chapter 3 vocabulary powerpoint
advertisement
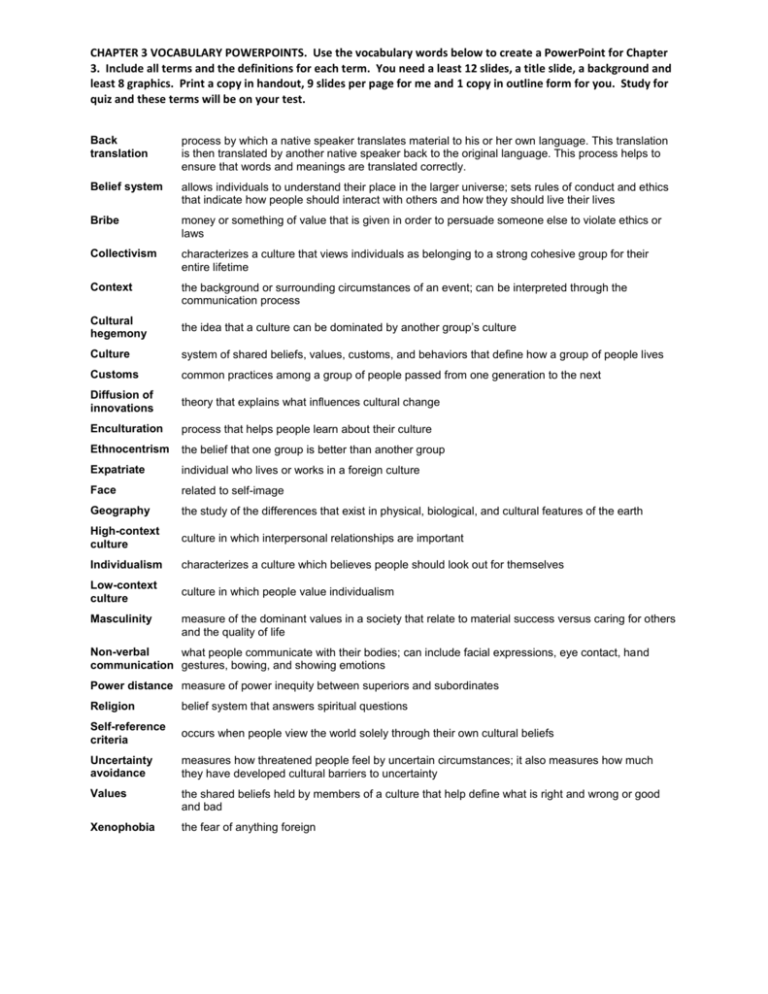
CHAPTER 3 VOCABULARY POWERPOINTS. Use the vocabulary words below to create a PowerPoint for Chapter 3. Include all terms and the definitions for each term. You need a least 12 slides, a title slide, a background and least 8 graphics. Print a copy in handout, 9 slides per page for me and 1 copy in outline form for you. Study for quiz and these terms will be on your test. Back translation process by which a native speaker translates material to his or her own language. This translation is then translated by another native speaker back to the original language. This process helps to ensure that words and meanings are translated correctly. Belief system allows individuals to understand their place in the larger universe; sets rules of conduct and ethics that indicate how people should interact with others and how they should live their lives Bribe money or something of value that is given in order to persuade someone else to violate ethics or laws Collectivism characterizes a culture that views individuals as belonging to a strong cohesive group for their entire lifetime Context the background or surrounding circumstances of an event; can be interpreted through the communication process Cultural hegemony the idea that a culture can be dominated by another group’s culture Culture system of shared beliefs, values, customs, and behaviors that define how a group of people lives Customs common practices among a group of people passed from one generation to the next Diffusion of innovations theory that explains what influences cultural change Enculturation process that helps people learn about their culture Ethnocentrism the belief that one group is better than another group Expatriate individual who lives or works in a foreign culture Face related to self-image Geography the study of the differences that exist in physical, biological, and cultural features of the earth High-context culture culture in which interpersonal relationships are important Individualism characterizes a culture which believes people should look out for themselves Low-context culture culture in which people value individualism Masculinity measure of the dominant values in a society that relate to material success versus caring for others and the quality of life Non-verbal what people communicate with their bodies; can include facial expressions, eye contact, hand communication gestures, bowing, and showing emotions Power distance measure of power inequity between superiors and subordinates Religion belief system that answers spiritual questions Self-reference criteria occurs when people view the world solely through their own cultural beliefs Uncertainty avoidance measures how threatened people feel by uncertain circumstances; it also measures how much they have developed cultural barriers to uncertainty Values the shared beliefs held by members of a culture that help define what is right and wrong or good and bad Xenophobia the fear of anything foreign