Theorist Research Eleanor and Joanna - uhs-cd2
advertisement
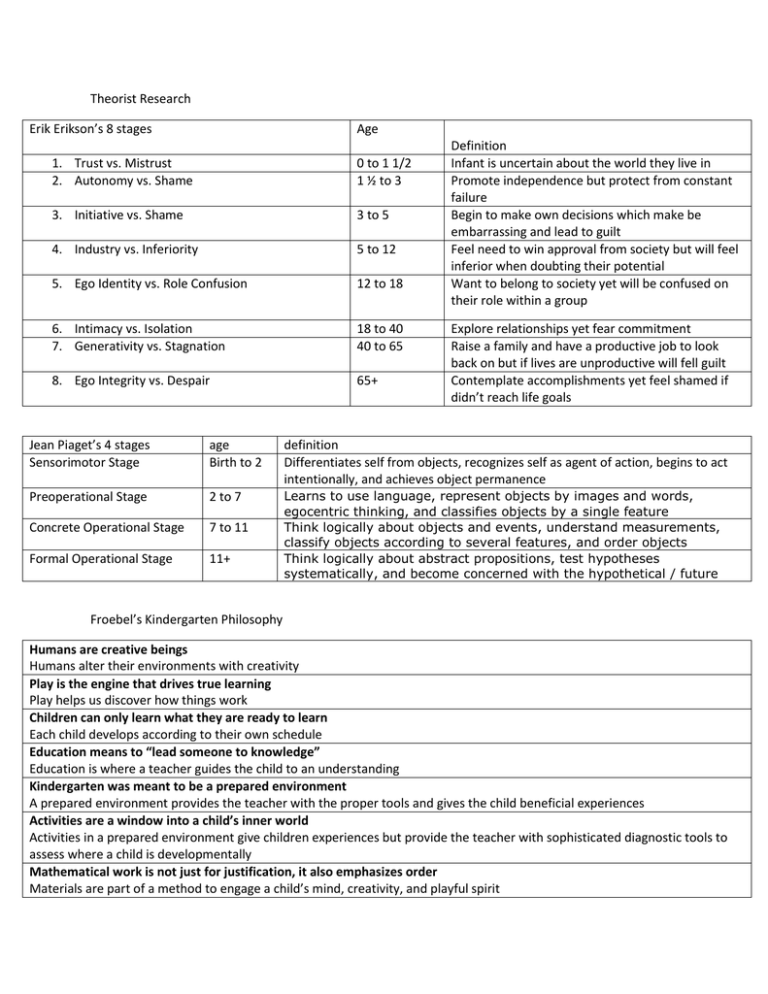
Theorist Research Erik Erikson’s 8 stages Age 1. Trust vs. Mistrust 2. Autonomy vs. Shame 0 to 1 1/2 1 ½ to 3 3. Initiative vs. Shame 3 to 5 4. Industry vs. Inferiority 5 to 12 5. Ego Identity vs. Role Confusion 12 to 18 6. Intimacy vs. Isolation 7. Generativity vs. Stagnation 18 to 40 40 to 65 8. Ego Integrity vs. Despair 65+ Definition Infant is uncertain about the world they live in Promote independence but protect from constant failure Begin to make own decisions which make be embarrassing and lead to guilt Feel need to win approval from society but will feel inferior when doubting their potential Want to belong to society yet will be confused on their role within a group Explore relationships yet fear commitment Raise a family and have a productive job to look back on but if lives are unproductive will fell guilt Contemplate accomplishments yet feel shamed if didn’t reach life goals Jean Piaget’s 4 stages Sensorimotor Stage age Birth to 2 definition Differentiates self from objects, recognizes self as agent of action, begins to act intentionally, and achieves object permanence Preoperational Stage 2 to 7 Concrete Operational Stage 7 to 11 Formal Operational Stage 11+ Learns to use language, represent objects by images and words, egocentric thinking, and classifies objects by a single feature Think logically about objects and events, understand measurements, classify objects according to several features, and order objects Think logically about abstract propositions, test hypotheses systematically, and become concerned with the hypothetical / future Froebel’s Kindergarten Philosophy Humans are creative beings Humans alter their environments with creativity Play is the engine that drives true learning Play helps us discover how things work Children can only learn what they are ready to learn Each child develops according to their own schedule Education means to “lead someone to knowledge” Education is where a teacher guides the child to an understanding Kindergarten was meant to be a prepared environment A prepared environment provides the teacher with the proper tools and gives the child beneficial experiences Activities are a window into a child’s inner world Activities in a prepared environment give children experiences but provide the teacher with sophisticated diagnostic tools to assess where a child is developmentally Mathematical work is not just for justification, it also emphasizes order Materials are part of a method to engage a child’s mind, creativity, and playful spirit Teaching should always be joyful, fun, and easy Teaching should always be positive and educational experience for both the teacher and student Montessori Method: The main goals of Montessori education are for children and teachers to engage in psychological selfconstruction by means of interaction with their environments and for children, especially under the age of six, to have an innate path of psychological development. Montessori believed that children should freely choose how to act and what to do within a prepared environment according to her model of development. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Mixed age classrooms are effective Uninterrupted blocks of work time with 3 hours as the goal facilitate productive learning Have a limitation of materials so that all of the materials are necessary for development There are 5 sensitive periods. Montessori classrooms for children from 2½ or 3 to 6 years old are often called Children’s Houses. Montessori used the term "cosmic education" for elementary schools in order to show the universal scope of lessons and that education should help children realize the human role in the interdependent functioning of society. Anne Frank, Julia Child (Chef), and Jeff Bezos (Founder of Amazon.com) attendee Montessori schools. Abstraction, order, and repetition are just some of the human tendencies. There should be nurture both inside and outside of the classroom. The classroom should be constructed in proportion to the child’s needs. Montessori Teaching Materials- 5- items you are interested in, 5 items we use/similar to ours 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Interested in the object permanence box Interested in the fabric box Interested in tasting experinces Interested in set of colored pencil holders Interested in subtraction strip board 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Have some of the multiple shape puzzles Have shoe lace, buckle, and button boards Have lower and upper case letters on cards Have numbers on cards Have shapes on cards Lev Vygotsky- Zone of Proximal Development B.F. Skinner’s Operant Conditioning Theory Freud- define Id, Ego, Superego (briefly) Howard Gardner’s 8 Multiple Intelligences 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8