27.5 –Prokaryotes play crucial roles in the biosphere
advertisement

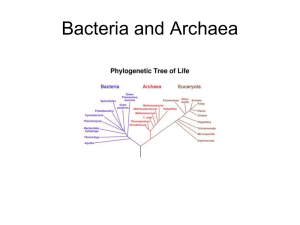
27.4 – Molecular systematics is illuminating prokaryotic phylogeny Lessons from molecular systematics Prokaryotes very genetically diverse Horizontal gene transfer resulted in prokaryotes acquiring genes from distantly related species Diverged into archaea and bacteria Archaea Live in extreme environments Extremophiles –lovers of extreme conditions o Extreme halophiles –live in highly saline environments o Extreme thermophiles –thrive in hot environments. Many organisms die in hot environments bc proteins denature and DNA does not stay together in double helix. Methanogens –obtain energy by using CO2 to oxidize H2, releasing methane as a waste product. Poisoned by O Euryachaeota –extreme halophiles also known as methanogens Bacteria Includes most prokaryotes o Proteobacteria Alpha Eukaryotic hosts Beta Nutritionally diverse. Gamma Some are pathogens. Delta Slime-secreting. Found new colonies in favorable environments Epsilon Pathogenic to humans or animals o Chlamydias –parasites can only survive within animal cells. Use hosts for ATP o Spirochetes –helical heterotrophs spiral through environment by rotating, internal, flagellum. Some free living, others parasites. o Cyanobacteria –photoautotrophs are prokaryotes with plantlike, oxygen-generating photosynthesis. Abundant in water. Provide food for ecosystems. o Gram-positive bacteria –rival proteobacteria in diversity. 27.5 –Prokaryotes play crucial roles in the biosphere Chemical recycling Decomposer –break down corpses, dead vegetation, and waste products, unlocking supplies of carbon, nitrogen, and other elements. Ecological interactions Symbiosis –two species live in close contact. o Host –large organism o Symbiont –small organism Mutualism –both benefit Commensalism –one benefits while other is neutral Parasitism –parasite eats the cell contents, tissue, or body fluids of host. Pathogens –parasites that cause diseases 27.6 –Prokaryotes have both harmful and beneficial impacts on humans Pathogenic bacteria Exotoxins - proteins secreted by certain bacteria and other organisms. Endotoxins –lipopolysaccharide components of the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria Released only when bacteria die and cell wall breaks down. Prokaryotes in research and technology Bioremediation –use of organisms to remove pollution from soil, air, or water. Can be used to make biodegradable products.