Historical Background of Pest Control Products
advertisement

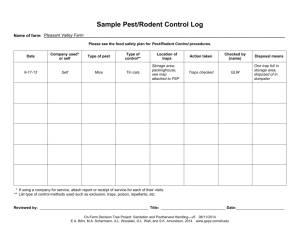
Pest Control Products Board Nairobi, Kenya INTRODUCTION • PCPB is a statutory organization of Kenya Government established by an Act of ParliamentPest Control Products Act Cap 346, 1982. • This is an Act of Parliament to regulate the importation, exportation, manufacture, distribution and use of products used for the control of pests and of the organic function of plants and animals and for connected purposes. MISSION To provide an efficient and effective regulatory service for the importation, exportation, manufacture distribution, transportation, sale, disposal and safe use of pest control products and mitigate potential harmful effects to the environment. Mandate • Assessing the safety, efficacy, quality, merit and economic value of pest control products. • Assessing suitability of premises used for manufacture/formulation, re-packing, storage and distribution of pest control products for purposes of licensing • Processing and issuing import/export permits • Advising the Minister on all matters relating to the Provisions of the PCP Act and Regulations Mandate- cont’d • Creating awareness to the general public on all aspects of safety, storage, handling, disposal and use of PCPs • Monitoring and ensuring adherence of quality standards of pest control products throughout the supply chain • Investigating and prosecuting contravention of the Pest Control Products Act. • Supervising the disposal of obsolete or undesired pest control products. Organizational structure Board of Directors MD/ Secretary Inspection, Training and Licensing Registration and Analysis Finance and Administration Inspectors Analysts, Registration Officers Accountants, Information Technology, Human Resource & Support Staff The Board of Directors • Chairperson-appointed by the president • Experts in pest control-crop and animal production • • • • (public officers) Rep. from ministries-Trade, Environment, Health, Water, The Govt. Chemist, Director KEBS, Director CRF, Director of Agriculture Farmer representatives-Livestock & Crop production Secretary/CE Co-opted-upto 5 Directors cont. Farmer representatives (2) for livestock & crop production Director of Agriculture Secretary to the Board/CE Co-opted- upto 5 persons whose assistance or service the Board may require ( no voting powers) Functions of PCPB 1) Regulatory Registration and approval of PCP for usage Analysis for quality Sale & distribution through licensing of premises, imports/exports, operators Functions cont. 2) Technical Evaluate products for efficacy testing Assess efficacy data before recommendations Post registration surveillance Functions cont. 3) Training & information Dissemination Train extension staff, students, formulators, retailers, etc on pesticide mngt. Advice govt./relevant authorities on pesticides. Contact point for pesticides - Codex, Rotterdam Convention, Stockholm Convention etc. Range of products regulated AGRICULTURE ANIMAL HEALTH PUBLIC HEALTH Weed control Tse tse fly control Cockroach control PESTICIDES Crop disease control Rodent control Tick control Insect control Mosquito control Range of products regulated May include; • Conventional chemical pesticides • Biopesticides; Botanicals, biochemicals, microorganisms, natural enemies • Any compound or substance that enhances or modifies the physical or chemical characteristics of a pest control product to which it is added e.g adjuvants and wetting agents • Technical grade active ingredients Pest control products Act, +Ten subsidiary legislations Legislation Section 4: “No person shall import into, or sell in Kenya any pest control product unless that pest control product has been Registered, packaged and labeled in accordance with regulations made under this act…” Definition; “A pest control product is a product, device, organism, substance, or thing that is manufactured , represented , sold, or used as a means for directly or indirectly controlling, preventing, destroying, attracting, or repelling any pest….” Registration procedure • Every person desiring to register a pest control product is required to submit an application for registration, a copy of full dossier of technical information and a label • Appointment of local agents • Board considers efficacy, quality and economic value and also ensures safety to the public, animals and the environment. Registration procedure cont’d • If the Board is satisfied with the information provided, the product is granted experimental permit for local biological efficacy trial. • This is carried out in institutions that have been accredited by the board for various trials • Public/Private based on capacity/speciality eg. Delmonte for pineapples, Kenya Agricultural Research Institute (KARI) • Sample delivered to PCPB Registration procedure cont’d • On completion of the biological efficacy trial, a confidential report is sent to PCPB • Submission of a commercial label reflecting the application rates, timing of application as recommended by the local researcher, mitigation measures to non targets, among other things • Registration committee (MOPH, KARI,CRF, KEBs etc) makes recommendations to the Board • If the Board is satisfied, it may grant full registration for 3 years and a certificate of registration issued. This is renewable after every 2 years. Suspension or deregistration • PCPB is empowered to suspend or revoke a certificate of registration if: • • • it realized later that the content of the application was false, new information indicates that the product is unsafe, the premises in which the product is manufactured, formulated or stored are unsuitable for the purpose. Risk assessment • All pest control products have to undergo registration process • It involves risk assessment ina) Health, b) Environmental • • • Behaviour in the environment (soil, water, air) eg degradation, mobility of active ingredient, adsorption Persistence of the metabolites in plants Effects on representative non targets organisms Risk assessment cont’d Studies required for the various non targets using representative species Birds Fish Daphnia Algae Bees Earthworms Soil micro-organisms Health Risk Assessment Acute Toxicity studies • Oral and dermal in laboratory animals eg 1) Acute oral rat 2) Acute dermal rat/rabbit 3) Inhalation 4) Irritation- skin, eye 5) Sensitization Health Risk Assessment Repeat dose studies • Reproduction- multigenerational studies • Teratogenicity • Neurotoxicity • Mutagenicity • Subchronic • Long term/ carcinogenicity Health Risk Assessment Other studies • Metabolism-pathways, accumulation, metabolites & their toxicity • Occupational/medical surveillance- hazards to humans, symptoms of poisoning, first aid, antidotes, Treatment, precautions/restrictions, containment of spilage & decontamination, disposal, protection of workers & by-standers • Residue studies for establishment of MRL and PHI based on GAP BIOPESTICIDES 1) Microbial pesticides (bacteria, viruses, fungi, etc 2) Biochemical pesticides Semiochemicals eg insect sex pheromones, Enzymes (proteins) Natural plant regulators and insect growth regulators Botanical pesticides etc 3) Natural enemies (Macrobials) Parasitoids Predators Pathogens of pests Special considerations; Microbial biopesticides: Kenya Technical Standing Committee on Imports & Exports (KSTCIE):-Import/export of live organisms National Biosafety Authority:- GMOs/LMOs Importation/Exportation of Pesticides • Unregistered products prohibited from importation • Registered products require an import license from PCPB • Importation should be from authorized sources only. • Imports for research purposes also require authority from PCPB. • Officers at the main port of entry ensure that only authorized products are allowed into the country. Importation of Pesticides in Kenya Import for 2011/2012 Quantities and Values 6,000.00 5,000.00 4,000.00 Fungicide Insecticide 3,000.00 Herbicide Others 2,000.00 1,000.00 Quantity(Tonnes,000) Value(Million,000,000) 2012 2012 Quantity(Tonnes,000) Value(Million,000,000) 2011 2011 Handling and distribution Premises license • The Board licenses premises dealing with pesticidesmanufacturers, formulators, stockists • Inspections of premises where pest control products are manufactured, formulated, repacked or large-scale users ensures the following: - - Only registered products are manufactured, formulated or repacked in those premises. Only correctly imported products are found therein. Products are correctly labeled using approved labels. Packages used are those that are approved • Over 4000 stockists dealing with pesticides Handling and distribution regulation - Products are properly stored and good store management is in place to avoid issues of obsolete products. - Products are within their shelf life. - Workers in these premises are adequately protected. - Any waste generated is properly handled and disposed off. 24 March 2016 29 Handling and distribution regulation - Fire fighting equipment are in place in case of fire outbreaks. - First-aid facilities are in place to take care of incidences of poisoning. - Pesticides are physically separated from other items to prevent risk of contamination. 24 March 2016 30 General Legal Provisions on labels • Legal Notice No. 89/1984;127/2006 • Regulation 3(1): No pest control product shall be distributed or sold without a label. • Regulation 3(2): No label shall be used on a pest control product unless it has been approved by the Board • Language- English and Kiswahili • Types Experimental /provisional • commercial Display panels: • Principal Display Panel • Secondary Display Panel • General guide: Pictograms • Pictograms shall be inserted according to the FAO/GHS • • • • • • Labeling Guidelines The symbols should convey safety information to users The Minimum size of each pictogram should be 7mm x 7 mm The ‘storage and wash after use’ pictograms must appear on every label. The face shield must be displayed instead of eye goggles Overall sleeves should be worn over gumboots and not stuck inside gum boots A pictogram of running tap water should be displayed MEAs • The Rotterdam convention on the Prior Informed Consent Procedure for Certain Hazardous Chemicals and Pesticides in international trade, adopted in 1998 and came into force in February 2004 • The Montreal Protocol on the Substances that delete the Ozone layer, adopted in 1987 and entered into force in 1989 • The Basel Convention on Control of Tran boundary movement of Hazardous wastes and their disposal, adopted in 1989 and entered into force in 1992 • The Stockholm convention on Persistent Organic Pollutant adopted in 2001 Challenges • How to deal with old molecules that are being withdrawn in the EU, and other countries • Residues in edible crops and animal products • Reducing counterfeit products Our contacts PEST CONTROL PRODUCTS BOARD Waiyaki Way (KARI-NAL) P.O. Box 13794 Nairobi, Westlands- 00800, Kenya Email: pcpboard@todays.co.ke Website: www.pcpb.or.ke Tel: +254-20-8021846/7/8 Mobile:+254-720 480 904/-735 778 743 Fax: +254-20-8021865 Regional offices- Coast, Western, Eastern Kenya