File - Science with Ms. C
advertisement

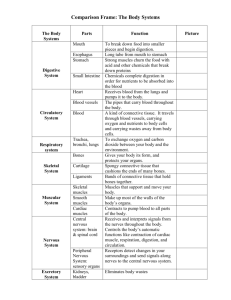
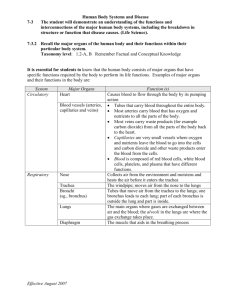
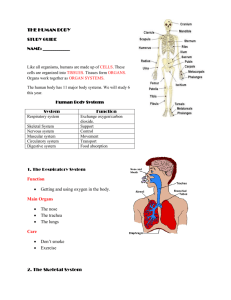
Human Body Vocabulary Cells: Basic units of structure and function Tissues: group of specialized cells that work together to perform the same function; 4 types of tissue Nerve Tissue: carries impulses back and forth to the brain from the body; Neurons Muscle Tissue: Contracts and shortens making body parts move (cardiac, smooth, skeletal) Epithelial Tissue: Covers the surfaces of the body, inside (lining of organs) and outside (skin) Connective Tissue: Connects all part of the body and provides support Organs: a group of two or more different types of tissues that work together to perform a specific function Systems: group of two or more organs that work together to perform a specific function System Circulatory System Respiratory System Organs Heart and Blood Vessels Digestive System Mouth, Esophagus, Stomach, Small/Large Intestines, Liver, Gallbladder, pancreas rectum and anus Kidneys, Ureters, Bladder, Urethra Brain, Spinal cord, Peripheral nerves Excretory System Nervous System Nose, Trachea, Bronchi, Lungs and Diaphragm Muscular System Skeletal System Skeletal, smooth and cardiac muscles Bones Integumentary Skin Function System that transports blood to all parts of the body System that provides gas exchange between the blood and the air System that breaks down food into nutrients that can be used by the body System that filters out cellular wastes, toxins and excess water System that receives stimuli from inside and outside the body and then initiates responses for survival System that provides movement System that provides support for the body to protect internal organs and provide an attachment site for muscles Covers the body and provides protection Organs Heart Blood Vessels Nose Trachea Bronchi Lungs Diaphragm Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small Intestines Large Intestines Rectum and Anus Liver Gallbladder Pancreas Kidneys Ureters Bladder Urethra Brain Spinal cord Peripheral Nerves Skeletal Muscles Smooth Muscles Cardiac Muscles Bones Function Causes blood flow through the body through pumping Tubes that carry blood throughout the entire body Takes air from the environment and moistens/hearts its before it enters the trachea Moves air from nose to lungs Tubes that move air from trachea to the lungs Gases are exchanged between air and the blood Muscle that aids in the breathing process Uses both mechanical and chemical digestion/ chewing and saliva Transport tube that carries chewed food to the stomach Secretes gastric juices that continue the process of chemical digestion and uses mechanical digestion Nutrients are absorbed; location of the most chemical digestion Water is absorbed from food and moved into the blood stream; prepares remaining food for elimination Short tube that stores solid waste til it is eliminated from the body Produces bile which is used to break up fat particles Stores bile produced by the liver Produces digestive juices that further the breakdown of food in the small intestines Get rid of urea, excess water and other waste minerals in the form of urine Tubes which connect the kidney to the bladder Stores urine until it is released from the body Tube which urine passes through before being eliminated Used to control and coordinate the activities of the body Bundle of nerves that begin at the brain stem and continues down the spine through the vertebrae Network of nerves that branch out from the spinal cord and connect to the rest of the body to transmit signals to and from the brain VOLUNTARY muscles attached to BONES and provide force needed to move the bones INVOLUNTARY muscles that control many types of movement INVOLUNTARY muscle that forms the HEART Provide shape and support for the body and protection for many organs and structures