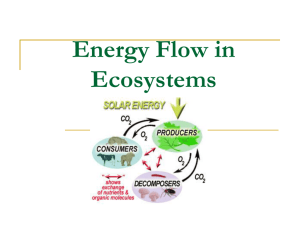
L.17.9 Energy Flow

Energy Flow
SC.912.L.17.9
Use a food web to identify and distinguish producers, consumers, and decomposers.
Explain the pathway of energy transfer through trophic levels and the reduction of available energy at successive trophic levels
Source: http://www.bigelow.org/bacteria/land.jpg
What do I need to know?
how to use a
producers, consumers, and decomposers
the pathway of
through
and the
at successive trophic levels
how
move through the
and
cycles
Food Chains vs.
Food Webs
Food chains are linked together into food webs
Who eats whom?
What type of organism do they both begin with?
How does energy flow from the sun to producer to the consumers?
Source: http://www.majordifferences
.com/2013/02/difference-betweenfood-chain-andfood.html#.U7tjc7fjiP8
Food Webs
Video Guiding Questions:
1.
Can you identify a food chain in the food web?
2.
What is the difference between a primary and a secondary consumer?
3.
What happens if an organism is removed from a food web?
The Food Chain Game
Energy Transfer
energy does not cycle through ecosystems but instead enters ecosystems and is used up within ecosystems
energy is not “lost” from ecosystems but primarily converted to waste heat
Source: http://www.tutorvista.com/co ntent/biology/biologyiv/ecosystem/ten-percent-law.php
Energy Transfer: Energy Pyramids
The 10% Rule
Video Guiding Questions:
1.
What is the 10% rule?
2.
If 90% of energy is lost within each level, where does it go?
Trophic Levels
greek ( trophē) referring to food or feeding
position that an organism occupies in a food chain
can be represented by numbers, starting at level 1 with producers
Guess the Trophic Level?
Trophic Level 2 Trophic Level 4
Trophic Level 3
Trophic Level 1
Vegetarians or Meat-eaters?
How many people can the Earth support?
If we are meat-eaters?
If we are vegetarians?
more people can live on Earth fewer people can live on Earth
Cycling of Energy & Matter
solid blue lines trace matter cycles and the broken red lines trace energy flow
energy flows through ecosystems, while matter cycles within them
Source: http://science.kennesaw.edu/~jdirnber/Bio2108/Lectu re/LecEcology/54-01-EcosystemDynamics-AL.gif
Ecosystem Inputs
nutrients cycle
Matter cannot be created or
Physics! biosphere nutrients can only cycle inputs
energy
nutrients
Biogeochemical Cycles
matter moves through these cycles, it is never created or destroyed
– just changed
involves biological, geological, and chemical processes
Source: http://pubs.usgs.gov/pp/p13
86a/gallery1-fig01.html
The Water Cycle
water moves continuously between the oceans, atmosphere and the land – sometimes outside living organisms and sometimes inside them
Source: http://ga.water.usgs.gov/ed u/watercycle.html
Water Cycle:
Main Processes
precipitation: moisture that falls to the ground
(rain, snow, sleet, hail)
evaporation: changing from liquid to gas (water to water vapor)
transpiration: plants give off water vapor from their leaves to the air
condensation: changing
Source: http://www.biofuelswatch.com/stepsof-the-water-cycle/
Water Cycle: The Basics
Reservoir
Assimilation
Release oceans, air (as water vapor), groundwater, lakes and glaciers; evaporation, wind and precipitation
(rain) move water from oceans to land plants absorb water from the ground, animals drink water or eat other organisms which are composed mostly of water plants transpire, animals breathe and expel liquid wastes
Water Cycle Animation
The Carbon Cycle
every organic molecule contains the element carbon
carbon is required for building organic compounds
carbon and oxygen form carbon dioxide gas (CO
2
)
Source: http://commons.wikimedia.o
rg/wiki/File%3ACarbon-cycle-full.jpg
Where’s the Carbon?
Carbon Cycle: The Basics
Reservoir
Assimilation
Release atmosphere (as CO
2
), fossil fuels (oil, coal), durable organic materials (for example: cellulose) plants use CO
2 in photosynthesis; animals consume plants plants and animals release CO
2 through respiration and decomposition; CO
2 is released as wood and fossil fuels are burned
Carbon Cycle Game
Show What You Know
A team of ecologists observed feeding patterns of several populations in the desert. The energy pyramid shown below depicts the feeding patterns the ecologists observed.
Show What You Know
Which of the following best explains the difference in the amount of available energy in the trophic levels of the desert ecosystem?
A.
There is less energy available in the producers because their tissues are less dense than those at higher trophic levels.
B.
There is more energy available in the second trophic level because less energy is needed for hunting compared to the higher trophic levels.
C.
There is more available energy in the birds of prey because they have greater muscle mass for storing energy than organisms in lower trophic levels have.
D.
There is less available energy in the fourth trophic level because of the loss of energy through metabolism in each of the lower trophic levels.
Show What You Know
The table below contains information about animal diets.
Animals Diet
Snakes Squirrels, chipmunks, gophers and mice
Hawks and owls Rodents and reptiles
Rodents Seeds, nuts, root, grass leaves and flowers
Which energy pyramid best represents the data in the table??
Show What You Know
Show What You Know
Which model correctly shows energy flow in a food chain?
A.
plants insects salmon bears
B.
insects plants bears salmon
C.
bears salmon insects plants
D.
salmon bears plants insects
Show What You Know
Which diagram correctly shows the direction of energy flow through a food web?
Show What You Know
Part of an everglades food web is diagrammed below.
Which of the following will most likely result if all of the primary consumers are removed from this ecosystem?
A.
Raccoons will become herbivores.
B.
American alligator populations will decrease.
C.
Grass carp will consume soil bacteria.
D.
Bladderwort and Butterfly orchid populations will decrease
Show What You Know
A student set up a terrarium, watered the soil, and covered the terrarium tightly with a lid. The next day, the student observed water droplets on the inside of the lid.
The droplets provide evidence that which of the following steps of the water cycle had occurred in the terrarium?
A.
runoff and evaporation
B.
precipitation and runoff
C.
evaporation and condensation
D.
condensation and precipitation
Show What You Know
Use the diagram of the water cycle to answer the following question.
Show What You Know
Which terms match the number order of the processes shown in the water cycle?
1
A vaporation
2 3 precipitation condensation
B condensation evaporation precipitation
C precipitation condensation evaporation
D evaporation condensation precipitation
Show What You Know
Which process is not essential for the water cycle to occur?
A.
water vapor condensing
B.
energy being transferred from the Sun
C.
liquid water evaporating
D.
oxygen being dissolved in water
Show What You Know
The natural cycling of oxygen between organisms and their environment is most directly accomplished through which of the following pairs of processes?
A.
fermentation and oxidation
B.
transpiration and evaporation
C.
precipitation and condensation
D.
photosynthesis and respiration
Show What You Know
The diagram below shows part of the carbon cycle.
Show What You Know
If many trees are removed from a forest by logging, what is the most immediate effect on the carbon cycle in that forest?
A.
increased rates of decomposition
B.
decreased use of atmospheric CO
2
C.
decreased combustion of fossil fuels
D.
increased production of organic compounds
Show What You Know
The diagram shows the flow of carbon in a terrestrial ecosystem.
Which will most likely happen if the decomposers are removed from the carbon cycle?
A.
The amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere will increase.
B.
The amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere will decrease.
C.
The amount of carbon dioxide used by producers will increase.
D.
The amount of carbon dioxide needed by consumers will decrease.