Document 10254381
advertisement

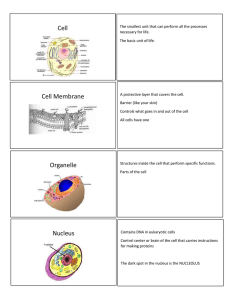
Chapter 3 Cell Structure Looking at Cells • Scientist use microscopes to look at cells • Light/electron scopes • Micrograph- image as seen through scope • Magnification 100X • Resolution-clarity of microscopic image Types of Microscopes • Compound light microscope has 2 lenses (multiply #’s) – one = eye piece, – one = objective lense • Electron Microscopes • Uses an electron beam inside a vacuum chamber • Stain specimen w/ metal ions • Can magnify up to 200,000X Cell Features • • • • Cell size (small cells have a greater surface area/volume ratio) Prokaryotes -lacks a nucleus and other internal compartments Eukaryotes- have nucleus Cell theory – All living things made of cells – Cells are basic units of structure and function – All cells arise from existing cells Eukaryotic Cells • Nucleus houses the cells’ DNA • Organelle-structure that carries out a specfic cell activity • Cytoskeleton- provides the interior framework of animal cell - anchors organelles to the cytoplasm Cell Membrane • Lipids form barrier b/w inside and outside of cell • Cell membrane only allows certain substances to enter/exit (permeable) • See diagrams on pages 60-61 Cell Organelles • Nucleus- controls most cell functions • Ribosomes- make proteins • ER - extensive system of internal membranes that move proteins and other substances through cell • Rough ER - ER that has ribosomes attached • Smooth ER- makes lipids and break down toxic substances • ER, Golgi apparatus, and lysosomes work together in the production, packaging and distribution of proteins (Figure 15 page 64) Cell Organelles Continued • Mitochondriaorganelle that makes energy from organic compounds (makes ATP) • Mitochondria also has DNA and ribosomes • Plant cell organelles – Cell wall is composed of proteins and carbohydrates – Chloroplasts use light energy to make carbohydrates – Central vacuole stores water and helps to control cell pressure