A view of the Cell
advertisement

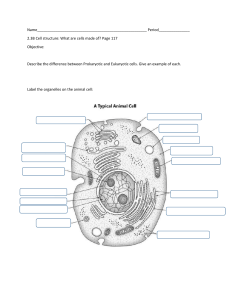
A view of the Cell Discovery of cells • Microscopes enabled biologists to see cells and develop the cell theory. • The cell theory states that the cell is the basic unit of organization, all organisms are made up of one or more cells, and all cells come from preexisting cells. • Using electron microscopes, scientists can study cell structure in detail. Cell Classification • Cells are classified as prokaryotic or eukaryotic. Prokaryotic • are molecules surrounded by a membrane & cell wall. They lack membrane enclosed organelles. kingdoms • Monera (Eubacteria) • Archaea Eukaryotic • have a nucleus and other organelles and are enclosed by a plasma membrane. Some cells have a cell wall. kingdoms: • Protista • Plantae • Fungae • Animalia prokaryote Eukaryotes The plasma membrane • Through selective permeability, the plasma membrane controls what enters and leaves a cell. • The fluid mosaic model describes the plasma membrane as a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Fluid Mosaic Model Nucleus • It contains most of the cell's genetic material. It’s function is to maintain the integrity of it’s genes and to control the activities of the cell by regulating gene expression. • Cells make proteins on ribosomes that are often attached to the highly folded endoplasmic reticulum. • Mitochondria break down sugar molecules to release energy. Chloroplasts convert light energy into chemical energy. • The cytoskeleton helps maintain cell shape and is involved in the movement of organelles and materials. The eukaryotic cytoskeleton. Actin filaments are shown in red, microtubules in green, and the nuclei are in blue.