Mineral resource
advertisement

Civilizations exists by geological
consent, subject to change without
notice
Will Durant
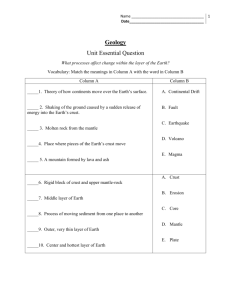
Geology and Mineral Resources
Unit 11
Earth is a Dynamic Planet
Geology: study of processes taking place in
earth’s interior and on its surface.
• core: hot, solid center of planet
• mantle: surrounds core; rocky near interior,
magma (molten rock) near exteriorasthenosphere
• crust: thinnest, outermost zone
-continental crust (includes continental ocean
shelf)
-oceanic crust: 71% of crust
• lithosphere: crust and rigid mantle
Volcanoes
Abyssal hills
Oceanic crust
(lithosphere)
Abyssal Oceanic
floor
ridge
Abyssal
floor
Trench
Folded
mountain
belt
Abyssal plain
Craton
Continental
shelf
Continental
slope
Continental
rise
Continental crust (lithosphere)
Mantle (lithosphere)
Fig. 15-2, p. 336
Tectonic Plates
Tectonic plates: plates of lithosphere
• created by convection currents in mantle
• move slowly on top of asthenosphere
• interaction of plate boundaries create
earthquakes, volcanoes, mountains
The Earth’s Major Tectonic Plates
Figure 15-4
Spreading
center
Collision between two
continents
Ocean
trench
Oceanic
crust
Oceanic
Subduction zone
crust
Continental
crust
Continental crust
Material cools Cold
as dense material
it reaches the falls back through
outer mantle
mantle
Mantle
convection
cell
Two plates move towards
each other. One is
subducted back into the
mantle on a falling
convection current.
Hot
material
rising
through
the mantle
Mantle
Hot outer
core Inner
core
Fig. 15-3, p. 337
Plate Boundaries
3 types of plate boundaries:
1. divergent: oceanic plates moving apart,
molten rock flows up into the void, creates oceanic
ridges (and new crust)
ex. Mid-Atlantic Ridge
2. convergent: colliding plates
-subduction zone: denser oceanic plate sinks beneath
a continental plate
ex. “Ring of Fire” in Western Pacific Ocean
-trench: colliding oceanic plates
-mountains: colliding continental plates
ex. Himalayas
Plate Boundaries
3. Transform fault: plates sliding past each
other
ex. San Andreas Fault (California), New
Madrid Fault (us)
Trench
Volcanic island arc
Transform
fault
Lithosphere
Rising
magma
Lithosphere
Asthenosphere
Divergent plate boundaries
Asthenosphere
Convergent plate boundaries
Lithosphere
Asthenosphere
Transform faults
Fig. 15-4b, p. 338
Internal Geologic Processes
• form mountains, volcanoes, earthquakes
Internal Geologic Processes
• volcanoes: weak area in crust
-magma reaches surface through a fissure
-release lava, ash, CO₂ and SO₂ gases
ex. Mount Pinatubo
• earthquakes: movement of plates at transform
boundaries
-seismic wave: outward movement of energy
from focus of quake
-epicenter: earth’s surface above focus
-tsunamis: ocean floor faults that suddenly rise
or fall
External Geologic Processes
• driven by solar radiation, gravity
• weathering: physical, chemical, biological
processes that break down rock into soil
-rock: solid combination of one or more
mineral
-rock types: sedimentary, igneous,
metamorphic
Erosion
Transportation
Weathering
Deposition
Igneous rock
Granite,
pumice, basalt
Sedimentary
rock
Sandstone,
limestone
Heat, pressure
Cooling
Heat, pressure,
stress
Magma
(molten rock)
Melting
Metamorphic rock
Slate, marble, gneiss,
quartzite
Fig. 15-8, p. 343
Mineral Resources
Mineral resource: useful inorganic material from
crust; 2 major types:
1. metallic (aluminum, gold, lead, nickel, silver)
-ore: rock containing concentration of valued
mineral; may be high-grade (lots of mineral) or
low-grade (small amounts of mineral)
2. nonmetallic (sand, limestone, talc, clay, salt)
• all minerals are considered nonrenewable
• country’s standard of living is tied to mineral
availability
Mineral Use
Al: packaging, structural material in cars, planes
Fe: make steel for buildings, vehicles
Cu: electrical, communications wiring
Au: electronics, jewelry, medical implants
Sand: glass, bricks, concrete
Limestone: concrete, cement
General Classification of Nonrenewable
Mineral Resources
U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) classifies mineral
resources into 4 major categories:
• Identified: known location, quantity, quality
based on direct evidence.
• Undiscovered: potential supplies are assumed to
exist.
• Reserves: identified resources that can be
extracted profitably.
• Other: undiscovered resources not classified as
reserves
General Classification of
Nonrenewable Mineral Resources
{Examples are fossil
fuels (coal, oil),
metallic minerals
(copper, iron), and
nonmetallic minerals
(sand, gravel)}.
Figure 15-7
Mining
Methods of removing minerals, fossil fuels:
• surface (strip) mining: depends on resource
sought, topography
-involves removal of vegetation and
overburden: overlying soil, rock
-excess soil is dumped in spoils on land
Mining (cont’d)
• mountaintop removal: exposes coal seams
-requires draglines (trucks with huge buckets)
-spoils are dumped in valleys, rivers, streams
• open-pit: creates huge holes to remove
metals (copper), sand, stone
Mining (cont’d)
• subsurface: underground metals, coal are
removed through tunnels, shafts
-requires explosives, exposure to poisonous
gases, methane, lung-damaging dust
Environmental Effects of Mining
(almost all degradation by mining is long-term)
• Strip mining: loss of topsoil, spoil banks are
easily eroded. Return to ecosystem is slow.
• Mountain top removal: destroys forests, buries
streams, toxic wastewater can release mercury,
arsenic, loss of property value, well
contamination.
(mercury used to separate gold from stream
sediments represents the 2nd worst humanrelated source of mercury pollution)
Environmental Effects of Mining
• Sub-surface mining: degrades biodiversity
(especially in rainforest). Clean up is possible,
but costly.
• Smelting: heating ores to release metals
emits large quantities of sulfur dioxide-acid
rain/acid mine drainage, green- house gases
Environmental Effects of Mining
• Cyanide Solution Mining/Heap-Leach
Extraction: runoff of cyanide in gold
extraction creates toxic ponds (can infiltrate
groundwater)
Human Health Impacts of Mining
• Black-lung disease: inhalation of coal dust
from subsurface mining
• Mercury poisoning: ingestion of Hg from fish
• Cyanide poisoning: exposure to smoke, or
ingestion in water.
Mineral Availability
Abundant: Al, Fe
Scarce: Mn, Cr, Co, Pt (strategic metals)
(-South Africa is largest producer of Cr, Pt
-US relies on these for economy, military,
but has limited reserves)
• US, Canada, Russia, South Africa, Australia
supply most of world’s mineral resources
• China has most of rare earth metals
Minerals from the Ocean
• Occur in low concentrations
• Include Cu, Fe, W (tungsten), Pt, diamonds
• Rarely mined due to:
-expense of extraction
-rights disputes
-concern about disruption to food chain
-risk to food supply near coast
Black
smoker
White
smoker
Sulfide
deposits
Magma
White
crab
White clam
Tube
worms
Fig. 15-17, p. 350
Supplies Of Mineral Resources
• Depletion curves for
a renewable resource
using three sets of
assumptions.
– dashed vertical lines
represent times
when 80% depletion
occurs.
Figure 15-16
Sustainable Mineral Use
• Substitution: silicon, plastics, ceramics can
replace some metals
• Nanotechnology; create materials out of atoms,
molecules
• Recycle, reuse: ex. recycling Al produces 95% less
air, water pollution
• Reduce mining subsidies/increase subsidies for
recycling
• Include cost of environmental damage from
mining in prices of items.
Core Case Study: The
Nanotechnology Revolution
• Nanotechnology uses science and engineering to
create materials out of atoms and molecules at
the scale of less than 100 nanometers.
-little environmental harm
-does not use nonrenewable resources
-potential biological concerns
(nanoparticles can cross the
placenta, penetrate lung tissue,
etc)
Figure 15-1
US Mining Laws
• The General Mining Law of 1872: encouraged
exploration, mining of minerals
-enables corporations to obtain large tracts of public
land cheaply without paying royalties or cleanup fees
• The Surface Mining Control and Reclamation Act of
1977: requires mined land to be restored to premining conditions
-proper disposal of mining wastes
-re-contouring land
-replanting vegetation
Restored areas are known as brownfields
Exam Focus
• Major geologic processes occurring within the
earth and on its surface
• Rocks, and how are they recycled by the rock
cycle
• Type of formation from diverging ocean plates
• Type of formation from converging continental
plates
• Example of transform fault
• Weathering from wind, water, heat
Exam Focus (cont’d)
• Definition of an ore (high and low-grade);
definition of an alloy
• Classification of minerals (renewable/non)
• Types of mining and harmful environmental
and human health effects results from each
-specifically mining source of air and water
pollution associated with heating ores
-disease associated with subsurface mining
• Environmental effects of smelting
• Nonmetal used in glass, bricks, concrete
Exam Focus
• 4 reasons the ocean is not mined for minerals
• Ways minerals can be used sustainably
• Which mineral substitute still uses oil, fossil
fuels
• Know the US Surface Mining Control and
Reclamation Act of 1977