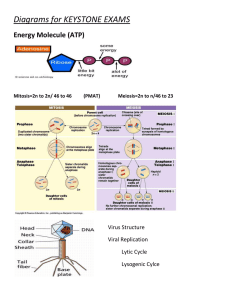
What is Cellular Respiration?
advertisement

Cellular Respiration What is Cellular Respiration? The process in which glucose is broken down and chemical energy is released for use by cells. What is Cellular Respiration? Once the energy that was in sunlight is changed into chemical energy by photosynthesis, an organism has to distribute the chemical energy into a size (amount) that can be used by cells. The energy in 1 glucose is distributed to 36 ATP’s 1 glucose = 36 ATP’s This process is cellular respiration. Describe Cellular Respiration • It is a series of reactions where carbohydrates, mostly glucose, are broken down to make CO2, water, and energy (in the form of ATP) • Takes place in all living things Cellular Respiration • Occurs in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells. • The highly folded inner membrane provides a lot of space for cellular respiration to occur. ( energy production) What is the chemical equation for cellular respiration? C6H12O6 + 6O2 Glucose + Oxygen 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy Carbon Dioxide + Water + ATP Look familiar? C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy It is the reverse process of photosynthesis! ATP • Most of the energy from cell respiration is converted into ATP (a substance that powers most cell activities) and used by the organism. • Some of the energy is lost as heat Cellular Respiration occurs in 3 stages: 1. Glycolysis 2. The Kreb’s Cycle 3. The Electron Transport Chain From Food to ATP video Cellular Respiration Stage One: Breakdown of Glucose Glycolysis •Glucose is broken in half to make pyruvate. •This process produces 2 ATP’s. Cellular Respiration Stages Two & Three: Production of more ATP •Krebs Cycle •Electron Transport Chain These 2 steps only occur when oxygen is present. This is called aerobic respiration. *aerobic means “in the presence of oxygen” The Krebs Cycle • During the Krebs Cycle, the break down of glucose is continued producing carbon dioxide in a series of energy-extracting reactions. • Net ATP Production is 2 ATP. Electron Transport Chain • The E.T.C. is made up of a series of molecules that transfer electrons from the original glucose molecule to oxygen. • After taking the electrons, oxygen then binds with hydrogen to form water. • That energy is used to create 32 ATP’s. Totals • • • • Gycolysis 2 ATP Krebs Cycle 2 ATP Electron Transport Chain 32-34 ATP Total = 36-38 ATP Comparing Photosynthesis & Respiration Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration Function Stores Energy Releases Energy Location Chloroplasts Mitochondria Uses Carbon dioxide & Glucose & oxygen water Glucose & oxygen Carbon dioxide & water Produces Equation 6CO2 + 6H2O C6H12O6 + 6O2 C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O Cellular Respiration Cellular Respiration requires oxygen. It is an aerobic process. What happens when oxygen is not present? •Fermentation will then occur. •Not much ATP is produced but it does allow the break down of glucose to continue. Fermentation • There are two types of fermentation: alcohol and lactic acid. • Alcohol fermentation is done by yeasts. It produces alcohol & carbon dioxide. • Lactic Acid is produced by muscles during rapid exercise when the body cannot supply enough oxygen – causes a burning sensation in the muscles. Comparing Photosynthesis & Respiration Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration Function Stores Energy Releases Energy Location Chloroplasts Mitochondria Uses Carbon dioxide & Glucose & oxygen water Glucose & oxygen Carbon dioxide & water Produces Equation 6CO2 + 6H2O C6H12O6 + 6O2 C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O Photosynthesis/Cellular Respiration Connection Describe the path energy takes C6H12O6 + O6 Describe the path carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen take Read how photosynthesis & respiration are related: http://www.usoe.k12.ut.us/curr/science/scib er00/8th/energy/sciber/photosyn.htm