Storage Media & Devices
advertisement
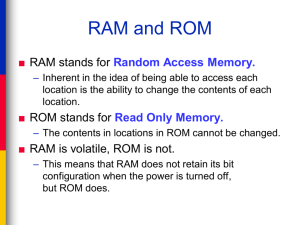
AS ICT Identify suitable uses of common storage media understand the types of access and access speeds required for each use (e.g. serial/sequential, direct/random) Describe the comparative advantages and disadvantages of using different backing storage media What’s the difference between a storage device and storage media? The media is where the data is stored – eg the CD ROM, the magnetic tape, the barcode. The device is the equipment that is used to store the data on the media – eg the CD writer, the magnetic tape deck, the barcode scanner. Magnetic Optical Solid state Hybrid When you are working on a computer, the data (and the programs) are stored in RAM. However, this is volatile. If you want your data to be available for future use, you have to save it permanently on some form of backing storage. Data is stored on these in the form of magnetized bits. Magnetic recording is a backbone technology of the electronic age. It is a fundamental way for permanently storing information. In the computer realm, magnetic recording is used on floppy disks, hard disks and magnetic tape as the main method for data storage. Magnetic data storage is popular because it is an easy and inexpensive technology, with good medium-term (10 to 20 years) storage characteristics. These are very high capacity (can store massive amounts of data) A tape can be written to instantly and kept for a long time, or the data can be erased and the media used again and again. Bit for bit, it is a much cheaper storage medium than CD-R DVD or Blu-Ray. Data is stored on the tape in the order it is written: Sequential - ie record by record. Retrieval is therefore slow. Anywhere that requires extremely large capacity data storage where speed of retrieval is not an issue Batch processing: updating bank accounts with cheques Producing utility bills etc – all customers’ bills are produced at the same time, and every record in the database has to be processed Making backups – every item of data has to be read and saved Payroll applications – all records have to be processed in sequence and at the same time Bit for bit, cheaper than using disks Very robust – the tape is encased in a cartridge Easier to remove and keep away from the computer than equivalent storage media Data transfer rate (ie putting the data on) is very fast Access is very slow, so use is limited Updating files requires a new tape to be created. Industry standard for storing data on a computer Used for storing software files and data files Vary fast access to data, both reading and writing Data is stored randomly on the surface of the disk Therefore access is Direct, or Random – this is much faster than serial/sequential access. Any system that requires fast data access times Any system that requires fast data transfer speeds Real-time systems eg robotics, rocket launching etc Online systems eg booking systems, EPOS stock control, EFT File servers in computer networks Fast data transfer rate Fast data access times Very large capacity Fixed hard disks are very easily damaged. Often used as a backup media Also used for transferring large files from one computer to another Large capacity – 1TB is now common Often used for transferring server software from one network to another Fast data transfer rate Fast data access times Very large capacity If dropped, they are easily damaged. Transfer rats are not quite as fast as fixed hard drives More expensive than other forms of removable media (eg CDs, DVDs etc) All optical devices operate by using a laser beam. The laser reads from and writes to the disk. It etches the data onto the surface as microscopic ‘pits’. Read Only Memory Can only be read from Cannot be written to DVDs can store about 10x as much as a CD DVD writers use a shorter wavelength of light, so pits are a lot smaller and therefore more data can be written onto a disk CD ROMs and DVD ROMs are used for applications which require the prevention of deletion of data (either accidental or otherwise) Software Computer games Music albums Reference books eg encyclopedias Storing films DVDs hold more data than a CD CDs are cheaper to buy than DVDs Both hold much more data than a floppy disk Both are cheaper than hard disks Both are more robust than hard disks Data transfer rates are slower than hard disks Data access times are longer than for hard disks