Ch. 3 - Chemical Reactions
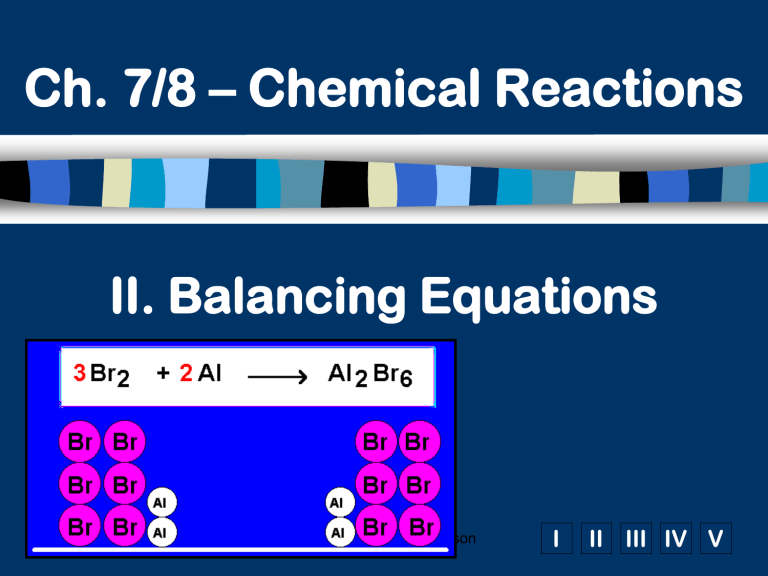
Ch. 7/8 – Chemical Reactions
II. Balancing Equations
C. Johannesson
A. Balancing Steps
1. Write the unbalanced equation.
2. Count atoms on each side.
3. Add coefficients to make #s equal.
Coefficient
subscript = # of atoms
4. Reduce coefficients to lowest possible ratio, if necessary.
5. Double check atom balance!!!
C. Johannesson
B. Helpful Tips
Balance one element at a time.
Update ALL atom counts after adding a coefficient.
If an element appears more than once per side, balance it last.
Balance polyatomic ions as single units.
“1 SO
4
” instead of “1 S” and “4 O”
C. Johannesson
C. Balancing Example
Aluminum and copper(II) chloride react to form copper and aluminum chloride.
2 3
2
3 2
3
2
1 1
2
3
3
6
6
C. Johannesson
Mr. Rapps slides next
C. Johannesson
Compare the numbers of each kind of atom in the balanced equation with the numbers of each kind of atom in the sketched representation. Both the equation and the sketch have the same number of atoms in the reactants and in the products.
Practice
Al(s) + O
2
(g) ---> Al
2
O
3
(s)
Inventory: 1Al and 2O’s on left and
2Al’s and 3O’s on right.
Start with Al
Need 2 on left to balance right
2 Al(s) + O
2
(g) ---> Al
2
O
3
(s)
Al is balanced but O is not.
Double everything but O
2
Practice
4 Al(s) + O
2
(g) ---> 2 Al
2
O
3
(s)
Al is still balanced, now we have
2O’s on left and 6O’s on right.
How can we balance that?
3x2 = 6 so we need 3 O
2 molecules
4 Al(s) + 3 O
2
(g) ---> 2 Al
2
O
3
(s)
Inventory: 4Al’s and 6O’s on left and
4Al’s and 6O’s on right
It’s balanced
Practice
Balance: FeCl
3
+ NaOH Fe(OH)
3
+ NaCl
Inventory: 1Fe, 3Cl’s, 1Na and 1OH on left and 1Fe, 3OH’s, 1Na and 1Cl on right
Balance Cl first need 3 on right
FeCl
3
+ NaOH Fe(OH)
3
+ 3 NaCl
Na is now unbalanced need 3 on left now
FeCl
3
+ 3 NaOH Fe(OH)
3
+ 3 NaCl
Inventory again: 1Fe, 3Cl, 3Na, and 3OH on left and 1Fe, 3OH, 3Na, and 3Cl on right
It’s balanced!!!
Practice
Ba(NO
3
)
2
+ Al
2
(SO
4
)
3
BaSO
4
+ Al(NO
3
)
3
Inventory: 1Ba, 2NO
3
’s, 2Al’s and 3SO
4 left and 1Ba, 1SO
4
, 1Al, and 3NO
3
’s on
’s on right
Balance SO
4
’s first need 3 on right
Ba(NO
3
)
2
+ Al
2
(SO
4
)
3
3 BaSO
4
Balance Ba next need 3 on left
+ Al(NO
3
)
3
3 Ba(NO
3
)
2
Al(NO
3
)
3
+ Al
2
(SO
4
)
3
3 BaSO
4
+
Balance NO3’s next 6 on left and 3 on right, use 2 as coefficient
Practice
3 Ba(NO
3
)
2
2 Al(NO
3
)
3
+ Al
2
(SO
4
)
3
3 BaSO
4
+
That gives 6NO
3
’s on both sides
Inventory: 3Ba’s, 6NO3’s, 2Al’s and 3SO4’s on left and 3Ba’s, 3SO4’s, 2Al’s, and 6NO3’s on right.
It’s balanced
Practice
Ca(OH)
2
+ H
3
PO
4
Ca
3
(PO
4
)
2
+ H
2
O
Inventory: 1Ca, 5H’s, 6O’s and 1P on left and 3Ca’s, 9O’s, 2H’s, and 2 P on right.
Balance Ca first need 3 on left
3 Ca(OH)
2
+ H
3
PO
4
Ca
3
(PO
4
)
2
+ H
2
O
Balance PO
4
’s next need 2 on left
3 Ca(OH)
2
+ 2 H
3
PO
4
Ca
3
(PO
4
)
2
+ H
2
O
Inventory again for H’s and O’s:
6O’s+8O’s(14) and 6H’s+6H’s(12) on left and 8O’s+1O’s(9) and 2H’s on right
Practice
To get 12H’s on right we can use 6 as a coefficient for water
3 Ca(OH)
2
6 H
2
O
+ 2 H
3
PO
4
Ca
3
(PO
4
)
2
+
Inventory: 3Ca’s, 2P’s, (6+6=12)H’s, and (6+8=14)O’s on left and 3Ca’s,
2P’s, (6x2=12)H’s and (8+6=14)O’s on right
It’s balanced
Practice
____C
3
H
8
(g) + _____ O
2
(g) ---->
>
_____CO
2
(g) + _____ H
2
O(g)
____B
4
H
10
___ B
2
O
3
2
(g) ----
2
O(g)
Practice
NH
4
NO
3
---> N
2
O + 2 H
2
O
Carbon monoxide reacts with nitrogen monoxide to form carbon dioxide and nitrogen gas (pairs)
Equation: CO + NO CO
2
2 CO + NO
2 CO
2
+ N
2
+ N
2
Practice
Phosphorus trichloride reacts with water to form hydrochloric acid and
phosphorous acid.
Equation: PCl
3
+ H
2
O
HCl + H
3
PO
3
PCl
3
+ H
2
O
3 HCl + H
3
PO
3
Magnesium nitride reacts with water to
form magnesium hydroxide and ammonia
Equation: Mg
3
N
2
+ H
2
O
Mg(OH)
2
+ NH
3
Mg
3
N
2
6
2
O
3
Mg(OH)
2
2
3