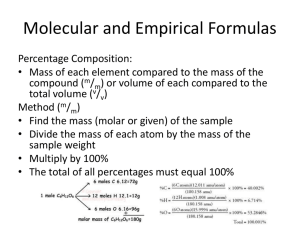
CPM.5: I can use data about a substance and its empirical formula to
advertisement

Chemistry Molecular Formulas CPM.5: I can use data about a substance and its empirical formula to determine the molecular formula of a substance. Empirical Formulas represent the lowest, whole-number ratio of the atoms in a compound. A molecular formula gives the actual composition of the compound. C6H12O6 is the molecular formula for glucose. What would be the empirical formula of glucose_______________? Another example is hydrogen peroxide, H2O2. What would be the empirical formula of hydrogen peroxide?_________ Notice that the molecular formula is always some multiple of its empirical formula. If a compound exists whose empirical formula is CH2, how many possible molecular formulas could this same compound have? ____________________. One way to identify the exact molecular formula of a compound is to know the molar mass of the compound. This mass would be the mass of the molecular formula. Consider these examples: Empirical Formula of Compound #1: CH2 Molar mass of the molecular formula of compound #1 is 70.0 grams. Molecular Formula of Compound #1?? Empirical Formula of Compound #2: N2O3 Molar mass of the molecular formula of compound #2 is 151.8. Molecular Formula of Compound #2?? Now let’s try to put all the concepts together: 1) Calculate the molecular formula of a compound that is 30.43 % nitrogen and 69.57 % oxygen. The molar mass of the compound is 92.0 gr. 2) Carbohydrates are organic compounds made up of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Determine the molecular formula of a carbohydrate compound that is 40.0 % carbon and 6.67 % hydrogen. The molar mass of the compound is between 85-115 gr. Sample Problems: 1) Find the molecular formula for a caffeine if it consists of 49.48 % carbon, 5.15% hydrogen, 28.87% nitrogen and 16.49% oxygen and has a molar mass between 150-280 grams.