Unit 5 Study Guide Answer Key
advertisement

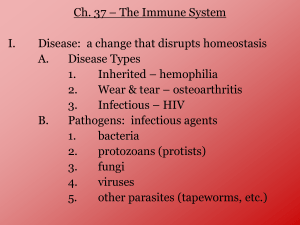
Name: _______________________ Date: ______________ Period: _____________ Unit 5 Study Guide 1. Describe the jobs of the circulatory system. Carry needed substances to the cells Carry waste products away from the cells Fight Disease 2. The Heart: Completed as a worksheet in class a. Label the following parts of the heart by writing the correct letter from the picture next to the correct name in the word bank below. b. Color the heart like we did in class. Oxygenated Blood = Red; Carbon Dioxide Blood (no oxygen)= Blue Left Ventricle Right Atrium Superior Vena Cava Right Ventricle Valve Inferior Vena Cava Left Atrium Aorta Pulmonary Artery Pulmonary Vein 3. Describe how blood travels through the heart. Tell me where the blood enters the heart, how/where it moves through the heart, and how/where it leaves the heart. Blood enters the body through veins and flow into the atrium. The atrium squeezes the blood through the valves and into the ventricles. The ventricles squeeze the blood into an artery and out of the heat. 4. Complete the chart below with the correct blood vessel, blood vessel structure, and blood vessel function. Blood Vessel Blood Vessel Function Blood Vessel Structure Artery Very thick wall, Carry blood away from withstands large pressure, the heart smooth inside Capillary Vein Carry oxygen and glucose to body cells away and carbon dioxide away from body cells Carry blood to heart Thin walls and tiny Thicker than capillaries but thinner than arteries 5. Describe the two loops of blood flow in detail. Once oxygen is inhaled into the lungs, oxygenated blood travels through blood vessels from the lungs to the heart. The oxygenated blood then travels away from the heart in the arteries to the body cells. This blood then travels into the capillaries where the capillaries give the body cells oxygen from the blood and the body cells give the blood carbon dioxide. The blood is now carbon dioxide blood. This blood travels through the veins towards the heart. The heart then pumps this carbon dioxide blood to the lungs so the carbon dioxide can be exhaled. 6. What are the parts of blood and their percentages? a. ___55%______ Plasma b. ____44.5%_____ Red Blood Cells c. _____0.5%____ White Blood Cells and Platelets 7. Draw a picture of white blood cells and red blood cells. _Red Blood Cells____ __White Blood Cells______ 8. What is the name of the fluid that moves through the lymphatic system? Lympj 9. Name 3 parts of the lymphatic system. Lymph Nodes, Lymph Vessels, Spleen, Tonsils 10. Why do your lymph nodes get inflamed (swell up) when you are sick? White blood cells fill lymph nodes and lymph nodes swell up 11. What did Joseph Lister do? Hypothesized that microorganisms made people sick 12. Define pathogen An organism that causes a diseas 13. Describe each of the following: a. Bacteria: single celled microorganisms b. Virus: tiny non-living particles that cannot reproduce unless living in a host cell c. Protist: tiny multicellular organisms d. Fungi: Molds and yeasts that grow best in warm, dark, moist places 14. In what two ways do bacteria cause diseases? 1. directly attack cells 2. Produce toxins that kill cells 15. What are the ways pathogens can infect humans. Soil, Food, Water, Infected Animal, Infected human, Contaminated objects 16. List 3 three lines of defense in your body. 1. barriers to keep out pathogens 2. Inflammatory Response 3. Immune System 17. What is in your breathing passageways that help to trap and kill pathogens? Cilia and Mucus 18. What is the purpose of sneezing and coughing? Get pathogens out of your body 19. Describe what happens during the inflammatory response. Blood vessels widen and increase blood flow to the area to increase the number of white blood cells near the pathogen. This makes the area look red and swollen but helps your body fight infection 20. What is the purpose of a fever? Many pathogens cannot grow or reproduce at high temperatures 21. Describe in detail how the immune system kills pathogens. When you have a fever, your immune system is called into action. T Cells are the first ones on the scene. These cells are responsible for identifying what pathogen is inside your body. They do this by recognizing the antigen that is on the pathogen. These cells then tell the B cells what pathogen is present. These cells produce a protein called antibodies. This protein gets thrown on the pathogen and marks it for destruction. Once the pathogen is covered in antibodies, another white blood cell comes to destroy the pathogen. Extra Credit for Period 2 22. What is active immunity and how do you get it? Active immunity is when you get a disease or vaccine and your body responds to the pathogen by producing antibodies. Your T and B cells remember the pathogen and can fight it off quicker in the future. 23. What is passive immunity and how do you get it? Passive immunity is when you get antibodies from someone else (injection or from your mom as an infant). These antibodies can fight diseases for a short time but since they weren’t made by your body, this immunity doesn’t last very long. 24. Why are antibiotics unable to kill viruses? Viruses are non-living, therefore they cannot be killed. 25. How do vaccinations help us? Vaccinations are when you are injected with a weakened or dead form of a pathogen but your body still responds by creating antibodies. Your T and B cells remember what it looks like so if you get that pathogen in the future your body can fight it off before you ever get sick.