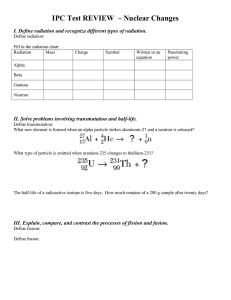
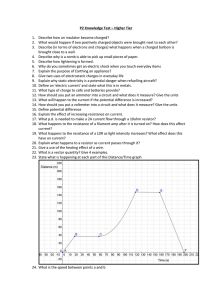
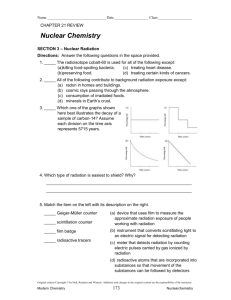
Guided Reading Questions 18.5 – 18.10 1. Define radiotracer. 2
advertisement

Guided Reading Questions 18.5 – 18.10 1. 2. 3. 4. Define radiotracer. How do radiotracers work in the body to diagnosis and treat illnesses? Nuclides used as radiotracers have short half-lives, how is this beneficial to humans? List 4 radioisotopes used in medical diagnosis or treatment, give their nuclear symbol and body part targeted. 5. How do the forces that hold an atomic nucleus together compare in strength with the forces between atoms in a molecule? 6. Define nuclear fusion 7. Define nuclear fission 8. How do the energies released by nuclear processes compare in magnitude with the energies of ordinary chemical processes? 9. Write an equation for the fission of U-235 by bombardment with a neutron. 10. How is it possible for the fission of U-235, once started, to lead to a chain reaction? 11. What does it mean to say that fissionable material possesses a critical mass? Can a chain reaction occur when a sample has less than the critical mass? 12. What was the Manhattan Project? 13. What type if reaction occurs in a nuclear power plants reactor? 14. What is the fuel for a nuclear power plant? 15. Describe the purpose of each of the major components of a nuclear reactor. a. moderator b. control rods c. containment d. cooling liquid 16. According to the schematic diagram on pg. 564, describe how the energy from the fission process is used to generate electricity. 17. Can a nuclear explosion take place in a reactor? State your reason for your answer 18. What is a meltdown and how does it occur? 19. Why have breeder nuclear reactors not been a popular alternative in the US? 20. Stars produce their energy through nuclear _________. 21. How does the energy released by fusion compare in magnitude with that released by fission? 22. During the fusion process, ___________ nuclides combine to form __________ nuclides and also releasing large amounts of energy. 23. What is the main reason why no practical fusion reactor has yet to be developed? 24. Differentiate between somatic and genetic damage as a result of radiation exposure. 25. Describe the tissue penetrating abilities of an α particle, a β particle and γ radiation. 26. What is the unit used to measure radiation exposure? 27. The biologic effects of radiation exposure depend on what 3 factors?