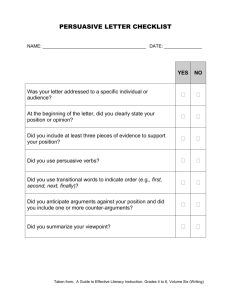
File
advertisement

Facts, Opinions, and Commonplace Assertions Directions: as we go over the powerpoint, fill in the blanks with the necessary information. • Opinion- Based on a belief or feeling on what seems true or probable. A judgment. • Ex. _____________________________________________ • Can it be proved? _________________________ • Commonplace assertion- A claim that a person makes but cannot always prove. Broad statements that reveal a personal judgement • Example: _____________________________________________________________________ • Word Cues for recognizing commonplace assertions: • - - - - - - - - Facts- Can be proved or disproved. Factual Claim – statement that can be proven from evidence such as fact, personal observation, reliable source, or expert’s opinion. Opinion – a statement of personal belief, feeling or thought. Does not require proof Commonplace Assertion – a statement that many people assume to be true but which is not necessarily so. Persuasive Techniques and Mistakes Persuasive Technique Bandwagon Appeal Definition Suggests that a person should believe or do something because “everyone else” does it Testimonial Relies on endorsements from well-known people or satisfied customers Appeal to Pity, Fear, or Vanity Uses strong feelings rather than facts to persuade Loaded Language Uses words with strongly positive or negative connotations Example “See the movie that everyone’s talking about!” “As an Olympic Athlete, I need a lot of energy. That’s why I drink Quench-Ade.” “Won’t you give this abandoned puppy a home?” “Start your day with Morning Glory’s refreshing, all-natural juice.” Type of Persuasive Fallacy Ad hominem Stereotyping Definition Attempts to discredit an idea by attacking the person’s character rather than his/her argument. Makes a broad statement about people on the basis of their gender, ethnicity, race, or political, social, professional, or religious group. Example My opponent cannot be trusted: Elect him, and city violence will surely increase. All musicians think the same way. Figurative Language Figurative language is a tool that an author uses, to help the reader visualize, or see, what is happening in a story or poem. Types of Figurative Language: Simile- is a comparison using like or as. It usually compares two unlike objects. Metaphor- states that one thing is something else. It is a comparison, but does NOT use like or as to make the comparison. Personification- is giving human qualities, feelings, actions, or characteristics to inanimate (not living) objects. Alliteration- is the repetition of the initial consonant. There should be at least two repetitions in a row. Onomatopoeia- is the imitation of natural sounds in word form. These words help us form mental pictures, or visualize, things, people, or places that are described. Sometimes a word names a thing or action by copying the sound. Symbolism- occurs when one thing stands for or represents something else. Hyperbole- is intentionally exaggerated figures of speech. Imagery- involves one or more of your five senses – the abilities to hear, taste, touch, smell, and see. An author uses a word or phrase to stimulate your memory of those senses and to help create mental pictures. Idioms- An expression that means something other than the literal meanings of its individual words. They are overused expressions.