Tools Historical nature of accounting information Changing economic conditions Comparisons with industry averages Seasonal factors Quality of reported income