Chapter 4
advertisement

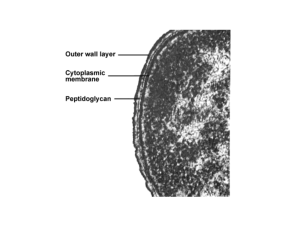
Chapter 3 Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Prokaryotes can be grouped based on morphology Genetically determined Monomorphic vs pleomorphic Size Range 0.2 to 80 um in diameter 2 to 600 um in length Average size: 0.2 -1.0 µm × 2 - 8 µm Morphology of Prokaryotic Cells Prokaryotes exhibit a variety of shapes Most common Spiral Uncommon Shapes Stella Haloarcula Cells may form groupings Cells adhere together after division Form characteristic arrangements Depends on plan of division Neisseria Enterococcus Micrococcus Sarcina Staphylococcus aureus Bacillus anthracis Bacillus megaterium Bordetella pertussis Layers External to Cell Wall Glycocalyx Made inside the cell; excreted to surface General functions Protection Attachment Motility Capsule or Slime Layer Chemical composition varies depending on species Flagella Naked filaments composed of flagellin Rotate clockwise/counterclockwise Runs and tumbles Taxis Flagella structure has three basic parts Filament Hook Basal body Polar - Monotrichous Polar -Lophotrichous Peritrichous Polar -amphitrichous Axial filaments Bundles of endoflagella that spiral around cell Spirochete bacteria only Corkscrew motion Attachment Proteins Fimbriae - bacteria Hami – archaea Filaments of pilin protein Attachment Hooked protein filament Attachment Sex Pili Pilin tubules Exchange of DNA • • Cannulae – thermophilic archaea Spinae - marine bacteria • • Connect cells over distances Creates mesh-like network Prokaryotic Cell Wall Determines shape of cell Protects from osmotic pressure Anchor point for flagella Contributes to virulence Unique chemical structure Bacteria vs. Archaea Gram positive vs. Gram-negative Peptidoglycan (PTG) (murein) Sugar found only in bacteria Archaea may have proteins or alternate sugars Basic structure of PTG Disaccharide polymer N-acetylglucosamin (NAG) N-acetylmuramic acid (NAM) Glycan chain held together by amino acids Tetrapeptide chain Protein crossbridges may or may not be present Mostly G+ Gram positive cell wall Thick layer of PTG Teichoic acids Lipoteichoic or Wall teichoic acids Polyalcohols that provide antigenic specificity May have external protein or sugar layer Gram-negative cell wall Little or no PTG Outer lipopolysaccharide membrane (LPS) O-specific polysaccharide side chain Lipid A endotoxin Significant periplasmic space GRAM STAINING Gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria can be identified using a “gram stain” Summary of Gram + vs. Gram – G+ cell many rigid layers of peptidoglycan teichoic acids No outer LPS membrane 2 ring basal body anchoring flagella G- cell Little or no peptidoglycan no teichoic acids LPS outer membrane 4 ring basal body anchoring flagella Atypical cell wall Acid-fast cell walls Classified as gram-positive mycolic acid bound to PTG Mycobacterium Nocardia Chlamydia Classified as Gram – with no PTG cysteine-rich proteins No cell wall Mycoplasmas Sterols in plasma membrane Structures Internal to Cell Wall Cytoplasmic membrane Delicate thin fluid structure Defines boundary Serves as a semi permeable barrier Fluid mosaic model Phospholipid Bilayer Amphipathic Embedded with numerous proteins receptors , transport, enzymes Prokaryotes typicallydon’t have membrane sterols Bacteria may have hopanoids Photosynthetic pigments on in-foldings chromatophores or thylakoids Archaea have distinct membrane lipids Ether linkage Diether or tetraether Glycerol group enantiomer Branched isoprenoid sidechain May form mono-layer with greater rigidity Top: archaeal phospholipid, 1 isoprene sidechain, 2 ether linkage, 3 L-glycerol, 4 phosphate group Middle:bacterial and eukaryotic phospholipid: 5 fatty acid, 6 ester linkage, 7 D-glycerol, 8 phosphate group Bottom: 9 lipid bilayer of bacteria and eukaryotes, 10 lipid monolayer of some archaea. Membrane is selectively permeable Few molecules pass through freely Movement involves both active and passive processes passive processes no energy (ATP) required Along gradient simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis Simple diffusion Facilitated diffusion Osmosis Osmotic pressure active processes energy (ATP) required Active transport Group translocation Phosphotransferase system PEP group translocation PEP transferase animation Internal Structures Structures essential for life Chromosome Ribosome Optional but may provide selective advantage Cytoskeleton Plasmid Storage granules Endospores Internal Structures Primary Chromosome Resides in nucleoid Typically single circular chromosome Archaea - histone proteins Bacteria - condensin protiens Asexual reproduction Binary fission, budding, fragmenting, spores Plasmids Small DNA molecules replicated independently nonessential information used in genetic engineering biotechnology Ribosomes (70S) Composed of large and small subunits made of riboprotein and ribosomal RNA differ in density from eukaryotic ribosomes • Inclusions Metachromatic granules Polysaccharide granules lipid inclusions sulfur granules carboxyzomes magnetosomes Gas vesicles Endospores “Resting cells” Highly resistant Heat, desiccation, chemicals and UV light Not reproduction! Endospore producers include Clostridium and Bacillus