The Presidency: Chapters 8-9 Outline | US Government
advertisement

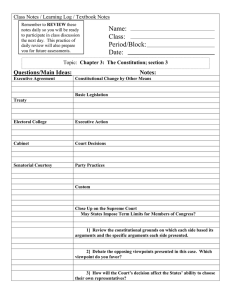
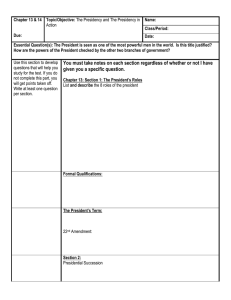
Chapters 8-9: The Presidency I. The Presidency A. Evolving Importance B. Duties Today C. Term 1. 22nd Amendment D. Salary E. Benefits II. Presidential Qualifications A. Constitutional (3) B. Government Experience C. Money D. Political Beliefs E. Personal Characteristics III. Presidential Succession A. Need for Mechanism B. 25th Amendment C. Gerald Ford anomaly D. Succession Act of 1947 E. Presidential Disability IV. Vice President A. Constitutional Duties (2) B. Balancing the Ticket C. Modern Responsibilities V. Electing the President A. Debate at Constitutional Convention B. Original System C. Impact of Parties D. Election of 1800 E. 12th Amendment VI. Electoral System Today A. Election Day B. Electoral Votes C. DC and 23rd Amendment D. Winner-takes-all VII. Electoral College Issues A. Winner takes all B. 3rd Party Candidates C. Election by the House D. Ideas for Reform E. Direct Popular Election VIII. The Cabinet A. Washington’s Cabinet B. Factors in Appointments C. Background of Members D. Nomination and Confirmation E. Role of Cabinet F. Factors limiting role IX. Executive Agencies A. Organization of the EOP B. OMB C. NSC D. Homeland Security E. Economic Advisors F. Other Advisors X. White House Office A. Staff B. Press Secretary C. White House Aides D. Specialists XI. Development of Presidential Power A. Articles of Confederation B. Article II Constitutional Powers C. Personal Exercise of Power 1. Thomas Jefferson 2. Theodore Roosevelt D. Immediate Needs of the Nation 1. Abraham Lincoln 2. Franklin Roosevelt 3. Lyndon Johnson E. Mandate of the People 1. FDR 2. Ronald Reagan F. Press and the President 1. Forum XII. Limits on Power A. Congress B. Courts C. Bureaucracy D. Public Opinion XIII. Role of President A. Head of State B. Chief Executive C. Chief Legislator D. Economic Planner E. Party Leader F. Chief Diplomat G. Commander-in-Chief XIV. Executive Privilege A. Confidentiality B. Separation of Powers C. Limits D. US v. Nixon Chapters 8-9: The Presidency