Meaning of Culture: Elements, Religion, & Government
advertisement

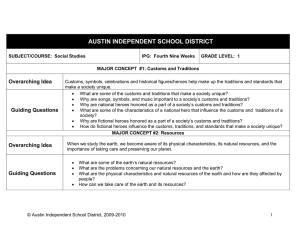
THE MEANING OF CULTURE ELEMENTS OF CULTURE • Culture • All things that make up a person’s way of life. • 7 Elements • Social Organization • Customs & Traditions • Language • Arts & Literature • Religion • Forms of Government • Economic System SOCIAL ORGANIZATION • Family Patterns • Nuclear Family (Traditional) • Comprised of mother, father, and children • Extended Family (Non-Traditional) • Several generations in one house • Farming communities, religious groups, Economic • Social Classes • Based on money, occupation, education, ancestry, or other factors • How do you increase your social class? • Marriage, Education, Money • You can move down in the social class too. CUSTOMS & TRADITIONS & LANGUAGE • Different Customs (Culturally Acceptable) • Greetings • Sitting Cross Legged • Dressing • Business • Social • Language – Cornerstone of culture • Uses • Communicate: thoughts, feelings, and knowledge • Passing on beliefs to new generations • All cultures have a language BUT not all have a written (Ebonics) ARTS & LITERATURE & RELIGION • Styles of Arts and Literature • Art, Music, Books, Movies, Stories • Used to teach culture and entertain • Religion – Linked to Arts • Major World Religions • Hinduism • Buddhism • Judaism • Christianity • Islam • Monotheism • Belief in one God • Polytheism • Belief in multiple Gods THREE QUESTIONS OF RELIGION: 1. WHERE DID WE COME FROM? WE LIVE OUR LIVES? 3. WHERE DO WE GO WHEN WE DIE? COSMOLOGY: THE STUDY AND EXPLANATION OF THE UNIVERSE THEOLOGY: A SYSTEM OF RELIGIOUS BELIEFS ANIMISM: THE BELIEF THAT SPIRITS INHABIT NATURE Agnosticism: Don’t know Atheism: Don’t believe in any divinity or spiritual existence Sect: A religious group, division, “branch” or faction FORMS OF GOVERNMENT • Why do we need an organized government? • People Organized Government • Historically • Chiefs or Elders • Today: National Governments • Thousands of officials • Collect taxes, enforce laws, and administer justice • Types of Government’s Today • Democracy • People have supreme power • Republic • Form of Democracy; people select leaders to represent them • Dictatorship • Ruler or group holds power by force • ECONOMIC SYSTEM Traditional Economy • Produce what they need to survive • Hunting and Gathering, Farming, and Herding • Surplus is traded • Market Economy • Buying and Selling • Command Economy • Government controlled • Individuals have little economic power • Mixed Economy • Individuals and Government make decisions • Cars are a great example: People pick & Government sets standards MARKET FORCES: WHAT MAKES SOMETHING VALUABLE?