6th grade vocabulary Earth Science Unit Mineral
advertisement

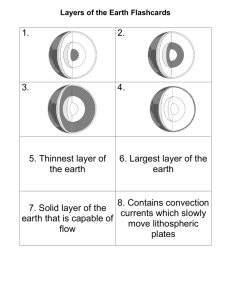
6th grade vocabulary Earth Science Unit 1. Mineral-element or compound, formed by nature but not formed by living things, that has a specific crystal structure and physical and chemical properties 2. Rock-hard and compact mixture of minerals that formed naturally 3. Rock cycle-process by which rocks, over geologic ages, can be changed into different kinds of rock 4. Mohs hardness scale-a system listing ten minerals that the hardness of other minerals can be compared with 5. Plate tectonics-theory that describes and explains the way that continents separated into today’s land masses from one large ancestral land mass (Pangea) 6. Luster-how the surface of a mineral appears when it reflects light 7. Sedimentary rock-rock formed when sediment is pressed and cemented together naturally, over millions of years 8. Igneous rock-one of three main kind of rock, made from cooled magma 9. Metamorphic rock-rocks that have been changed over time by high pressures and temperatures inside Earth’s crust 10. Crust-outermost, rocky layer of Earth 11. Mantle-a layer of Earth’s surface, lying just below the crust and above the inner core 12. Inner core-innermost part of Earth, made of solid iron and nickel 13. Outer core-layer inside Earth, between the mantle and inner core, which has some properties of a liquid 14. Asthenosphere-layer in the upper part of Earth’s mantle that is made of material that can be reshaped and deformed, and on which the continents move 15. Lithosphere-outermost layer of Earth’s surface, which is rocky and solid, includes the crust and the rigid part of the upper mantle 16. Transform boundary-boundary between two lithospheric plates where the plates are sliding past each other 17. Convergent boundary-formed where two sections of Earth’s crust are colliding 18. Divergent boundary-forms where lithospheric plates are moving away from each other 19. Subduction-the process in which one lithospheric plate slides under another; occurs at converging plate boundaries