Human Body Systems Overview: Functions & Components
advertisement
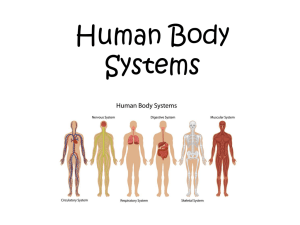
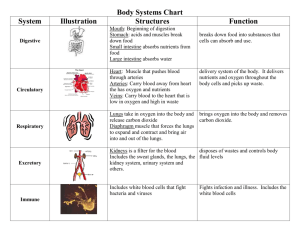
Integumentary system • Forms the external body covering and protects/cushions the body • Synthesizes vitamin D • Location of cutaneous receptors like pain, pressure, temp • Oil/sweat glands • Excretes salts and urea • helps regulate body temp • Consists of bones, cartilages, ligaments, and joints • Hematophoisis happens inside skeletal system to make cells from bone marrow. • Main function to contract == movement! • “machines of the body” • Skeletal muscles- large fleshy muscles • Allow us to walk and stand up etc. • Distinct from other muscles like heart muscles which move fluid • The CNS (Central Nervous System– Brain and spinal cord--- receive stimuli and respond by activating appropriate part of the body • Controls bodies activities like the nervous system but acts more slowly • The endocrine glands produce chemical molecules called hormones and release them into the blood to travel to target organs • Organs in this system are not really “connected” but they ALL secrete hormones • Also carry hormones and other substances to and from tissues where exchanges occur Lymphatic system • Picks up fluid leaked from blood vessels and returns it to the blood • Disposes of debris in the lymphatic system • Houses white blood cells involved in immunity • Compliments the cardiovascular system • Lymph nodes and lymph organs cleanse the blood • Within the lungs are tiny air sacs that have thin walls– these thin walls are where gas exchange occurs. • Tube that runs down the body from mouse to anus • Undigested food that is NOT transported to the blood is excreted. • Breakdown of nutrients and absorption happens in the small intestine. After this, the digestion system reclaims WATER in large intestine. Goal is to produce offspring! What do you notice?