Chemical Bonds & Reactions
advertisement

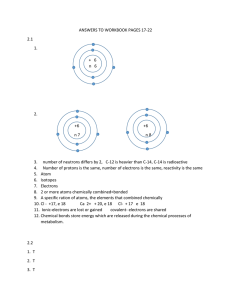
Product Bond Reactant Stable Yields Synthesis Equation Decomposition Subscript Replacement Compound Catalyst Write a story using the Element Ionic Covalent words on the list Underline each word used Circle words you’ve never heard in RED Circle words you’re familiar with but unsure of in YELLOW Circle words you know well in GREEN Valence Electrons - all the electrons on the outer-most energy level (ROMAN NUMERAL) Dot Diagram Chemical Bond – a force that holds two or more atoms together when their outermost energy levels become filled by each other. Creates a chemical reaction Stable – when all of an atom’s energy levels are filled and it can no longer react Stable atoms become charged Unstable atoms have empty spaces on their energy levels and have no charge because their e- balance out with p+ Ionic Bond – when an atom becomes stable by giving or taking (exchanging) electrons from another atom. Ion- an atom that has gained or lost electrons and has a charge Cation –gives away e-, has a positive charge clue to remember (ca+ion) Anion- takes e-, has a negative charge clue to remember (/-\nion) Ions with opposite charges bond together – opposites attract An atom’s charge is neutral if its p+ and e- are balanced Atoms are usually unstable if they are neutral (except column VIII) Covalent Bond – when 2 atoms fill their outer energy levels by SHARING a pair of electrons Both atoms keep their electrons on the outer ring Charge doesn’t change, atoms stay neutral AND become stable Ionic Covalent Chemical Formula- a way to write the name of bonded atoms (compounds) Ex. NaCl: uses Chemical Symbols Compound - _____________________ Chemical formulas show how many of each atom are in the compound Subscript- a number written to the lower right of a chemical symbol in the chemical formula DO NOT WRITE ONE (1)! Ex. H2O, NaCl, C6H12O6 Chemical Reaction- when new substances are created from chemical bonds being formed or broken These new substances have new properties and are often compounds! Two parts: Reactants – what you start with (what reacts) Products – what you end with (what is created) Conservation of Matter - matter can’t be created or destroyed in a reaction The items and the amount of items you start with MUST be the same as what you end with LIKE BAKING A CAKE Catalyst – changes how reactions happen, doesn’t actually react Speed up or slow down Chemical Equation- written reaction Adding zinc to hydrochloric acid looks like: Zn + HCl ZnCl2 + H2 Reactants (start) products (end) is like an equals sign “yields” Synthesis – 2 or more substances react to form a new compound 2Na + Cl2 2NaCl Decomposition – One substance breaks down during a reaction 2NaCl 2Na + Cl2 Replacement – one element takes over the spot of an item in a compound CuSO4 + Fe FeSO4+ Cu Combustion – reaction involving oxygen that produces light and heat. CH4 + 2O2 CO2 + 2H20