Four Major Organic Molecules: Roles, Monomers, Examples
advertisement

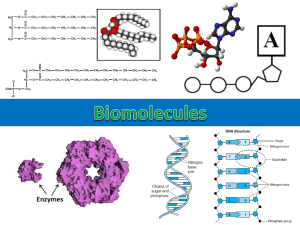
The Four Major Organic Molecules Organic Molecules contain the element carbon and bond to hydrogen and oxygen Each organic molecule contains different ratios of these atoms Type of Organic Molecule Roles of Molecule in the Body Monomers Specific Examples Carbohydrates Carbohydrates provide the body with energy needed to perform daily functions. It’s important that our bodies have a constant supply of energy to function properly and eliminate fatigue. The monomer of carbohydrate is a monosaccharide. Monosaccharides are made up of one sugar molecule and contain 6 carbons. The formula for a monosaccharide is C6 H12 O6. Glucose, Galactose, and Fructose are all specific examples of Carbs. Glucose is the most common because it is found in our blood sugar and needed by the brain for energy. Lipids Lipids also provide the body with energy. A lot of the energy, however, is stored. Lipids generally store the extra energy as fat. This fat is good for cushion, insulation, and protection of the internal organs. The monomer of lipids is triglycerides which are made up of one molecule of glycerol and three fatty acids. The glycerol and fatty acids are formed by dehydration synthesis. Triglycerides, Phospholipid, and Steroids Proteins Proteins help to keep the skin, hair, and nails healthy. Proteins are building blocks that repair damaged areas of the body. Proteins are also a form of energy for the body. Nucleic Acids Nucleic Acids are needed in order to maintain and reproduce the cells that make up the body. Nucleic Acids are what make everyone unique. They are also used for energy. The monomers of proteins are amino acids. Amino acids are joined together by dehydration synthesis. Covalent bonds hold the amino acids together and also link the carboxyl group of one amino acid to the amino group of the next. Enzyme proteins The monomers of nucleic acids are known as nucleotides. Nucleotides are made up three main parts: nitrogenous base, pentose sugar, and a phosphate group. DNA RNA