Storage 101 - tikiwikiwoki
advertisement

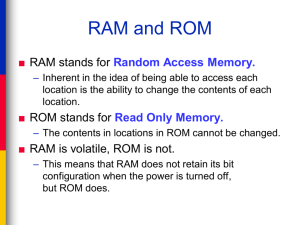
Input Processing Storage Output Storage refers to the media and methods used to keep information available for later use. Some things will be needed right away while other won't be needed for extended periods of time. So different methods are appropriate for different uses. Are both measured in kilobytes, megabytes and gigabytes With memory the information is stored electronically on chips Storage is saved on media, either magnetically on disks or optically on disks (CD/DVD) Magnetic Devices Magnetic disks come in various sizes and materials. This method uses magnetism to store the data on a magnetic surface. ◦ Hard Drive Consist of one or more magnetic metal platters which are sealed inside a case. Step Measured as: 1. seek move the head to proper track seek time (ms) 2. rotate rotate disk under the head to the correct sector rotational delay (ms) 3. settle head lowers to disk; wait for vibrations from moving to stop (actually touches only on floppies diskettes) settling time (ms) 4. data transfer copy data to main memory data transfer rate (kbs) where ms stands for millisecond = .001 second and kbs is kilobytes per second. optical disks include CD and DVD discs. You may guess from the word "optical" that it has to do with light. You'd be exactly right! Laser light, in fact. 1's and 0's are formed by how the disk absorbs or reflects light from a tiny laser. How It Works (a simple version) An optical disc is made mainly of polycarbonate (plastic). The data is stored on a layer inside the polycarbonate. A metal layer reflects the laser light back to a sensor. To read the data on a disk, laser light shines through the polycarbonate and hits the data layer. How the laser light is reflected or absorbed is read as a 1 or a 0 by the computer. Flash drive USB drive Memory stick SD drive Trivia Fact SD used to stand for Secure Digital but not usually means ScanDisk Devices like digital cameras, digital camcorders, and cell phones may use CompactFlash, SmartMedia, These are solid-state devices (no moving parts) that read and write data electrically instead of magnetically. Laptop computers use PCMCIA cards, another type of flash memory, as solid-state hard disks. Storage is the third step in the computing cycle. The fourth and final step is on its way … in the next slide show!