Atoms
advertisement

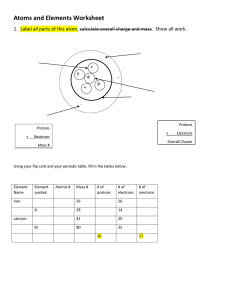
Chemistry is: The Study of Matter Objective: Describe the structure of atoms, including the location of protons, neutrons, and electrons. History Greek philosopher Democritus around 1600 said matter was composed of small particles called atoms and that different types of matter where made of different types of atoms. English schoolteacher John Dalton around 1810 said: 1. 2. 3. 4. Matter was made up of atoms Atoms cannot be divided into smaller pieces All atoms of an element are the same atom Different elements mean different atoms are present 1. Atoms: 2. 3. 4. Basic building blocks of matter Have no charge (neutral) Tiny particles that make up matter Particles that make up the atom: 1. 2. 3. Protons Neutrons Electrons Definitions Matter – anything that has mass and takes up space Element – matter made up of one kind of atom Compound – matter made of two or more different atoms Proton – positively charged particle inside the nucleus of an atom Neutron – neutral particle inside the nucleus; gives atom extra mass Electron – negatively charged particle Electron cloud – region surrounding nucleus where electrons travel Atomic particles Protons Neutrons Electrons Same as: Atomic number Location: Nucleus Neutrons + ---------------Protons = atomic mass Nucleus Electron cloud Charge: Positive No Charge Negative Energy Levels / Orbitals: ---------------- ---------------- 1st = 2 2nd = 8 3rd = 18 Model of an Atom negative Negatively charged Positively charged What kind of charge do atoms have? The atom is neutral because the charges of the protons are balanced by the negative charges of the electrons. An atom of carbon has six protons and six neutrons(maybe) in its nucleus. How many electrons will it have? What will be the atomic mass? Part 2 Atom contains protons positive contains contains neutrons Atomic number neutral With protons give Mass number electrons In electron negative cloud Definitions Atomic number – number of protons in the nucleus of an element. Atoms of an element are identified by the atomic number because it never changes without changing the identity of the element Mass number – number of protons plus neutrons Isotopes- atoms of an element with different numbers of neutrons Valence electrons- electrons in the outermost level Symbols used for elements The elements are on the periodic table and are abbreviated with one or two letters The first letter is always capitalized If a second letter is present it will be a lowercase letter Examples: – – – – – H = hydrogen Al = aluminum Na = sodium C = carbon Hg = mercury Calculating Neutrons Remember, protons and neutrons are in the nucleus Nucleus is what gives the atom its mass Atomic number the same as proton number Subtract atomic number from mass number to get neutrons Isotopes?? 13 Protons 14 Neutrons 13 Electrons 13 Protons 16 Neutrons 13 Electrons 2 Protons 2 Neutrons 2 Electrons 3 Protons 3 Neutrons 3 Electrons 21 Protons 20 Neutrons 19 Electrons 21 Protons 18 Neutrons 21 Electrons Valence Electrons The group / family number determines the number of valence electrons (outermost electrons) All elements in group 1 have 1 electron in their outermost energy level. All elements in group 14 have 4 electrons in their outermost energy level.