Antigen Presentation - UAB School of Optometry
advertisement

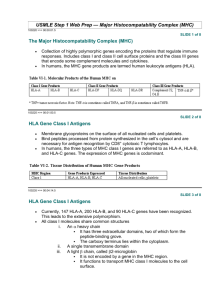
Antigen Presentation Fundamentals I for Dentistry & Optometry Textbook: Medical Microbiology, 6th Edition, Murray Chapter 11 Jim Collawn, MCLM 350 jcollawn@uab.edu 934-1002 Study Objectives 1. Compare and contrast class I and class II MHCrestricted responses with regard to A. source of antigens B. antigen processing requirements C. role of chaperones D. types of T cell involved 2. Discuss the invariant chain’s role in the demarcation between class I and class II MHCrestricted responses. 3. Discuss HLA-DM’s possible role in antigen processing. Humoral and Cellmediated Immune Responses Major Players in T cell Responses T lymphocyte and Macrophage (right) Types of T cells 1. Cytotoxic T cells (CTLs) A. Kill virally infected cells B. Kill cells containing cytosolic bacteria C. Kill tumor cells 2. Inflammatory T cells (TH1) A. Activate macrophages to kill intracellular bacteria 3. Helper T cells (TH2) A. Activate B cells to make antibody Schematic Diagrams of MHC class I and class II Molecules MHC class I (top view) Major Histocompatibility Complex HLA-DR1 (blue) and HLA-A2 MHC class I MHC class II Anchor Residues for MHC class I peptides Conformation of Peptides Bound to MHC class I Solvent-accessible Area of H-2Kb Anchor Residues for MHC class II peptides Antigen Processing is Necessary for Helper T cell Activation Antigen-presenting Cells (MHC Class II-positive cells) HLA-DR, HLA-DP, HLA-DQ Target Cells (MHC Class I-positive cells) HLA-A, HLA-B, HLA-C All nucleated cells Degradation of Intracellular Proteins Transporter associated with Antigen Processing Generation of Peptide-class I MHC Complexes Demarcation between MHC class I and class II Processing Pathways Cytosolic and Endocytic Pathways for Antigen Processing Assembly of MHC class II Molecules Study Objectives 1. Compare and contrast class I and class II MHCrestricted responses with regard to A. source of antigens B. antigen processing requirements C. role of chaperones D. types of T cell involved 2. Discuss the invariant chain’s role in the demarcation between class I and class II MHCrestricted responses. 3. Discuss HLA-DM’s possible role in antigen processing. Sample Questions • • • • The MHC class II molecule – is associated with ß-2 microglobulin. – binds peptide antigens from the endogenous pathway. – is associated with the invariant chain. – is expressed on all cell types. Exogenous antigens – are taken up by cells through endocytosis or phagocytosis. – are bound to MHC class I molecules. – are processed by the proteasome. – become associated with MHC class I molecules in the endoplasmic reticulum. Sample Questions • • • HLA-DR – presents antigens to cytotoxic T cells. – is a chaperone that facilitates CLIP removal and peptide binding. – is an MHC class II molecule. – binds to endogenous antigens. The proteolytic activity necessary for the generation of MHC class IIassociated peptides is provided by – the proteasome. – the lysosome. – furin. – the endoplasmic reticulum.





![Anti-HLA-DQA1 antibody [HI118] (PerCP) ab91329 Product datasheet Overview Product name](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/012448198_1-1438860d79d2655f551f9001711a64ba-300x300.png)