Power Point
advertisement

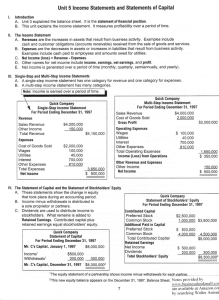
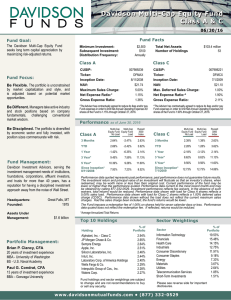
Unit 7 Financial Unit R-E=P/L Revenue - Expenses = Profit or Loss Expenses-money owed Revenue-money that is coming in Timeframe-the actual dates of the budget Create a list of income and expenses Categorize the income and expenses Assign amounts to the categories Keep track of money spent or earned Start-up Budget–the initial income and expenses of a new business. Operating Budget-the financial plan for ongoing operations of a business for a specific time period. Cash Budget-Estimate of the actual money received and paid out for a specific time period. Inventory Records-accounts of what you own Accounts Payable-who you owe money to Accounts Receivable-who owes you money Cash Records-details where money is Payroll Records-details about the employeespay, ◦ Taxes, and days missed Reasons for ◦ Develop fiscal plans ◦ Determine business strategies ◦ Analyze numeric data Balance Sheet-measures the assets, liabilities and the owner’s equity. This shows where the company is currently Income Statement-reports the revenue, expenses, and net loss or gain. This shows how the company is doing whether they are making money or not. Parts of a Balance Sheet Assets-are items such as land, equipment Items that are owned by the company and can be sold. Liabilities-are the bills of the company- what a company owes to others. Owner’s equity-how much money the owner has put into the business Expenses-money owed Revenue-money that is coming in Net Loss/Profit-what is left over after the bills have been paid. Gross Pay-actual pay Net Pay-Bring home pay after taxes Taxes-income (state, federal) Taxes-OASDI(FICA) Medicare Taxes-Unemployment(FUTA) Direct Deposit Where companies trade ownerships by selling pieces of stock NYSE New York Stock Exchange –major Dow Jones-30 major American Companies NASDAQ-Top 100 Companies Current Ratio-tells you if the business can pay its debts as they become due ◦ Current Assets/Current Liabilities-should be 1:1 Debt to Equity Ratio-tells you how much the business is relying on money borrowed from others ◦ Total liabilities/Owner’s Equity-should be 1:1but no higher than 2:1 Return to Equity Ratio-shows the rate of return the owners are getting on their money ◦ Net Profit/Owner’s Equity Net Income Ratio-how much profit is being made on each sales dollar. ◦ Total Sales/Net Income Number of trades in a day Natural Disasters Government Stability Shortages/surpluses Hi/Lo Price of stock-for the year Market Trends-how the entire stock market is doing or specific industries Competition-people who sell the sames items Dividends-money that is paid out to stock holders after all bills are paid History of the company Type of stock-common or preferred