Ch. 3 PPT Notes
advertisement
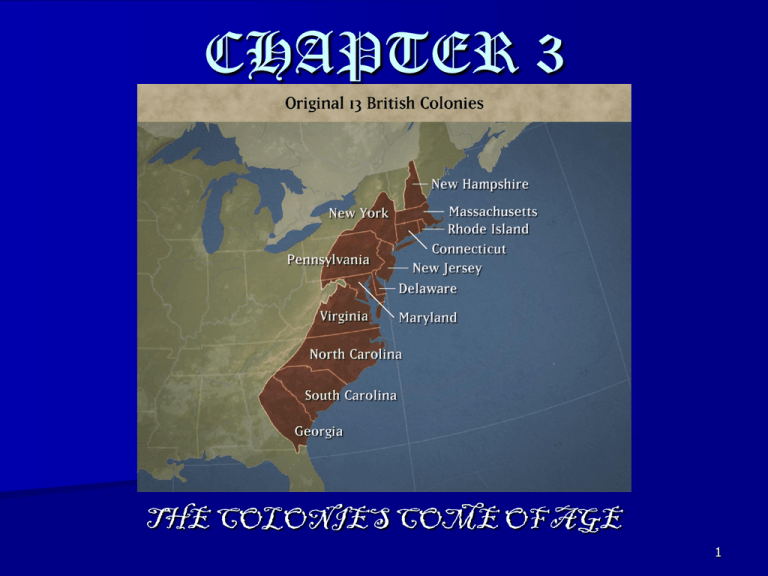
CHAPTER 3 THE COLONIES COME OF AGE 1 13 Colonies Divided New England: Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Connecticut, Rhode Island Middle: New York, Delaware, New Jersey, Pennsylvania Southern: Virginia, Maryland, North Carolina, South Carolina, Georgia 2 The Agricultural South Farmers specialize in cash crops grown for sale Tobacco known as “brown gold” a predominantly agricultural society emerges. 3 Mid-1700s Plantation Life Small farmers were the majority But plantation owners controlled the govt. and churches. Why so few towns in South? Plantations develop instead of towns b/c they had access to long deep rivers>>> allowed plantation owners to ship directly to other places Plantations produce most of what farmers need on their property- no need for a town’s shops 4 Evolution of Slavery 5 Middle Passageslave’s journey from west coast of Africa to America A horrible journey of 3,000 miles packed into the hull of a ship Triangular Trade 6 7 8 SLAVE IMPORTATION http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pDukq8 npXBk 9 • 80–90% of slaves work in fields; 10–20% work in house (cook, clean, mind children) or as artisans (blacksmith, bricklayer, carpenters) Some colonies slaves outnumbered whites 2 to 1 • Slaves work full-time from age 12 until death • Majority of owners beat, whip slaves considered disobedient, disrespectful (VA courts did not consider the killing of a slave during punishment as murder). 10 STONO REBELLION: 1739 • 20 slaves took up arms and killed several planter • • families. Rebellion put down. Despite its failure, many towns tightened slave laws even more. 11 THE COMMERCIAL NORTH Produced several crops Cold winters = short growing season & rocky soil = smaller farms>> Why less slavery in the North? No plantations= less need for slaves Could not develop plantations because of the geography 12 • Philadelphia second largest city in British empire; a planned city with a grid like street system, very modern • Growth in trade leads to large port cities: New York, Boston, Philadelphia Jamestown (in South)and New York chosen because of access to rivers 13 Influx of Immigrants 14 Salem witchcraft trials In 1692, false accusations of witchcraft lead to trials, hysteria- how and why did this happen? strange things in Salem Social tensions Poor brought charges against the rich In the end 25 women killed as “witches”over 150 imprisoned 15 The Great Awakening 1730s-1740s colonists begin to question traditional authority Religious awakening Jonathan Edwards tried to revive intensity of original Puritan vision. This Great Awakening preacher was famous for his fiery message referred to as “sinners in the hand of an angry God.” 17 French territory in the Americas originally claimed by Cartier and in 1608 Samuel Champlain founded Quebec – 1st permanent French settlement in N America Different from British settlers • Most French settlers came for the fur trade • And missionaries, spreading Christianity • Had much better relationship with Native Americans 18 Navigation Acts>>Colonial trade is “restricted”. By 1688 England does not enforce laws if colonies maintain economic loyalty to England Colonies pretty much left alone known as Salutary Neglect 19 Beginning of the End 20 Why was the policy of Salutary Neglect the first step in the colonies’ quest for independence? ***Colonies got very used to being left alone by England & making their own decisions Still loyal to England but developing taste for self govt. French and Indian war French and Indians vs. British Why? 1754-1760 • Who can defend colonists? • http://www.youtube.com/w atch?v=VuQ5SzExJNc 21 Benjamin Franklin (A&E Library Video) Assignment Enlightenment>>Leading figure: Benjamin Franklin was a symbol of mobility and individualism. Enlightenment and Great Awakening had similar results: people question old ideas and authority How did Benjamin Franklin exemplify individualism and social mobility? Was he born into wealth, and how did he become successful and well known? Social mobility is the ability one achieves to move up or down the social hierarchy (rich, middle, or poor), resulting in a higher or lower social class of wealth and status. Write a 1/2 page response to the video citing specific examples answering this question. 22 1756 War Is Formally Declared! • France claims land/builds a fort in Ohio>>> already belonged to British settlers>>>both claim same land • William Pitt helps British Win> Iroquois join British • 1759 British capture Quebec and win French and Indian war • battle scene • Book pg 89 24 1763 Treaty of Paris At the end of the war France --> lost their Canadian possessions, most of her empire to England England --> got all French lands in Canada, exclusive rights to Caribbean slave trade, future American colonies North America in 1763 • Colonists want to move west. • Indians don’t want them there. • British intervene • Proclamation Line of 1763 • Colonists can’t move west of this line • established to keep colonists in and Indians out. Effects of the War on Britain? 1. It increased her colonial empire in the Americas. 2.Cost A LOT OF $$$$$ to send troops to defend the colonists>> Debt for England Britain wants colonists to help pay for cost of their defense.>>>TAXES The Aftermath: Tensions Along the Frontier 1763 Pontiac’s Rebellion Ottawan chief>>captures 8 British forts- Indian attacks on settlers Fort Detroit British “gifts” of smallpox-infected blankets from Fort Pitt.







