Introduction to Fission and Fusion
advertisement

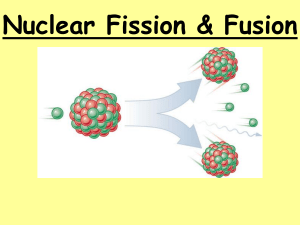
Name Class Date Introduction to Fission and Fusion Fission and Nuclear Power Plants History: _____ and Strassman bombarded __________ with neutrons, but the products showed different _____ properties that they could not explain. Meitner and _____ = _____ found that instead of heavier uranium, it had __________. _____ into smaller Nuclear Forces 1. Electric repulsion – ___________ charge particles repel each other 2. Strong nuclear force causes protons and neutrons to • Stable nuclei = strong nuclear force is • Unstable nuclei = strong nuclear force is Considered unstable if the atoms: o Have too many or too few o Have more than o Will 3. ____________ each other ____________ than repulsion force ___________ than repulsion force. ______________ in the nucleus (an ________!) protons in nucleus ________________ into a more stable nucleus Define fission: Nuclear Chain Reactions • Nuclear fission releases more reactions • The number of ________ which trigger more ___________ _____________ released determines the success of a chain reaction How did the mousetrap video show a chain reaction? Applications of Controlling Chain Reactions 1. Atomic Bomb (fission bomb) – triggering a chain reaction in • 2. __________ or 239Pu Must have a minimum amount of radioactive isotope to sustain a chain reaction = __________ Nuclear power plants – Convert heat energy from fission chain reaction into • Control chain reaction with fission reaction. _______ that absorb ____. _______ emitted after Nuclear Energy Powerpoint 1. Nuclear energy powers 3/24/16 10:39 AM in U.S. homes and businesses. 1 of 2 Oelfke (elf-ka) 2. In the nuclear power plant, heat produces steam, which generates _______. 3. List two safety designs engineered into a nuclear power plant to help prevent explosions. Nuclear Reaction Video Questions 1. In what year was nuclear power first used to generate electricity? 2. What is the principle element used in nuclear power plants? Nuclear Power Plant Benefits • Do not release _______ like fueled by _______. • Much plants. ___ efficient in producing power because it uses less __ than power • A very ___ pellet of uranium releases ton of coal. ______ into the atmosphere like power plants __ energy than Fusion and The Sun Define fusion. A large amount of _________ is required to start a fusion reaction o Need this energy to overcome o Extremely high __ forces of protons. ____________ can provide start-up energy. ______ energy in fusing hydrogen than ________ of uranium Where in the universe is there enough extreme heat needed for fusion to occur? • Fusion of ________ into ______ in the Sun’s core generates the Sun’s energy. How long ago did fusion generate the energy we now receive as sunlight? Fusion created the energy we receive today about a ______ years ago. This is the time it takes for photons and then convection to transport energy through the Sun’s core to the ______________. Once sunlight emerges from the photosphere, it takes only about minutes to reach Earth. Fusion Energy Advances Video Questions 1. When creating energy by fusion, there is no 2. Fusion is the opposite of 3. A challenge of producing fusion reactions is that the lasers are _____ very frequently. 3/24/16 10:39 AM __________ waste. _______. 2 of 2 ____________ and cannot Oelfke (elf-ka)