cross border mergers & acquisitions
advertisement

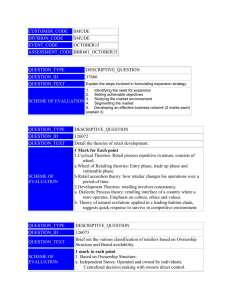
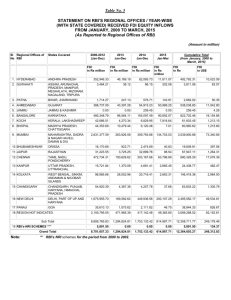
Investment in India Overview MADHURENDRA NATH JHA Destination India Amongst Fastest growing market Economies in the World, @ over 7% p.a. last 4 years Liberal FDI Policy Framework FDI up to 100% allowed in most sectors Rationalization of Tax Structure to promote Investment High Foreign Exchange Reserves Liberal outbound investment Currency appreciation Entry Routes for Investment in India Approval Automatic Foreign Investment in India The Driving Force Well diversified Industrial Base A large & sophisticated financial Architecture A healthy GDP composition An acknowledged strength in knowledge driven Industry FDI and Portfolio Flows to India Source: RBI, 2007 Investor Confidence India Ranked 2nd by AT Kearney's Foreign Direct Investment Confidence Index 2007 Has progressively moved ahead in the rankings; was ranked 15th in 2003 Attractive location across all broad sectors especially Manufacturing and high valueadded services industries like financial services and information technology. Investor Attractiveness Source: 2007 A T KEARNEY 90 80 70 60 India US UK Poland Germany 50 40 30 20 10 0 Manuf. Service Telecom & Utility retail Sectors Attracting Highest FDI Equity Flows Computer Software & Hardware Construction Activities 3000 2500 Automobile Industry 2000 Housing & Real Estate 1500 Power 1000 Drugs and Pharmaceuticals Mettalurgic Industries 500 All Figures in US $(Million) 0 2004-05 2005-06 2006-07 2007-08 Advantage India One of the Largest Free Market Democracies in the world Unparalleled resource of educated, hardworking, skilled and ambitious workforce Youngest workforce in the world - Working age population estimated to rise 70% of the total population by 2030 - 70 million new entrants to its work force every 5 years Advantage India English the language of business in India - one of the largest Pools of English Speaking Manpower after the US Manpower - Over 3 million scientific and technical manpower - Over 2.5 million graduates added to the workforce every years - 3rd largest pool of educated personnel A large and Growing Middle class with per capita income of more than 1000 US $ p.a. Advantage India Amongst the largest and ever growing domestic market Abundant Resources Sound economic Fundamentals; Stable Economic reform regime Vibrant Financial Sector M&A Band Wagon Frenzied Activity in the field of M&A in recent years In 2007 out of Total 348 Cross Border Deals: Outbound: 240 ($32.37 billion) Inbound: 108 ($15.61 billion) In First Quarter of 2007 while Inbound FDI flows were at an all time high they still exceeded by outbound investment Increase in M& A 700 600 500 400 No. of Deals Amount (USD million) 300 200 100 0 2006 2007 India Inc. Goes Global Tata Motors acquired Jaguar & Land Rover for 23 billion Tata Steel acquired UK based Corus for $ 8 billion. Suzlon Energy Ltd acquired German firm Repower Systems AG for $ 1.7 billion. United Spirits bought Scotch whisky distiller Whyte & Mackay for US$ 1.11 billion Hindalco acquired Novelis for $ 6 billion Inbound Transactions Sistema, Russian Joint Stock Company’s acquisition of 74% stake in Shyam Telelink – Telecommunications French banking major BNP Paribas’s acquisition of 45% stake in financial services firm Sundaram Home Finance for $45.81 million Standard Chartered Bank bought 49% stake for $34.19 million in UTI Securities and Interpublic Group hiked its stake in Lintas India to 100% for $100 million Fursa Mauritius’s acquisition of 42.63% equity in Gayatri Starchkem UBS Global Management’s Acquisition of Standard Chartered Asset Management Company for $ 117.78 Million EMC Corporations Acquisition of Valyd Software Pvt. Ltd. Orkla’s Acquisition of MTR foods for $ 100 Million Indian Overseas Investment Favourable Policy framework - Overseas Investment Limit – 400% of Net Worth for Companies Incorporated in India including Subsidiaries of Foreign Co. - - Overseas portfolio investment - 50 per cent of Net Worth RBI approval on case by case basis if in excess of the above specified limit Funding Permissible Funding: Drawal of foreign exchange from an AD; Capitalization of exports; Swap of shares Utilization of proceeds of External Commercial Borrowings (ECBs) / Foreign Currency Convertible Bonds (FCCBs); in exchange of ADRs/GDRs Balances held in EEFC account of the Indian party; Utilization of proceeds of foreign currency funds raised through ADR / GDR issues. India’s Direct Investment Abroad Source: RBI 2007 Entry Routes Investing In India Automatic Route General Permission No Prior Permission Required RBI to be informed within 30 days of inflow /issue of shares Approval Route Discretion Govt. Approval required Decision generally within 4-6 weeks Entry Strategies for Foreign Investors Incorporation of companies Act) a company As a Foreign Company through: Liaison office/Representative office Project Office Branch Office foreign company As an Indian company through: a Joint Venture Wholly Owned Subsidiary (governed by Joint Ventures As An Entry Strategy JV’S regulated by Policies and Laws governing FDI Two Tier Approval Mechanism for JV’S: - Automatic Approval Route - FIPB Approval Route If the Foreign Partner has entered into JV in the same field before then NOC of the previous JV partner and approval of the Joint Ventures …… Cont’d ‘Same Field’ may be defined as the 4 digit National Industrial Classification (NIC) Code Illustration: If the foreign investor has collaboration for the manufacture of tarpaulin Code 268.3, he can invest in the manufacture of rubberized cloth Code 268.2 as there is no restriction to enter into JV’s in allied fields. The restriction shall apply to any item whose code NIC code is 268.2. Joint Ventures …… Cont’d A ‘Conflict of Interest’ clause advisable in the JV/Collaboration agreement in case one of the Partners to the JV wants to set up another JV or wholly owned subsidiary in the same field Joint Ventures …… Cont’d The Following are exempted from the restriction of entering into JV in the same field: 1) Information Technology sector 2) Investments made by multinational financial institutions 3) mining sector for the same area/mineral Joint Ventures …… Cont’d Prior government approval not required in certain cases: - Investment to be made by venture capital funds is registered with SEBI - Existing JV investment is less than 3% - Existing venture is defunct or sick Remittances Determination of sale Price of Shares - Listed Company - Unlisted Company/Shares Thinly Traded on the Stock Exchange Remittance of Sale Proceeds: i. NOC from Income Tax Authority required ii. If the security has not been sold on a recognized stock exchange then prior approval of the RBI in form TS 1 has been obtained Regulatory Framework Some applicable Indian Laws - Companies Act - Competition Act - SEZ Act - Income Tax Act - Indian Stamp Act - SEBI Takeover Code - FEMA - FDI Policy Competition Law, 2002 Salient Features: Anti-competitive agreements; Prohibition of abuse of dominant position Regulation of Combinations including mergers Unfair Trade Practices India : Merger Law Monopolies and Restrictive Trade Practices Act, 1969 Inadequate Obsolete Still Prevailing New Merger Law Competition Act, 2002 Combination The Indian law uses the word combinations to cover acquisition of control, shares, voting rights and assets, and mergers and amalgamations Relevant Sections: 5-6 & 29-32 Areas of Concern Applicable threshold Limits Based on: Value of Assets Turnover Notice Requirement Mandatory Within 30 days of Approval of proposal by BOD Execution of agreement/ document Competition proposals Mandatory waiting Period for Approval 210 Days Extra Territorial Jurisdiction of CCI CCI has power to inquire about combinations taking place outside India Intent of National Security Legislations Right to Intervene in case of perceived threat to National Security Discretionary powers to prevent certain foreign companies from doing business in the country Foreign Investments & National Security Legislations United States- Foreign Investment & National Security Act, 2007 (Exon-Florio Provision) China- Anti Monopoly Law European Union- Members are free to regulate International Mergers (Articles 81-85 EC Treaty regulates Competition) National Security … Cont’d. United Kingdom- Enterprises Act 2002 India- National Security Exception Bill yet to be passed by the Parliament FDI Policy Sno. Sector Sectoral Cap 1. Manufacturing (ExceptionsDefense products, Products reserved for Small Scale Sector 100% 2. Coal Mining 100% 3. Electricity (Generation, Transmission, Distribution and Power Trading) 100% 4. Roads & Highways 100% 5. Airport Projects (Greenfield) 100% 6. TelecomBasic & Cellular, Unified Access Services ISP without Gateway Infrastructure Provider providing Dark fibre, right of way, duct space, tower etc. 74% 100% FDI Policy 7. Hotels & Tourism 100% 8. Shipping & Ports 100% 9. Industrial Parks 100% 10. Hospitals 100% 11. SEZ’S 100% FDI Policy – Prohibited Sectors Atomic Energy Lottery Business Betting & Gambling Agriculture (excluding Floriculture, Horticulture, Development of seeds, Animal Husbandry, Pisciculture and Cultivation of vegetables, mushrooms etc. under controlled conditions and services related to agro and allied sectors) and Plantations (Other than Tea plantations) Special Economic Zones “Fuelling India’s Economic Growth” FDI- 100% permitted under automatic route Regulated by the SEZ Act 2005 Objectives Investment Promotion Engine for economic growth Development of infrastructure SEZ (Objectives)… Cont’d. Promotion of Export of Goods & Services Generation of Employment oppurtunities minimum possible regulations. attractive fiscal package both at the Centre and the State SEZ Procedures - Establishment By Central/State or any other entity Requirements - Minimum Area Requirements for different class of SEZ’s SEZ divided into Processing area (for units) and Non Processing Area (for supporting infrastructure) Single Window Clearance available SEZ – Current Statistics 496 SEZ’s Approved after SEZ Act 2005 - 282 EH/IT/ITES SEZ’s 9 Multi Product SEZ’s 13 Pharmaceuticals and chemical SEZ’s 4 Bio Tech SEZ’s 8 Textile/Apparel/Wool SEZ’s 136 In principle approvals 207 SEZ’s have been notified Incentives: SEZ Developers Customs/Excise exemptions Income Tax exemption - On export Income for 10 years out of 15 Exemption from Dividend Distribution Tax Exemption from Sales Tax/Service Tax Incentives: SEZ Units Duty free import/domestic procurement of goods Income Tax exemption Exemption from minimum alternate tax External commercial borrowing by SEZ units up to US $ 500 million in a year without any maturity restriction through recognized banking channels. Exemption from Central Sales Tax/VAT/State Acts & Service Tax Single window clearance. Real Estate “Developing India’s Tomorrow” Overview - Amongst the largest employers only after agriculture - US $12 Billion Industry - 30% growth rate - Housing Sector contributes 5% of GDP Real Estate- Growth Potential Requirements of housing, commercial and industrial infrastructure bound to rise 367 Million Sq. Ft. of additional office space needed by 2012-13 ( Estimated by Ernst & young) Indian Ministry of Tourism forecasted requirements of 2.9 and 6.6 Million hotel rooms to meet the tourism and business by 2010 and 2020. Fast growing Medical tourism will become US$2 billion industry by 2012 Asian Development Bank estimates requirements of 10 million units by 2030 and will require huge investment in Health Services Real Estate- FDI Policy FDI not permitted in Business of buying & selling property FDI up to 100% under the automatic route in townships, housing, built-up infrastructure and construction-development projects including housing, commercial premises, hotels, resorts, hospitals, educational institutions, recreational facilities, city and regional level infrastructure) subject to: - Minimum Area requirements - Minimum Capitalization requirement - Divestment clause i.e. No repatriation before 3 years Real Estate DevelopersIncentives - Tax exemptions up to 100% on profits derived by an undertaking Developing/operating/maintaining Industrial Parks Developing & Building Housing Projects Developing/operating/maintaining SEZ’s Constructing Hotels & Hospitals in Tier 2 cities Real EstateForeign Players in India Investor Country Emmar Group U.A.E Kontur Bintang/ Westport Malaysia Singapore Housing Board Singapore Keppel Land Singapore Salim Group Indonesia Lee Kim Tah Holdings Singapore Retail Sector - - Overview Amongst the largest employers in the country at par with Real Estate Amongst the highest outlet density in the world with around 12 mn Outlets Largely unorganized; Large no. of local players; Scope of Market consolidation FDI in Retail FDI not allowed in Multi-Brand Retail 100% permitted through the Automatic route in Wholesale Cash & Carry operations 51% in Single Brand Retailing - Requires FIPB Approval Product to be single brand only Should be sold under same Brand Internationally Covers only Products Branded during Manufacturing Retail Sector Foreign Players Player Wal Mart Marks & Spencer Nike Christian Dior Jimmy Choo French Connection Lee Cooper Retail Activity Whole Sale Cash & Carry Operations Single Brand Retail Single Brand Retail Single Brand Retail Single Brand Retail Single Brand Retail Single Brand Retail Areas of Concern Transfer Pricing Issues - Method of escaping Tax Liability - Tax Avoidance hence Illegal RBI approval required - Source of Funds National Security issues Judicial System Robust, well-developed legal and administrative system Derived from the Common Law System Commercial Disputes: - Arbitration Preferred mode of settlement - International Commercial Arbitration Possible Strong Intellectual Property laws Investing in India It is advisable to have a thorough Due Diligence done before investing Non-Compete clause - It is advisable to have a clearly worded noncompete clause if entering into a JV Dispute Resolution clause - Must be clearly worded in terms of Governing Law, Jurisdiction, Mode of Dispute Resolution Investing in India…cont’d. Intellectual Property Clause - To protect IP rights from Infringement THANK YOU Should you have any questions on issues reported here or on other areas of law, you may contact Paras Kuhad and Associates at the following co-ordinates: Madhurendra Nath Jha Paras Kuhad and Associates, Advocates Tel: +91 (0) 11 46562525, 46562727 Fax: +91 (0) 11 46562000 Mob: +91(0)-9811319922 Email : mnjha@paraskuhad.com, mnjha@hotmail.com Delhi Mumbai Kolkata Chennai Jaipur Pune Jodhpur Disclaimer The contents of this document are intended for informational purposes only and are not in the nature of a legal opinion or advice. They may not encompass all possible regulations and circumstances applicable to the subject matter and readers are encouraged to seek legal counsel prior to acting upon any of the information provided herein. This Note is the exclusive copyright of Paras Kuhad and Associates, Advocates and may not be circulated, reproduced or otherwise used by the intended recipient without the prior permission of its originator. © Paras Kuhad and Associates, Advocates 2008