Root and Tuber Crops in Definitions the Tropics Cassava
advertisement

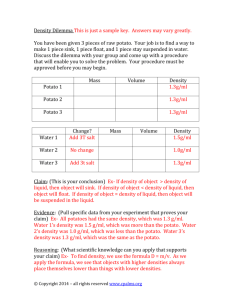
Root and Tuber Crops in the Tropics Definitions ] Root (cassava, sweet potato) Cassava Cocoyam Potato Sweet Potato Taro Yam \ No leaves or reproductive organs ] Tuber (potato, yams) \ Fleshy underground stem \ Minute scale leaves with buds (eyes) ] Corm (aroids, cocoyam and taro) \ Short, bulblike underground upright stem \ With scale leaves Tropical Horticulture - Texas A&M University World Production of Root and Tuber Crops (106 mt) Definitions ] Rhizome Million mt \ Rootlike stem \ Upper part with leafy stems \ Lower part with roots ] Bulb (lily, onion, tulip) FAOSTAT, 2003 300 200 100 About half of the potato production is in the temperate zone Tropical Horticulture - Texas A&M University Cassava Potato Production (1,000 mt) Cocoyam Taro Tropical Horticulture - Texas A&M University Food Utilization of Root and Tuber Crops (1996 data) Crop Yams [ Roots from below [ Overlapping scalelike leaves SwPotato Potato Cassava 0 \ A bud, usually underground \ Short thick stem 92,500 % in Developing Countries > 99.9% Feed Utilization of Root and Tuber Crops (1996 data) Crop Production (1,000 mt) Cassava 31,000 % in Developing Countries 71% 161,200 40% Potato 54,900 72% Sweet potato 70,100 98% Sweet potato 58,100 >99% Yam 16,000 99% Yam 400 100% Total 350,900 Total 144,800 Tropical Horticulture - Texas A&M University Tropical Horticulture - Texas A&M University 1 Cassava - Manihot esculenta Origins of Major Root and Tuber Crops Yuca, Mandioca, Tapioca ] Plant Yam Cocoyam Sweet Potato \ Slender shrub, 5 m \ Enlarged roots [ Sweet to bitter [ White to yellow \ Palmate leaves Cassava Taro ] Propagation \ Stem cuttings Potato Tropical Horticulture - Texas A&M University Cassava - Manihot esculenta ] Origin Tropical Horticulture - Texas A&M University Cocoyam - Xanthosoma sagittifolium Malanga, Tannia, Elephant’s Ear ] Plant \ South America ] Distribution \ Tropics and subtropics ] Staple food in many tropical regions \ Excellent carbohydrate source \ Perennial herb \ Corms and cormels ] Propagation \ Harvest same plant multiple times \ Portions of central corm Tropical Horticulture - Texas A&M University Cocoyam - Xanthosoma sagittifolium Malanga, Tannia, Elephant’s Ear Tropical Horticulture - Texas A&M University Potato - Solanum tuberosum ] Plant ] Origin \ West Indies and northern S. America ] Distribution \ Tropical regions \ Common in Indonesia ] Adaptation \ Herbaceous \ Subterannean stems \ Leaves ] Propagation \ Eyes from tubers ] Important staple crop \ Lowland tropics Tropical Horticulture - Texas A&M University Tropical Horticulture - Texas A&M University 2 Potato - Solanum tuberosum Sweet potato - Ipomoea batatas ] Plant ] Origin \ Highlands of South America ] Distribution \ Widely cultivated from highland tropics to temperate zones ] Adaptation \ Cool climate adaptation \ Creeping herb \ Enlarged roots vary in shape and color \ Leaves variable in size, shape, color ] Propagation \ Young stem cuttings ] Important carbohydrate source Tropical Horticulture - Texas A&M University Sweet potato - Ipomoea batatas ] Origin \ Central America ] Distribution \ Widely cultivated both in tropics and subtropics ] Adaptation \ Tropics to subtropics \ Below 2200 m altitude Tropical Horticulture - Texas A&M University Taro - Colocasia esculenta ] Plant \ Perennial herb \ Subterraneous stem [ Calcium oxalate crystals \ Heart shaped leaves ] Propagation \ Suckers \ Corm apices with leaf Tropical Horticulture - Texas A&M University Tropical Horticulture - Texas A&M University Yam Taro - Colocasia esculenta Dioscorea alata, cayenensis and rotundata (Sixty species cultivated for food and pharmaceuticals) ] Plant ] Origin \ Southeast Asia ] Distribution \ West Africa \ Caribbean \ Pacific islands ] Staple food \ Climbing vine, 10 m \ Tubers vary in shape \ Leaves ovate with cordate base ] Propagation \ Tubers ] Staple food in arid regions of Africa Tropical Horticulture - Texas A&M University Tropical Horticulture - Texas A&M University 3 Yam Dioscorea alata, cayenensis and rotundata (Sixty species cultivated for food and pharmaceuticals) ] Origin Plant Characteristics Crop \ Asia and West Africa ] Production \ Mainly Africa ] Adaptation \ Lowland tropics \ Drought tolerant Cassava Growth period (mo) 9-24 Annual or perennial Perennial Cocoyam 9-12 Perennial Corms Potato 3-7 Annual Tubers Vine cuttings Sweet potato 3-8 Perennial Taro 6-18 Perennial Corms Yam 8-11 Annual Tubers Tropical Horticulture - Texas A&M University Tropical Horticulture - Texas A&M University Plant Adaptation Crop Rain (mm) Planting material Stem cuttings Plant Soil Adaptation Temperature (ºC) Drought Crop Fertility needs OM Tolerant of requirement swampy land Cassava 1,000-1,500 25-29 Yes Cassava Low Low No Cocoyam 1,400-2,000 13-29 No Cocoyam High High No Potato 500-750 15-18 No Potato High High No Sweet potato 750-1,000 >24 Yes Sweet potato Low Low No Taro 2,500 21-27 No Taro High High Yes Yam 1,150 25-30 Yes Yam High High No Tropical Horticulture - Texas A&M University Tropical Horticulture - Texas A&M University Plant Storage Duration Crops compared for Dry Matter Production Crop Storage time in ground Post harvest storage life Crop Cassava Long Short Yam 2.4 Potato 2.2 Cocoyam Long Long Potato Short Sweet potato 2.1 Long Rice 1.9 Bananas 1.5 Wheat 1.3 Maize 1.3 Sweet potato Long Short Taro Moderate Variable Yam Long Long Tropical Horticulture - Texas A&M University Cassava Dry matter production Mt/ha/day 3.0 Tropical Horticulture - Texas A&M University 4 Crops compared for Edible Energy Production Crop Crops compared for Edible Protein Production Crop Edible energy production MJ/ha/day 216 Potato Edible protein production kg/ha/day 2.0 Cabbages Yam 182 Potato 1.4 Maize 159 Dry peas 1.4 Sweet potato 152 Wheat 1.3 Rice 151 Lentils 1.3 Wheat 135 Tomatoes 1.2 Cassava 121 Chickpeas 1.1 Tropical Horticulture - Texas A&M University Tropical Horticulture - Texas A&M University Nutritional aspects of root and tuber crops FW = fresh weight Crop Starch Protein Vitamin A Vitamin C % FW % FW mg/100g FW mg/100g FW Cassava 27-36 0.5-2.0 17 50 Potato 13-16 2.0 Trace 31 Sweet potato 18-28 1.0-2.5 900 35 Yam 18-25 2.5 117 24 Aroids 19-21 2.0 0-42 9 Tropical Horticulture - Texas A&M University Importance of Root and Tuber Crops ] Important source food and income for the most food insecure households ] Why? \ High energy production per ha/day \ Yield better under adverse conditions than other crops Nutritional Composition of 100 g of Food Crop Cassava Beans Sweet potato Rice Yam (raw) Potato Plantains Maize (grits) Percent water 68 69 71 73 74 80 80 87 Protein (g) Food energy kcal 0.9 124 7.8 118 1.7 114 2.0 109 2.1 101 2.1 76 1.3 77 1.2 51 Fats (g) 0.1 0.6 0.4 0.1 0.2 0.1 0.1 0.1 Tropical Horticulture - Texas A&M University Future Trends for Root and Tuber Crops ] Increased regional production concentration [ Sub Saharan Africa, 60% cassava production [ West Africa, 90% yam production [ China, 82% of sweet potato production ] Increased specialization of End Use [ Increase of processed forms of food [ Increased use of root/tubers for feed and starch derived products ] Relative importance remain same \ 10.5% of agricultural value Tropical Horticulture - Texas A&M University Tropical Horticulture - Texas A&M University 5 International Research Centers involved with Root and Tuber Crops International Research Centers involved with Root and Tuber Crops ] CIAT (Colombia) \ Cassava for Americas and Asia ] CIP (Peru) \ Potato \ Sweet potato \ Andean roots and tubers ] IITA (Nigeria) \ Cassava for Africa \ Yam for Africa Tropical Horticulture - Texas A&M University CIAT IITA CIP Tropical Horticulture - Texas A&M University Any Questions? Tropical Horticulture - Texas A&M University 6