PowerPoint - Balancing Equations - Chemical and
advertisement
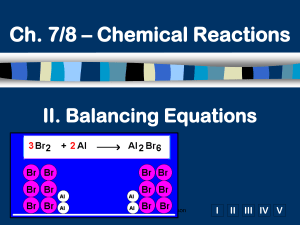
How molecules are symbolized Cl2 2Cl 2Cl2 • Molecules may also have brackets to indicate numbers of atoms. E.g. Ca(OH)2 • Notice that the OH is a group O Ca O H • The 2 refers to both H and O H • How many of each atom are in the following? a) NaOH Na = 1, O = 1, H = 1 b) Ca(OH)2 Ca = 1, O = 2, H = 2 c) 3Ca(OH)2 Ca = 3, O = 6, H = 6 Balancing equations: MgO • The law of conservation of mass states that matter can neither be created or destroyed • Thus, atoms are neither created or destroyed, only rearranged in a chemical reaction • Thus, the number of a particular atom is the same on both sides of a chemical equation • Example: Magnesium + Oxygen (from lab) • Mg + O2 MgO Mg + O O Mg O • However, this is not balanced • Left: Mg = 1, O = 2 • Right: Mg = 1, O = 1 Balance equations by “inspection” Mg + O2 MgO 2Mg + O2 2MgO is correct Mg + ½O2 MgO is incorrect Mg2 + O2 2MgO is incorrect 4Mgwith + 2elements O2 4MgO is incorrect Hints: start that occur in one compound on each side. Treat polyatomic ions that repeat as if they were a single entity. a) P4 + 5 O2 P4O10 b) 2 Li + 2 H2O H2 + 2 LiOH c) 2 Bi(NO3)3 + 3 K2S Bi2S3 + 6 KNO3 d) C2H6 +3.5 O2 2 CO2 + 3 H2O 2 C2H6 + 7 O2 4 CO2 + 6 H2O From Balance these skeleton equations: a) b) c) d) e) f) g) h) i) Mg + 2HCl MgCl2 + H2 3Ca + N2 Ca3N2 NH4NO3 N2O + 2H2O 2BiCl3 + 3H2S Bi2S3 + 6HCl 2C4H10 + 13O2 8CO2 + 10H2O 6O2 + C6H12O6 6CO2 + 6H2O 3NO2 + H2O 2HNO3 + NO Cr2(SO4)3+ 6NaOH 2Cr(OH)3+ 3Na2SO4 Al4C3 + 12H2O 3CH4 + 4Al(OH)3 Returning to reaction types • We have looked at several types of reactions without worrying about balancing • However, all equations should be balanced • Predict the products and balance these: (recall, metals above replace metals below, reactions with water yield metal hydroxides) 2 Fe + 3 CuSO4 3 Cu + Fe2(SO )3 Ni + NaCl NR (no 4reaction) 2 Al + 3 CuCl2 3 Cu + 2AlCl3 2 Li + ZnCO3 Zn + Li2CO3+ ½H2 2 Li + 2 H2O 2 LiOH 2 Al2O 4 Al + 3O2 K Na Li Ca Mg Al Zn Fe Ni Sn Pb H Cu Hg Ag Au Discovery of Radioactivity • Radioactivity is the release of energy or particles when an atom disintegrates (demo) • Radioactivity was discovered when minerals were exposed to film through an opaque cover • The 3 types of radioactivity can be shown by passing emissions through an electrical field: Lead block + Radioactive substance – Phosphorescent zinc sulfide detection screen Strong magnetic or electrostatic field Types of Radioactivity Types of radiation: 1) , 2) , 3) 1. Alpha () particles are symbolized as 42He 2. Beta () particles (essentially electrons) are 0–1e 3. Gamma () rays are symbolized as 00 • You can determine the composition of each: : mass of 4 u, charge of +2 (2 p+, 2 n0, 0 e–) • Other symbols: proton = 11p, neutron = 10n • There are different terms to describe the different types of nuclear reactions • “alpha decay” means an particle is given off. • Other: beta decay, fusion (meaning to bring together), fission (meaning to break apart) Nuclear equations Q. Write the beta decay for C-14 Q. Write the alpha decay for 209Po 14 6C 209 84 0 -1 e Po + 14 7N 4 205 2 He + 82 Pb Q. Complete this fission reaction 235 1 1 139 94 + 0 n 3 0 n + 56 Ba + 36 Kr 92 U In all cases, charge and mass must be balanced • Practice: pg. 222-3, Q6, Q3 6. a) 32 b) 99 c) 187 d) 38Sr 75Re 15P 3. a) 226 88 b) 84 35 c) 242 94 Ra 4 222 2 He + 86 Rn Br 0 -1 e Pu 4 238 2 He + 92 U 1 14 + p 1 7N e) 18 + 1 0n 8O d) e) 99 4 2He 43Tc + 84 36 Kr 4 11 2 He + 6 C 0 19 -1 e + 9 F Here are some more to balance: a) b) c) d) e) f) g) h) i) 2KNO3 2KNO2 + O2 2Pb(NO3)2 2PbO + 4NO2 + O2 P4 + 6I2 4PI3 3MgO + 2H3PO4 Mg3(PO4)2 + 3H2O Br2 + 2KI I2 + 2KBr Ca(OH)2 + 2HNO3 Ca(NO3)2 + 2H2O Bi2O3 + 3H2 2Bi + 3H2O 3Fe + 2O2 Fe3O4 2CaO + 5C 2CaC2 + CO2 Question 3 pg. 252 a) b) c) d) e) f) g) h) 2Li + 2H2O H2 + 2LiOH P4 + 5O2 P4O10 2C2H6 + 7O2 4CO2 + 6H2O CS2 + 3O2 CO2 + 2SO2 2AsCl3 + 3H2S As2S3 + 6HCl 3AgNO3 + FeCl3 3AgCl + Fe(NO3)3 2KClO3 2KCl + 3O2 2SO2 + O2 2SO3 For more lessons, visit www.chalkbored.com