Cell Structure and Function
Chapter 7 Cell Structure & Function
Section 7.1 “Life is Cellular” http://youtu.be/gFuEo2ccTPA
I. Cells
1. Smallest living unit
2. Most are microscopic
II. Discovery of Cells
A. Robert Hooke (mid-1600s)
1. Observed sliver of cork
2. Saw “row of empty boxes”
3. Coined the term cell
III. Cell theory
1. (1839)Theodor Schwann & Matthias Schleiden
“ all living things are made of cells”
2. (50 yrs. later) Rudolf Virchow
“all cells come from cells”
IV. Principles of Cell Theory
1. All living things are made of cells
2. Smallest living unit of structure and function of all organisms is the cell
3. All cells arise from preexisting cells
(this principle discarded the idea of spontaneous generation)
Cell Size
V. Cells Have Large Surface
Area-to-Volume Ratio
VI. Characteristics of All Cells
1. A surrounding membrane
2. Protoplasm(Cytoplasm) – cell contents in thick fluid
3. Organelles – structures for cell function
4. Control center with DNA
VII. Cell Types
1. Prokaryotic
2. Eukaryotic
Prokaryotic Cells
1. No membrane bound nucleus
2. Nucleoid = region of DNA concentration
3. Organelles not bound by membranes
4. Cell type of Bacteria
B. Eukaryotic Cells
1. Nucleus bound by membrane
2. Include fungi, protists, plant, and animal cells
3. Possess many organelles
Protozoan
VIII. Types of Microscopes
A. Compound Light Microscopes--- use a series of lenses to magnify objects in steps. Can magnify up to
1500 times.
B. Electron Microscopes---developed in the
1930s and 1940s.
1. This microscope uses a beam of electrons to magnify structures up to 500,000 times their actual size.
2. Specimens must be examined in a vacuum.
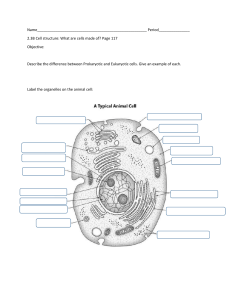
Representative Animal Cell
Representative Plant Cell