IA: Week 2 Risk
advertisement

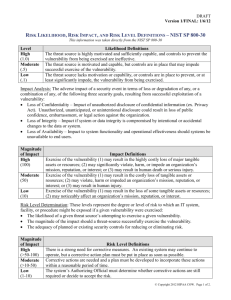
IA: Week 2 Risk Risk Management Risk Assessment Risk Mitigation Risk evaluation and reassessment Risk Management & SDLC System Development Life Cycle (SDLC) Initial concept and need Development/Acquisition Implementation Operation and Maintenance Disposal Key Personnel for Risk Management Risk Management is a management responsibility. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Senior Management CIO, ISSO System owners Information Owners IT security folks Risk Assessment 1.System Characterization 2.Vulnerability Identification 3.Threat Identification 4.Control Analysis 5.Likelihood Determination 6.Risk Determination 7.Control Recommendations 8.Results Documentation Step 1 System Characterization Gather information about the system and its role in the organization. What information? How to gather it? System Characterization Hardware, software, interfaces Communication channels, network configuration Data, information IT personnel System description and mission System and data criticality System and data sensitivity System Characterization additional information Functional requirements of the IT system Users Security policies Security architecture Information storage controls Technical controls Management controls Operational controls Physical and environmental security Information Gathering Techniques Questionnaire Interviews Corporate documents System documents Security plans, policies and procedures Step 2 Vulnerability Identification “A vulnerability is a flaw or weakness in system security procedures, design, implementation of internal controls that could be exercised and result in a security breach or violation of the system's security policy.” Identifying the vulnerabilities of a system is necessary for a realistic threat analysis of a system. Methods for Vulnerability ID Security checklists and vulnerability sources System testing Sources of Vulnerability Info Previous risk assessments IT Audit reports Vulnerability databases Security advisories Incident response reports Vulnerability alerts System software security analysis System Security Testing Automated vulnerability scanning tools Nmap, nessus Security test and evaluation Penetration testing Vulnerability Identification Output A vulnerability assessment report and vulnerability list This report and list is updated and amended throughout the system life cycle. Step 3 Threat Identification “A threat is a potential for a threat source to exercise a specific vulnerability.” “A threat source is (1) an intent and method targeted at the intentional exploitation of a vulnerability or (2) a situation and method that may accidentally trigger a vulnerability.” Common Threat Sources Natural: Floods, earthquakes, tornadoes, landslides, etc. Environmental: Long-term power failure, pollution, chemicals, liquid leakage, fire, smoke, etc. Human: Unintentional acts or deliberate acts Machine: Failure, malfunction, incorrectly configured. Threat Sources Hackers Criminals Terrorist Industrial Espionage Insiders Threat Profile A threat profile is a list of threat-sources and their associated vulnerabilities and potential harm/damage to the IT system. Step 4 Control Analysis Analyze the controls that have been implemented or are planned to minimize or eliminate the likelihood of a threat's exercising a system vulnerability. Control Methods Control Categories Control Analysis Techniques Control Methods NIST Technical Controls Operational Controls Management Controls HIPAA Technical Safeguards Physical Safeguards Administrative Safeguards Technical Controls Identification & Authentication Logical control access Audit trails System protection Operational Controls Personnel Security Physical & Environmental Protection Contingency Plan Configuration Management HW & SW Maintenance Media Protection Incident Response Training Management Controls Risk Assessment Security Plan System & Services Acquisition Security Control Review Processing Authorization Control Categories Preventive Controls Policy enforcement Access controls, encryption, authentication Detective Controls Warn of policy violations Intrusion detection Audit trails Checksums Control Analysis Techniques Checklists Security requirements lists versus security controls & design Step 5 Likelihood Determination Derive a likelihood rating (probability) that a potential vulnerability may be exercised by the associated threat environment. Threat source motivation and capability Nature of vulnerability Effectiveness of current controls Likelihood Definitions Likelihood Level High Likelihood Definition The threat-source is Highly motivated and capable and existing controls are ineffective. Medium Threat-source is motivated and capable but controls may impede successful exploit. Low Threat-source lacks motivation or capability or controls are in place to prevent significantly impede exploit. Step 6 Impact Analysis Determine the impact of a successful exploit of a vulnerability by a threat source. Input: System mission System and data criticality System and data sensitivity Incident Impact The adverse impact of a security incident is described in terms of : Loss of Integrity Loss of Availability Loss of Confidentiality Lost revenue Cost of repair Damage of intangibles Impact Metrics High: Sever or catastrophic adverse effect on organizational operations, assets or individuals. Medium: Serious adverse effect on organizational operations, assets or individuals. Low: Limited adverse effect on organizational operations, assets or individuals. Step 7 Risk Determination Determine risk of a particular threat/vulnerability pair as a function of: Likelihood of the threat source exploiting the vulnerability Magnitude of the impact of the successful exploit Adequacy of protective security controls for the pair Risk-Level Matrix Step 8 Control Recommendations Recommend controls the reduce the level of risk to the system and/or data to an acceptable level. Considerations Effectiveness of recommendations Legislation and regulation Organizational policy Operational impact Safety and reliability Step 9 Results Documentaiton Risk assessment report that describes each threat and vulnerability, measurement of the risk and the recommended controls for risk mitigation. Risk Mitigation Risk Assumption Accept the potential risk Risk Avoidance Shut down until Vulnerability is fixed Risk Limitation Implement controls to limit risk Risk Transference Insurance