O'Brien - Intro. to Information Systems
advertisement

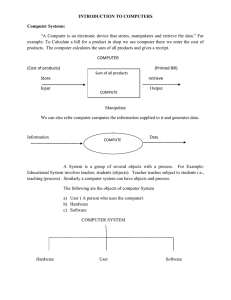
Module II – Information Technologies Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Computer Hardware Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-1 Learning Objectives Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END 1. Major types, trends, and uses of microcomputer, midrange and mainframe computer systems 2. The major technologies and uses of computer peripherals for input, output, and storage 3. Identify and give examples of the components and functions of a computer system 4. Identify the computer systems and peripherals you would acquire or recommend for a business of your choice, and explain the reasons for your selections. Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-2 Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END End User and Enterprise Computing Types of Computer Systems Use of a Variety of Designs Real World Case 1… Progressive Insurance and UniFirst Corp: The Case for Mobile Computing Click to go to Case 1 Systems Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-3 Types of Computers Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT Computer System Categories –Mainframe Computers –Midrange Computers –Microcomputers –Client-Server Networks –Information Appliances END Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-4 Microcomputer Systems Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Personal Computer (PC) Professional Workstations Multiuser Systems Desktop Systems Laptops Workstation Computers Network Servers Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-5 Microcomputer Systems Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Boeing, Monster.Com, and Others: Corporate PC Criteria • Solid Performance at a Reasonable Price • Operating System Ready • Connectivity Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-6 Network Computers Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Used by Workers in Networks Sealed Low-Cost Systems Network Microcomputers No or Minimal Disk Storage Dependent Upon Internet or Intranets for Operations Standardization Reduced Costs of Maintenance and Upgrades Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-7 Information Appliances Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Smart Gadgets Cellular Phones and Pagers Hand-Held PCs Web-Based Games Personal Digital Assistants (PDAs) Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-8 Computer Terminals Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Dumb Terminals Intelligent Terminals Network Terminals –Windows Terminals –Internet Terminals Transaction Terminals –ATM Machines –POS Terminals Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-9 Midrange Systems Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END High-End Network Servers Process Business Applications Less Costly to Busy and Maintain that Mainframes Scientific Research Engineering Analysis Process Monitoring and Control CAD Systems Front-End to Mainframes Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-10 Midrange Systems Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Los Alamos Laboratory and Blackboard, Inc.: Moving to Blade Servers • Rack System Slide-Ins • 30 – 50% Lower Cost • Smaller Size, Less Power Use • Reduced Cabling • Don’t Need Environmental Requirements • No Raised Flooring Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-11 Mainframe Systems Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Large, Fast, and Powerful Hundreds of Millions of Instructions per Second (MIPS) Large Primary Storage Superservers for Large Client/Server Networks Data Warehousing and Mining Electronic Commerce Applications Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-12 Supercomputer Systems Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Extremely Powerful Systems Large-Scale Data Mining Parallel Processing Floating Point Decimal Operations – –Billions - Gigaflops –Trillions - Teraflops Symmetric Multiprocessing – SMP Minisupercomputers Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-13 The Computer System Concept Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases Central Processing Unit Input Devices Control Arithmetic Unit Logic Unit System Bus Special Cache Purpose Processors Memory • Keyboard • Mouse • Touch Screen • Optical-Scanner • Voice Recognition etc. Secondary Storage Devices KEY TERMS BACK NEXT Primary Storage Memory END Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. Output Devices • Visual Display Unit • Printer • Audio-Response • Physical Control Devices, etc. Magnetic Disk Tape Units Optical Disks, etc. 3-14 Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Computer Processing Speeds Thousandths – Milliseconds Millionths – Microseconds Billionths – Nanoseconds Trillionths – Picoseconds MIPS Megahertz (MHz) Gigahertz (GHz) Internal Clock Registers and Caches Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-15 Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Input - Output and Storage Technologies Using the Right Peripherals Value of Consolidating Operations Real World Case 2… Delta and Northwest Airlines: The Business Value of Customer Self-Service Click to go to Case 2 Kiosks Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-16 Peripheral Devices Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Online vs. Offline Devices Natural User Interface Pointing Devices –Graphical User Interface (GUI) –Electronic Mouse –Trackball –Pointing Stick –Touchpad –Touch Screens Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-17 Pen-Based Computing Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Tablet PCs PDAs Digitizer Pens Graphics Tablets Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-18 Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Speech Recognition Systems Discrete Speech Recognition Continuous Speech Recognition (CSR) Training Time –Dragon Naturally Speaking –IBM’s Via Voice Speaker Independent Systems Voice Messaging Computers Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-19 Optical Scanning Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases Document Management Flatbed Scanners Optical Character Recognition (OCR) Wands and Bar Coding Uniform Product Code (UPC) KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-20 Other Input Technologies Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases Magnetic Stripe Smart Cards Digital Cameras Magnetic Ink Character Recognition (MICR) KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-21 Output Technologies Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases Voice Response Video Output –Video Monitor –Cathode Ray Tube (CRT) –Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) –Flat-Panel TVs –Plasma Display Panels KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-22 Printed Output Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Inkjet Printers Laser Printers Color Laser Printers Multifunction Inkjet Printers Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-23 Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT Magnetic Tape Primary Storage Secondary Storage Storage Trade-offs END Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-24 Computer Storage Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Binary Representation Bit Byte Kilobytes (KB) - k Megabytes (MB) Gigabytes (GB) Terabytes (TB) Petabytes – Over 1 Quadrillion Bytes Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-25 Computer Storage Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Direct Access –Random Access (RAM) –Direct Access Storage Devices (DASD) Sequential Access Semiconductor Memory –RAM Memory – Random Access –ROM Memory – Read Only Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-26 Computer Storage Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Sequential Access Storage Device Direct Access Storage Device Read/Write Head Read/Write Head C A A B E D C E D Real World Cases B KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-27 Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Magnetic Storage Floppy Disks Hard Disk Drives RAID Storage Magnetic Tapes Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-28 Optical Disks Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END CD-ROM CD-R and CD-RW CD-RW/DVD DVD-ROM Drive DVD-R DVD-RW Image Processing Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-29 Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Summary 1. Three Major Types of Computer Systems – Microcomputer – Midrange Systems – Mainframe Systems Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-30 Summary Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases 2. Microcomputers are Used as Personal Computers, Network Computers, Personal Digital Assistants, Technical Workstations, and Information Appliances. KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-31 Summary Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END 3. Midrange Systems are used for Many Multiuser Business Data Processing and Scientific Applications. 4. Mainframe Systems are Larger and More Powerful than Midrange Systems, Have More Memory, and Support More Users and Peripheral Devices, and High Volumes of Data. Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-32 Summary Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END 5. Computer Systems Perform Input, Processing, Output, Storage, and Control Functions. 6. Hardware Consists of Input and Output Devices, a Central Processing Unit, Primary and Secondary Storage Devices. Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-33 Summary Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT 7. Supercomputers are a Special Category of Extremely Powerful Mainframe Systems Designed for Massive Computational Assignments. 8. Peripheral Devices are used for a Wide Array of Input, Output, and Storage Applications. END Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-34 KEY TERMS Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Binary Representation Central Processing Unit (CPU) Computer System Computer Terminal Digital Cameras Direct Access Generations of Computing Information Appliance Laptop Computer Liquid Crystal Displays (LCD) Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-35 KEY TERMS Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Magnetic Disk Storage - Floppy Disk - Hard Disk - RAID Magnetic Ink Character Recognition (MICR) Magnetic Stripe Magnetic Tape Mainframe Computer Microcomputer Microprocessor Midrange Computer Minicomputer Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-36 KEY TERMS Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Network Computer NetPC Network Server Network Terminal Offline / Online Optical Character Recognition (OCR) Optical Disk Storage - CD-ROM - CD-R - CD-RW - DVD - WORM Disk Optical Scanning Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-37 KEY TERMS Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Pen-Based Computing Peripheral Devices Personal Digital Assistant Pointing Devices Electronic Mouse - Pointing Stick Touchpad - Trackball Primary Storage Printers Secondary Storage Semiconductor Memory - RAM - ROM Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-38 KEY TERMS Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Sequential Access Smart Cards Speech Recognition Storage Capacity Elements - Bit - Byte - Kilobyte (K or KB) - Megabyte (MB) - Gigabyte (GB) - Terabyte (TB) Storage Media Trade-offs Supercomputer Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-39 KEY TERMS Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT Time Elements - Millisecond - Microsecond - Nanosecond - Picosecond Touch-Sensitive Screen Trends in Computers Video Output Volatility Wand Workstation END Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-40 Optional Case Studies Real World Case 1 Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Progressive Insurance and UniFirst Corp: The Case for Mobile Computing Systems Click to go to Case 1 Real World Case 2 Delta and Northwest Airlines: The Business Value of Customer SelfService Kiosks Click to go to Case 2 Real World Case 3 Nappi Distributors and Old Dominion Freight Line: The Business Value of Wireless Handhelds Click to go to Case 3 Real World Case 4 Wisconsin Physicians Service and Winnebago: Moving to Linux on the Mainframe Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. Click to go to Case 4 3-41 Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Computer Software Real World Cases Chapter 4 KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-42 Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT Progressive Insurance and UniFirst Corp: The Case for Mobile Computing Systems 1- What are the business benefits and limitations of Progressive’s IRV system and the UniFirst PDA system? Return to Chapter 3 Return to Cases Page END Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-43 Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT Progressive Insurance and UniFirst Corp: The Case for Mobile Computing Systems Progressive’s IRV system Benefits would include: • A competitive edge in providing fast claims service. • Improved customer relations. • More productive claims reps. • Claims settled in less time. END Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-44 Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Progressive Insurance and UniFirst Corp: The Case for Mobile Computing Systems Progressive’s IRV system Limitations would include: • All necessary information to settle the claim may not be available to the claims reps and settlements may be incorrect. • Reduced data verification by company supervisory staff may lead to a higher error occurrence of incorrect claims settlements. Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-45 Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Progressive Insurance and UniFirst Corp: The Case for Mobile Computing Systems UniFirst PDA system Benefits would include: • Information provided to field sales professionals to support their sales and service activities in real time. • Information provided to sales professionals in the field to assist in follow-ups. • Lower costs Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-46 Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Progressive Insurance and UniFirst Corp: The Case for Mobile Computing Systems UniFirst PDA system Benefits would include: • Increased revenues. • Reduction of number of employees – data entry. • Reduction in past-due invoices. • Managers can create calendars, prioritize accounts and help the reps sell. Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-47 Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Progressive Insurance and UniFirst Corp: The Case for Mobile Computing Systems UniFirst PDA system Limitations would include: • PDA technology must be used by “people who often shun the stuff.” • Verification of input data is lost by the elimination of data input employees. Sales reps are responsible for data input accuracy. • IT improvements limited to the business processes and have not been made to differentiate UniFirst from competition. Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-48 Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT Progressive Insurance and UniFirst Corp: The Case for Mobile Computing Systems 2- What computer system technologies could Progressive add to improve the business value of their IRV program? Why? END Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-49 Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Progressive Insurance and UniFirst Corp: The Case for Mobile Computing Systems Discussion Points Include: Limitations would include: • PDA technology must be used by “people who often shun the stuff.” • Verification of input data is lost by the elimination of data input employees. Sales reps are responsible for data input accuracy. • IT improvements limited to the business processes and have not been made to differentiate UniFirst from competition. Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-50 Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Progressive Insurance and UniFirst Corp: The Case for Mobile Computing Systems 3- Should UniFirst switch from PDA’s to laptop PCs or tablet PCs? Why or why not? Checkout websites like www.cnet.com or www.pcworld.com for the latest product reviews to help you answer. Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-51 Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Progressive Insurance and UniFirst Corp: The Case for Mobile Computing Systems Discussion Points Include: • Cost savings vs. cost of a change to a different technology. • Anticipated improvement in revenues. Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-52 Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT Progressive Insurance and UniFirst Corp: The Case for Mobile Computing Systems Discussion Points Include: • Cost savings vs. cost of a change to a different technology. • Anticipated improvement in revenues. • Improved customer relations. Return to Chapter 3 Return to Cases Page END Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-53 Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Delta and Northwest Airlines: The Business Value of Customer Self-Service Kiosks 1- What computer system technologies and functions are included in self-service kiosks? What other technologies should be provided? Why? Visit the Kinetics USA website for more details. Return to Chapter 3 Return to Cases Page Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-54 Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Delta and Northwest Airlines: The Business Value of Customer Self-Service Kiosks Items to Discuss Include: • Special-purpose microcomputer terminals. • Video touch screens • High speed thermal printer • Magnetic stripe card reader Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-55 Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT Delta and Northwest Airlines: The Business Value of Customer Self-Service Kiosks 2- What is the customer value of self-service kiosks for airline check-in? What other services should be provided? Take the Delta demo tour of check-in at www.delta.com/travel/trav_s erv/kiosk to help you answer. END Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-56 Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Delta and Northwest Airlines: The Business Value of Customer Self-Service Kiosks Discussion Points Include: • Reduced customer waiting time • Customer relationship is improved. • Costs reduced or minimized by the reduction of employee cost of handling routine procedures for travelers. Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-57 Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Delta and Northwest Airlines: The Business Value of Customer Self-Service Kiosks 3- What is the business value of self-service kiosks in the airline industry? Do selfservice kiosks give airlines a competitive advantage? Why or why not? Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-58 Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Delta and Northwest Airlines: The Business Value of Customer Self-Service Kiosks Points About Business Value: • Reduces costs or at least reduces the increase in cost. • Improves customer relations by making check-in and subsequent activities are easy as possible. • Reduces the waiting time for customers that increase after Sept. 11. Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-59 Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Delta and Northwest Airlines: The Business Value of Customer Self-Service Kiosks Points About Competitive Advantage: • Self-service kiosks maintain industry competitiveness. • Enhancement of the services available through self-service kiosks increases an airlines competitive advantage by improving customer relations. Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-60 Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Delta and Northwest Airlines: The Business Value of Customer Self-Service Kiosks Points About Competitive Advantage: • The need to continuously improve and streamline traveler check-in activities, especially after Sept. 11, is a factor in a highly competitive industry. Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-61 Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS Delta and Northwest Airlines: The Business Value of Customer Self-Service Kiosks Points About Competitive Advantage: • The need to continuously improve and streamline traveler check-in activities, especially after Sept. 11, is a factor in a highly competitive industry. • A reduction of costs or a reduction in the increase in costs Return to in a highly competitive Chapter 3 industry is critical. Return to Cases Page BACK NEXT END Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-62 Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Nappi Distributors and Old Dominion Freight Line: The Business Value of Wireless Handhelds 1- What are the business benefits and limitations of the use of wireless handheld computers by Nappi Distributors? How could their mobile sales application be improved? Defend your proposals. Return to Cases Page Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-63 Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Nappi Distributors and Old Dominion Freight Line: The Business Value of Wireless Handhelds Discussion Points Include: Benefits – • Reduced waiting time for sales reps • Reduced time to process an order. • Reduction in employee costs or number of employees required to input sales orders. Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-64 Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Nappi Distributors and Old Dominion Freight Line: The Business Value of Wireless Handhelds Discussion Points Include: Limitations – • Interference from radar sites in the area. • Upgrade of system to include new features is more difficult to learn. • Transmission speed is slow. Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-65 Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Nappi Distributors and Old Dominion Freight Line: The Business Value of Wireless Handhelds Improvement in Mobile Sales Application Includes: • Speech recognition to reduce keying in of orders. • Table PCs • Touch screen technology • PDAs Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-66 Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Nappi Distributors and Old Dominion Freight Line: The Business Value of Wireless Handhelds 2- What are the business benefits and limitations of the use of wireless handheld computers by Old Dominion Freight Lines? How could their mobile freight management application be improved? Defend your proposals. Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-67 Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Nappi Distributors and Old Dominion Freight Line: The Business Value of Wireless Handhelds Discussion Points Include: Benefits – • Increased customer satisfaction. • Improved driver efficiency. • Reduction in loading errors. • More stops per day. • Improved accountability by drivers. Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-68 Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Nappi Distributors and Old Dominion Freight Line: The Business Value of Wireless Handhelds Discussion Points Include: Limitations – • Requires better trained drivers. • Charges by character requires communications be brief. • Dependent upon a network of wireless service providers. System failure causes company delivery service to be delayed. Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-69 Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Nappi Distributors and Old Dominion Freight Line: The Business Value of Wireless Handhelds Improvements in the mobile freight management application could include: • Speech recognition to reduce keying in of orders. • Optical scanning wands. Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-70 Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Nappi Distributors and Old Dominion Freight Line: The Business Value of Wireless Handhelds 3- Would you recommend the use of wireless laptop or tablet PCs to either Nappi or Old Dominion? Why or why not? Visit the Symbol Technologies website to help you answer. Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-71 Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT Nappi Distributors and Old Dominion Freight Line: The Business Value of Wireless Handhelds Discussion should include: • Duties required to employees – sales reps and drivers. • Nature of packaging for products and the easy with which certain input devices could be used to improve efficiency by the employee. END Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-72 Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Nappi Distributors and Old Dominion Freight Line: The Business Value of Wireless Handhelds Discussion should include: • The benefit to the company in terms of customer relations. Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-73 Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases Nappi Distributors and Old Dominion Freight Line: The Business Value of Wireless Handhelds Discussion should include: • The benefit to the company in terms of customer relations. • The cost savings to the company. KEY TERMS BACK NEXT Return to Cases Page END Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-74 Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Wisconsin Physicians Service and Winnebago: Moving to Linux on the Mainframe 1- How can a mainframe use Linux to replace the equivalent of hundreds of Unix or Windows servers? Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT Return to Cases Page END Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-75 Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Wisconsin Physicians Service and Winnebago: Moving to Linux on the Mainframe Server consolidation – replacing dozens or even hundreds of separate Intelbased Linux or Windows servers with a partition on the mainframe that dedicates a single processor, memory and other system sources to running Linux. Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-76 Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT Wisconsin Physicians Service and Winnebago: Moving to Linux on the Mainframe 2- What are the business benefits and challenges of using Linux on a mainframe to replace Windows or Unix servers? Use WPS and Winnebago to illustrate your answer. END Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-77 Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END • • • • Wisconsin Physicians Service and Winnebago: Moving to Linux on the Mainframe WPS move to Linux on the mainframe To leverage the mainframe’s reliability To keep support costs low WPS created a virtual Linux Server running on one 250-MIPS processor available within an IBM mainframe • Costs were only 40% of that for ordering, installing and configuring a new Intel-based server • Virtual servers can be created within 2 to 3 minutes and deliver as much as 9 times the throughput of a stand-alone server Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-78 Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Wisconsin Physicians Service and Winnebago: Moving to Linux on the Mainframe • Winnebago implemented a groupware application for Linux on an IBM mainframe • Windows NT servers had to be rebooted weekly in an effort to improve their stability • On the mainframe, everything is geared to run 24/7 • It was more cost-effective to use part of his existing mainframe capacity and his staff’s mainframe skills to run its Linux-based e-mail system Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-79 Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Wisconsin Physicians Service and Winnebago: Moving to Linux on the Mainframe 3- What business applications are best suited to servers? To mainframes? Explain your reasoning. Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-80 Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Wisconsin Physicians Service and Winnebago: Moving to Linux on the Mainframe Servers – Windows application since they don’t run on Linux and applications that have complex graphical user interfaces or that perform complicated data analysis can use so much processing power that it’s more cost-effective to keep running them on stand-along servers. Users have also been reluctant to move complex applications such as SAP R/3, which can take years to implement on distributed servers, onto a new environment. Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-81 Types of Computer Systems The Computer System Concept Section II Peripherals Input Technologies Output Technologies Storage TradeOffs Semiconductor Memory Magnetic Disks Magnetic Tape Optical Disks Real World Cases KEY TERMS BACK NEXT END Wisconsin Physicians Service and Winnebago: Moving to Linux on the Mainframe Mainframes – Some of the best candidates for consolidation are infrastructure applications such as file and print services, e-mail, domain name servers and Web servers. Return to Cases Page Copyright 2005, McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Inc. 3-82