20-2 PowerPoint Notes
advertisement

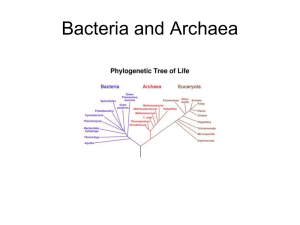
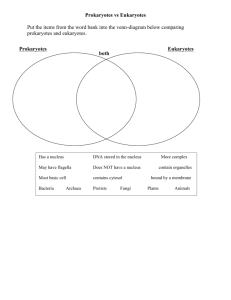
Microbiologist ___________________________ Date ______________ 20-2 Prokaryotes Classifying Prokaryotes The smallest and most abundant microorganisms on Earth are prokaryotes— unicellular organisms that ___________ a ______________. Prokaryotes DNA is located in the _____________. Bacteria Bacteria live almost ___________ Bacteria are usually surrounded by a cell ___________ that protects the cell from injury and determines its ___________. The cell walls of bacteria contain ___________. Some bacteria, such as E. coli, have a second ___________ outside the peptidoglycan wall that makes the cell especially resistant to damage. Some also have ___________ that they use for movement, or ___________, which in E. coli serve mainly to anchor the bacterium to a surface or to other bacteria. Archaea Under a microscope, archaea look very ___________ to bacteria. The walls of archaea ______ peptidoglycan, and their membranes contain different lipids. The DNA sequences of key archaea genes are more like those of ___________ than those of bacteria. Based on these observations, scientists have concluded that archaea and eukaryotes are ___________ more closely to each other than to bacteria. Many archaea live in extremely ___________ environments. Size, Shape, and Movement Prokaryotes are much ___________ than eukaryotic cells. Rod-shaped prokaryotes are called ___________. Spherical prokaryotes are called ___________. Spiral and corkscrew-shaped prokaryotes are called ___________. Prokaryotes can also be distinguished by whether they _______ and _____ they move. Nutrition and Metabolism Energy is ___________ from these fuel molecules during cellular respiration, fermentation, or both. Prokaryotes vary in the ways they ___________ energy and the ways they ___________ it. Growth, Reproduction, and Recombination When a prokaryote has grown so that it has nearly doubled in size, it replicates its DNA and divides in half, producing two identical cells. This type of asexual reproduction is known as ___________ ___________. During favorable conditions some bacteria can reproduce in ____ minutes. When growth conditions become unfavorable, many prokaryotic cells form an ___________ —a thick internal wall that encloses the DNA and a portion of the cytoplasm. Endospores can remain ___________ for months or even years. Mutation Mutations are one of the main ways prokaryotes ___________. Mutations are random changes in ___________ that occur in all organisms. Conjugation Many prokaryotes exchange genetic information by a process called ___________. During conjugation, a hollow bridge forms between two bacterial cells, and ___________ material, usually in the form of a plasmid, moves from one cell to the other. Decomposers By decomposing dead organisms, prokaryotes, supply raw materials and thus help to maintain ___________ in the environment. Producers Photosynthetic prokaryotes are among the most important ___________ on the planet. Food chains everywhere are dependent upon prokaryotes as producers of ___________ and biomass. Nitrogen Fixers All organisms need nitrogen to make ___________ and other molecules. The process of nitrogen fixation converts nitrogen _____ into ___________ (NH3). Ammonia can then be converted to nitrates that plants use, or attached to amino acids that all organisms use. Nitrogen-fixing bacteria and archaea provide ____ percent of the nitrogen used by other organisms. Human Uses of Prokaryotes Prokaryotes, especially bacteria, are used in the production of a wide variety of ___________ and other commercial products. Some bacteria can ___________ petroleum and remove human-made waste products and poisons from water. Other bacteria are used to synthesize ___________ and chemicals through the techniques of genetic engineering.